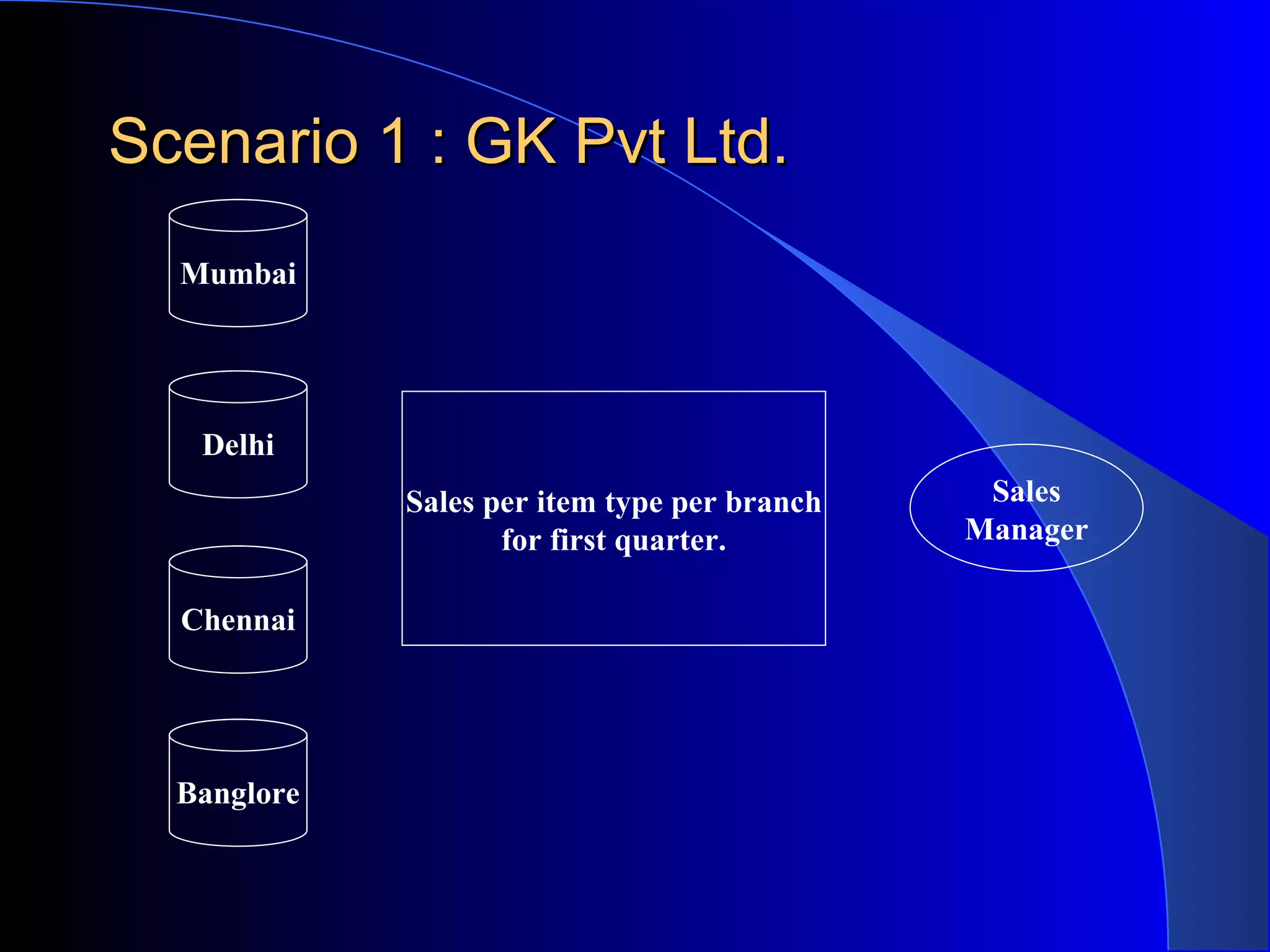
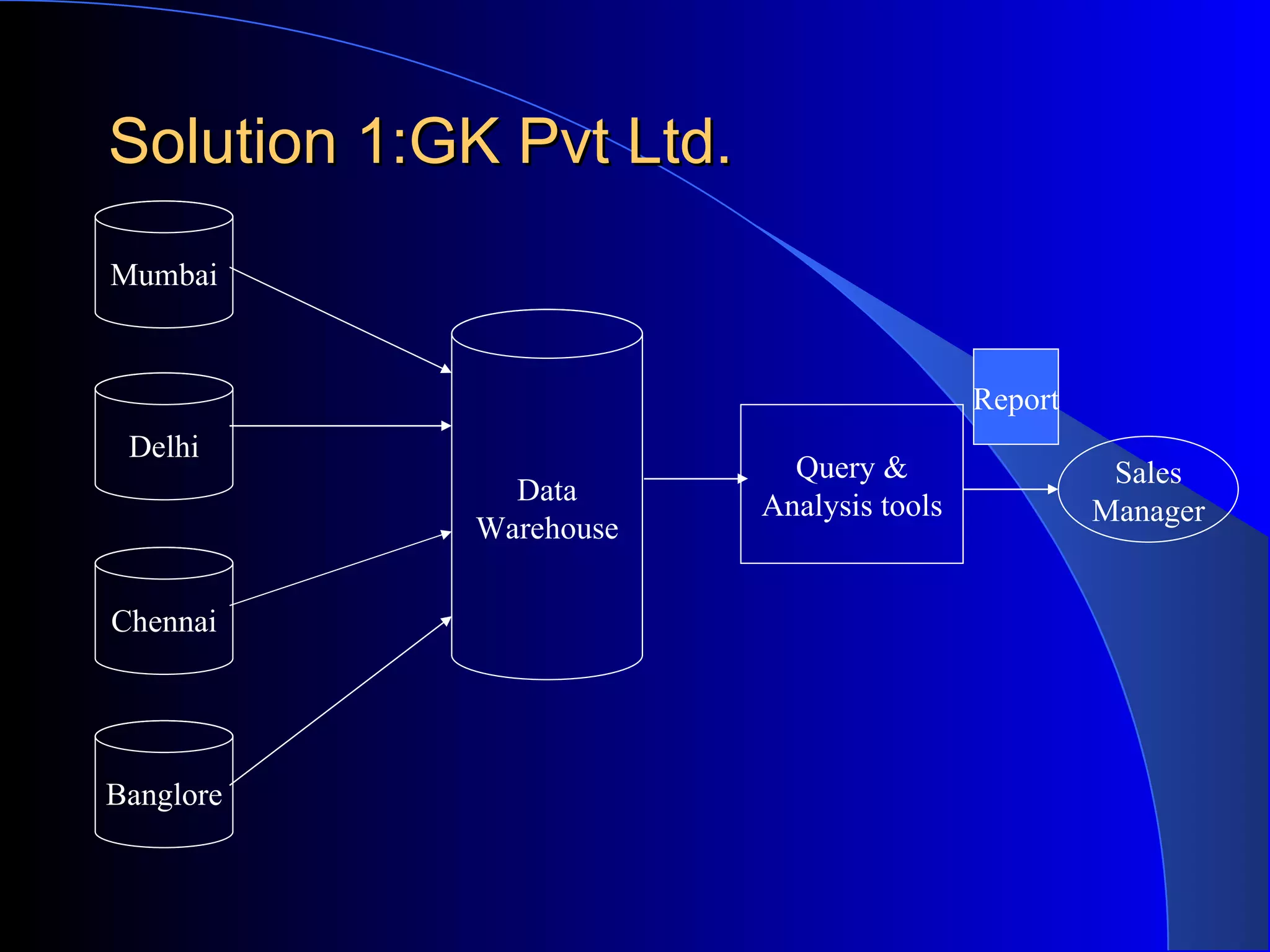
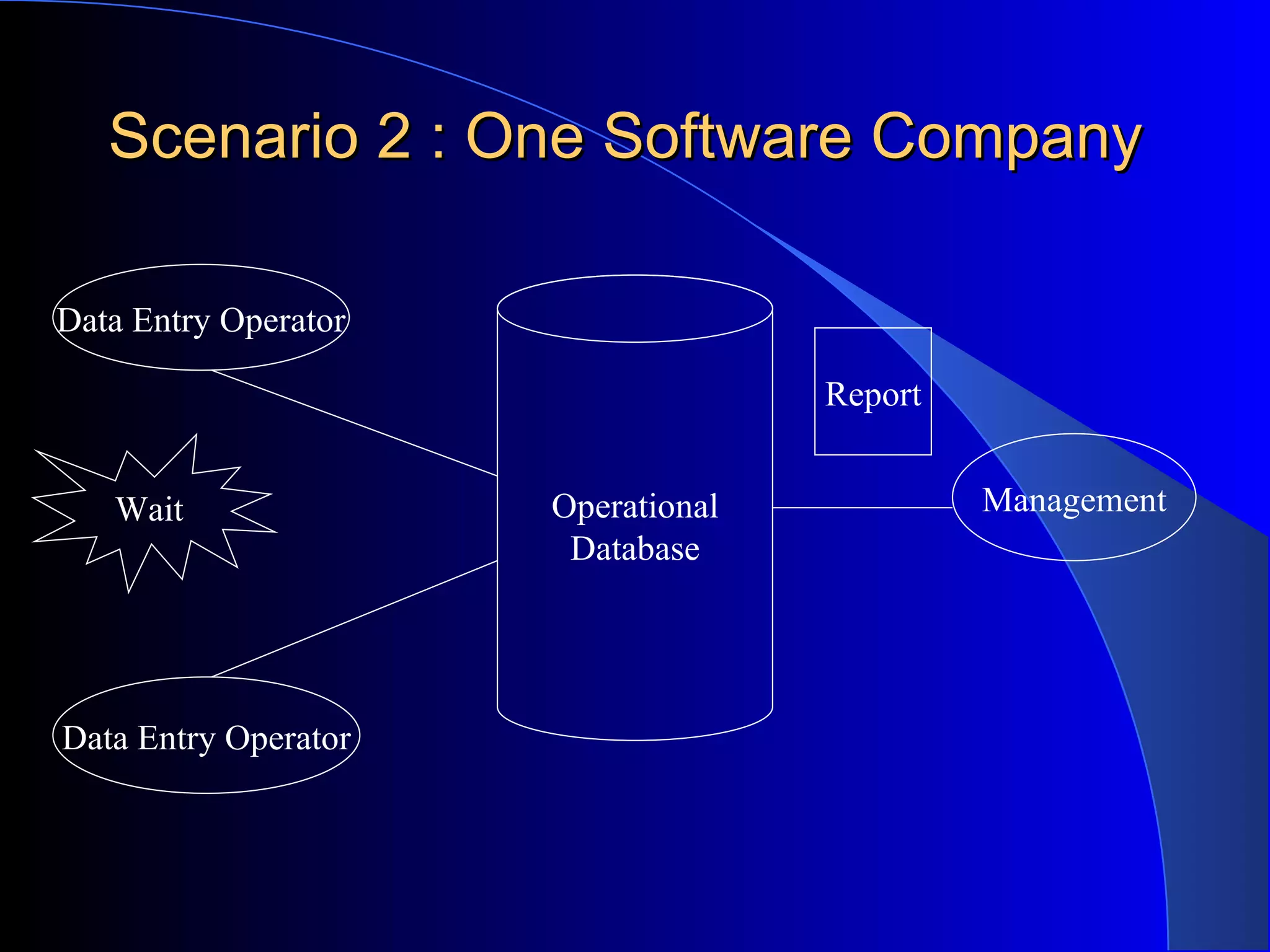
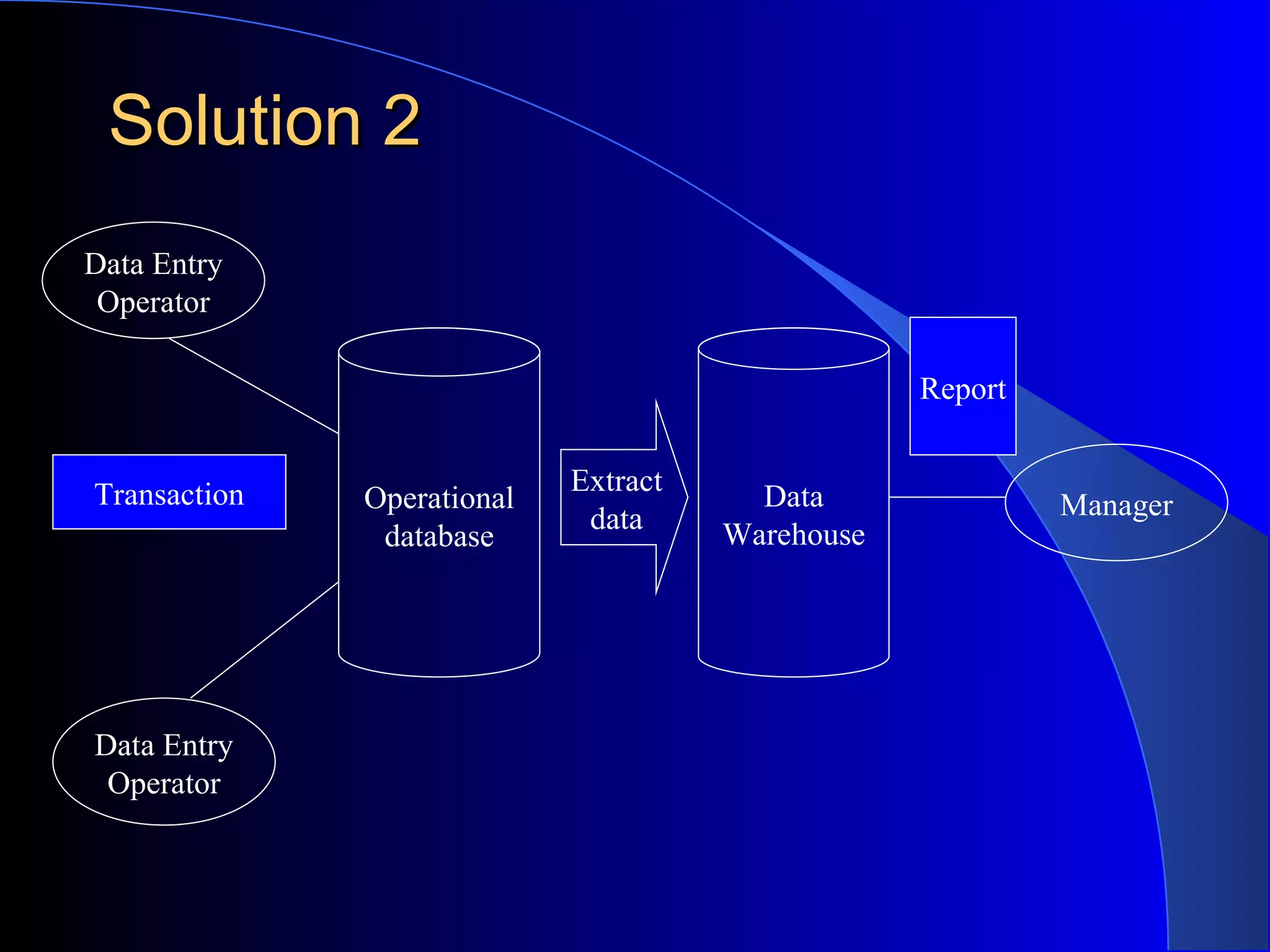
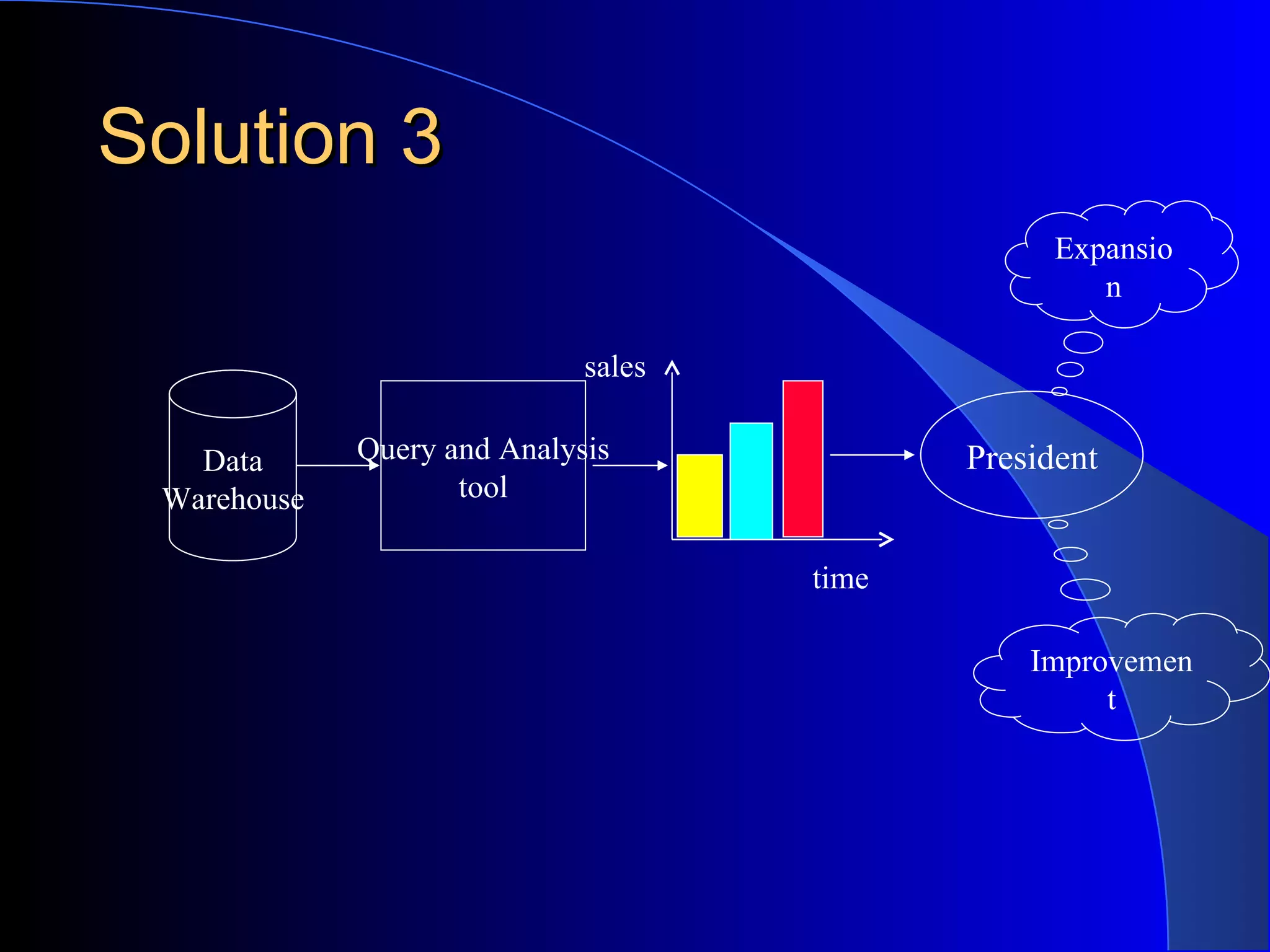
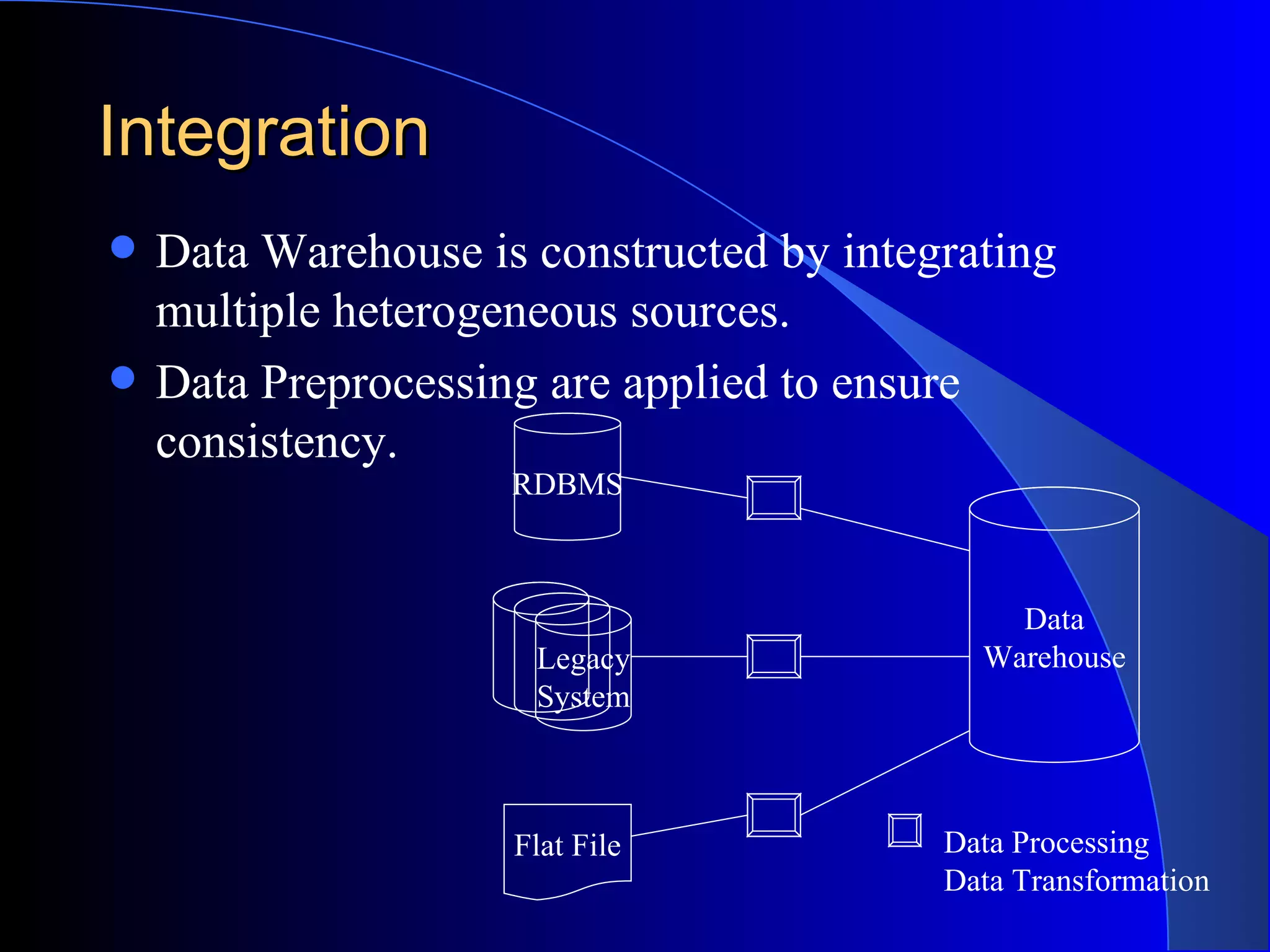
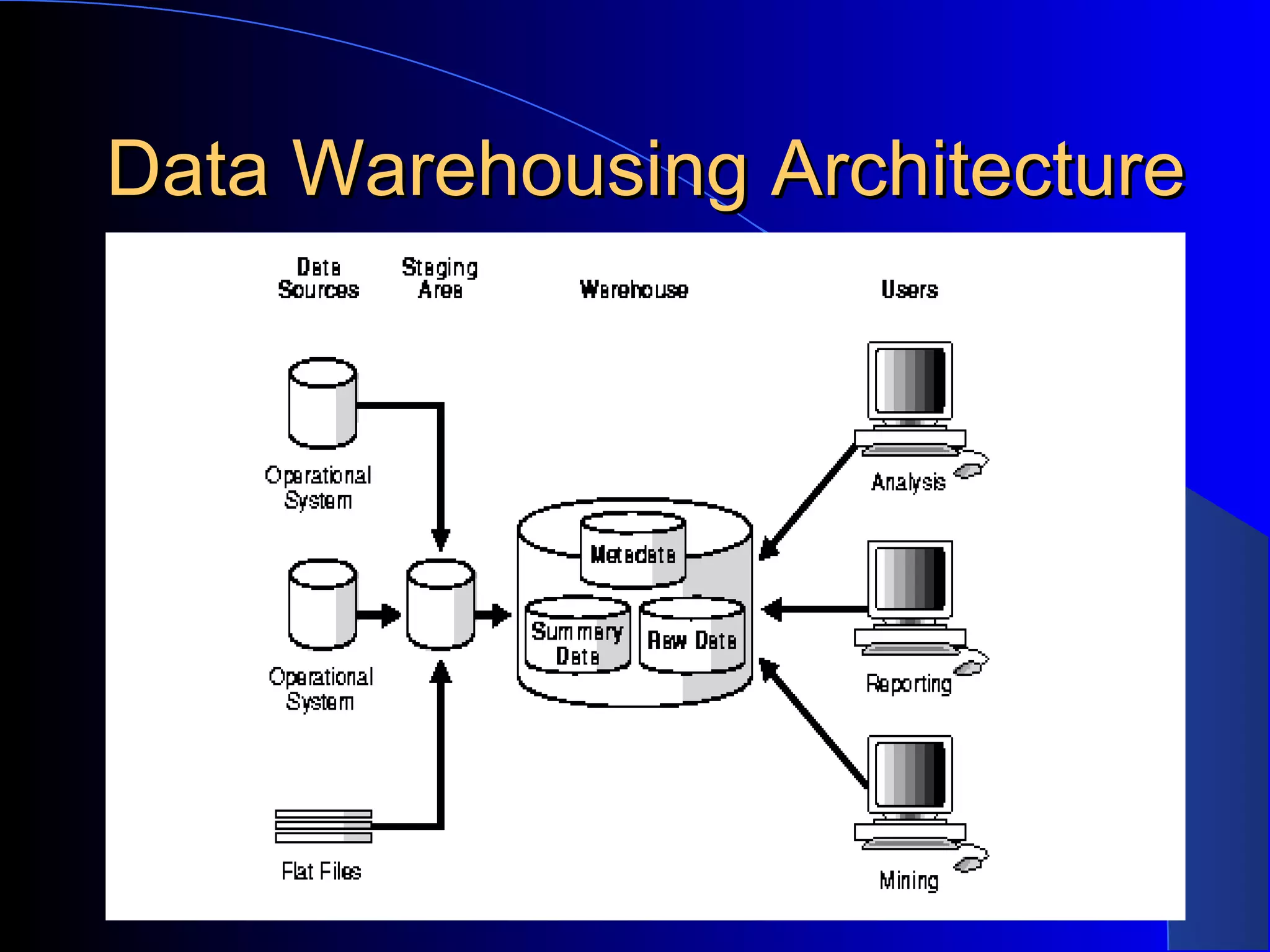
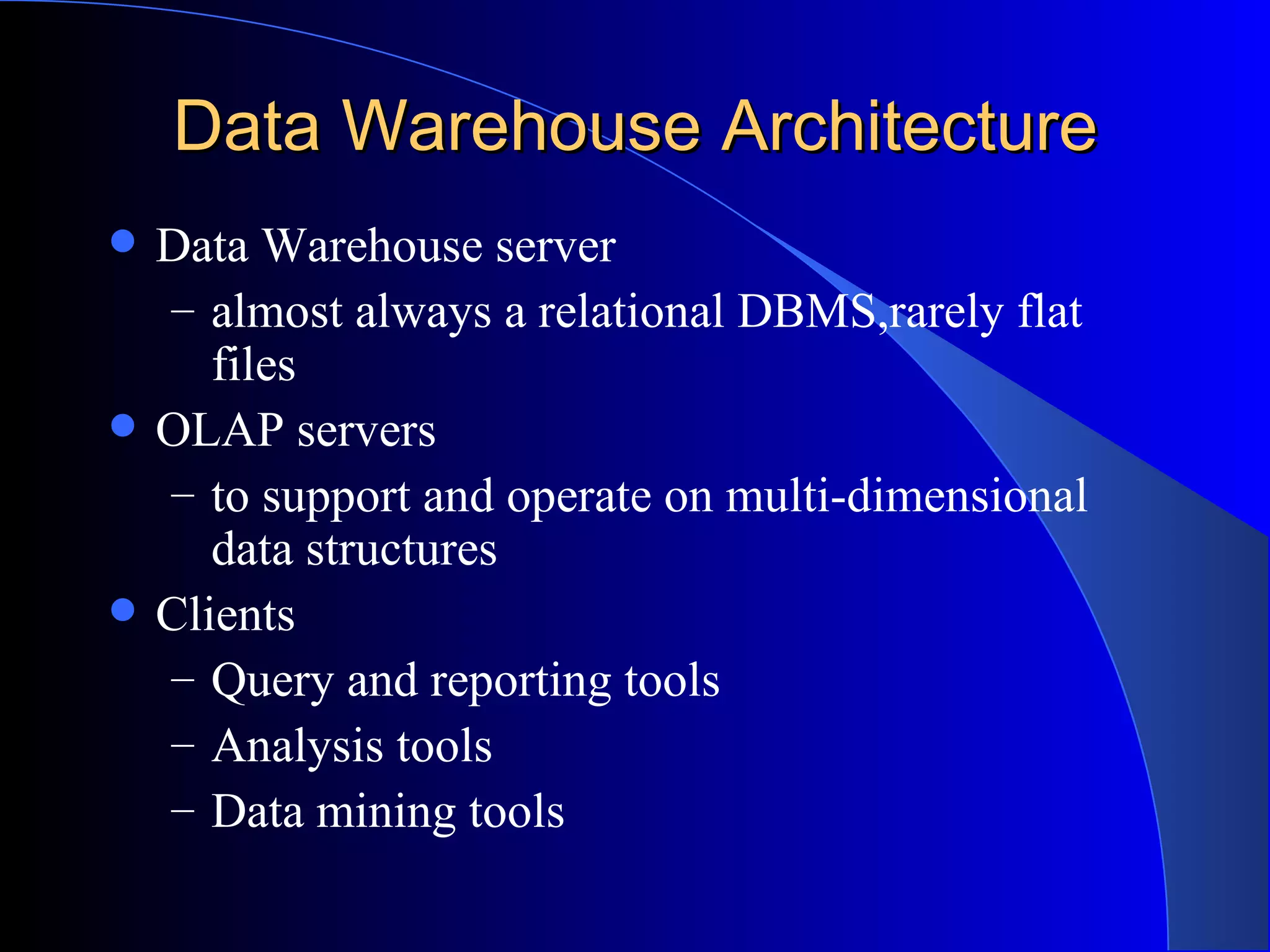
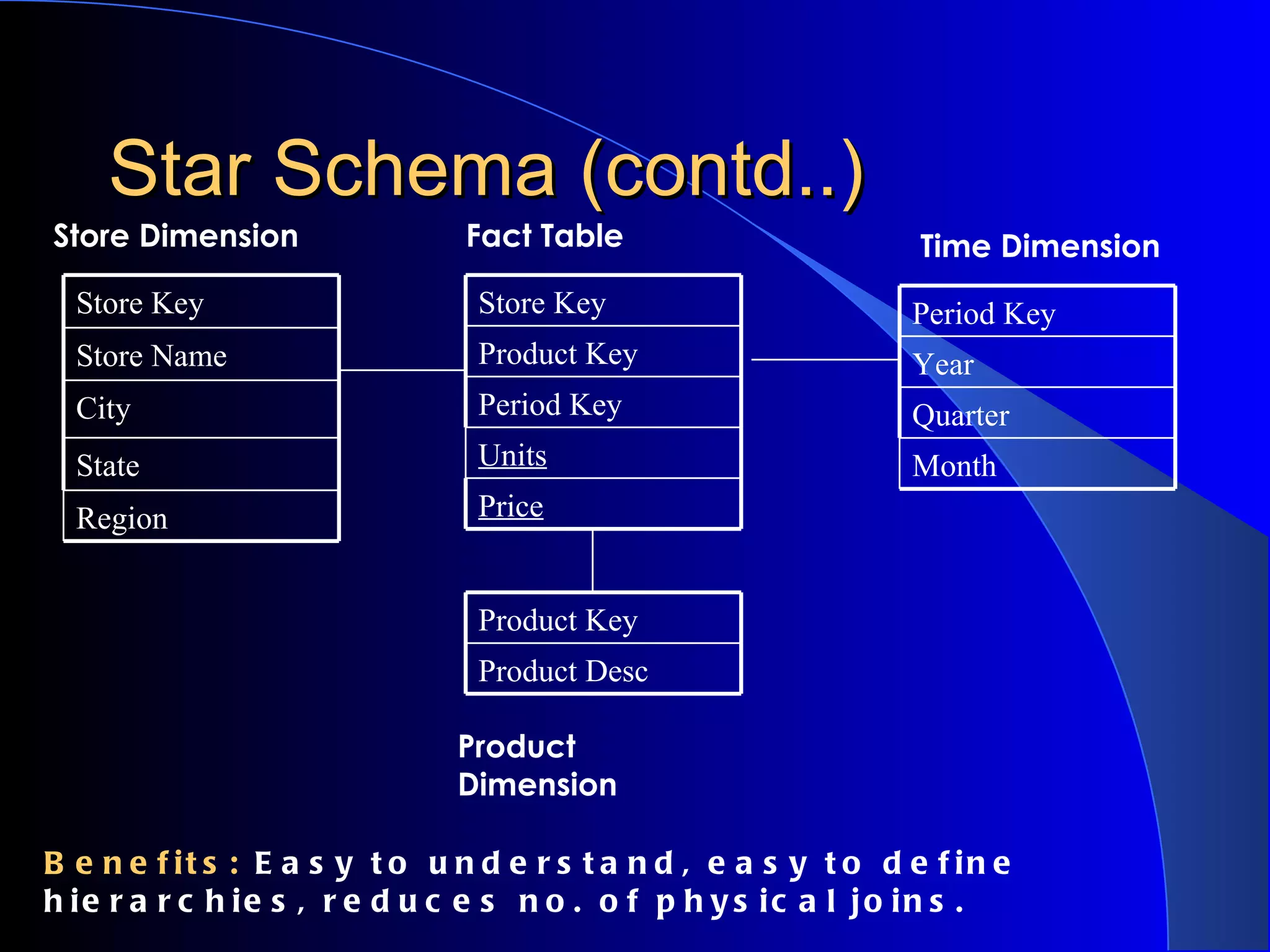
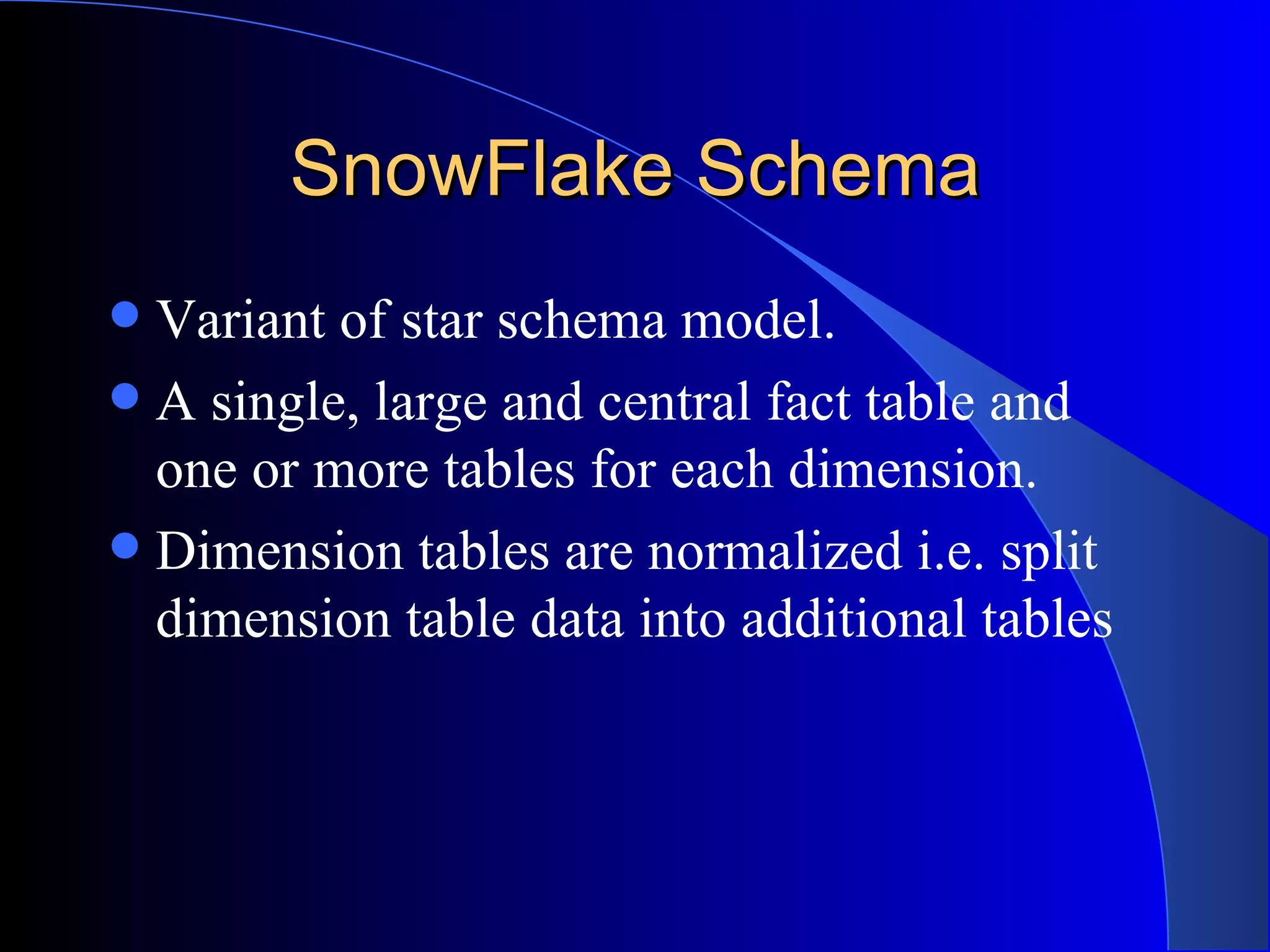
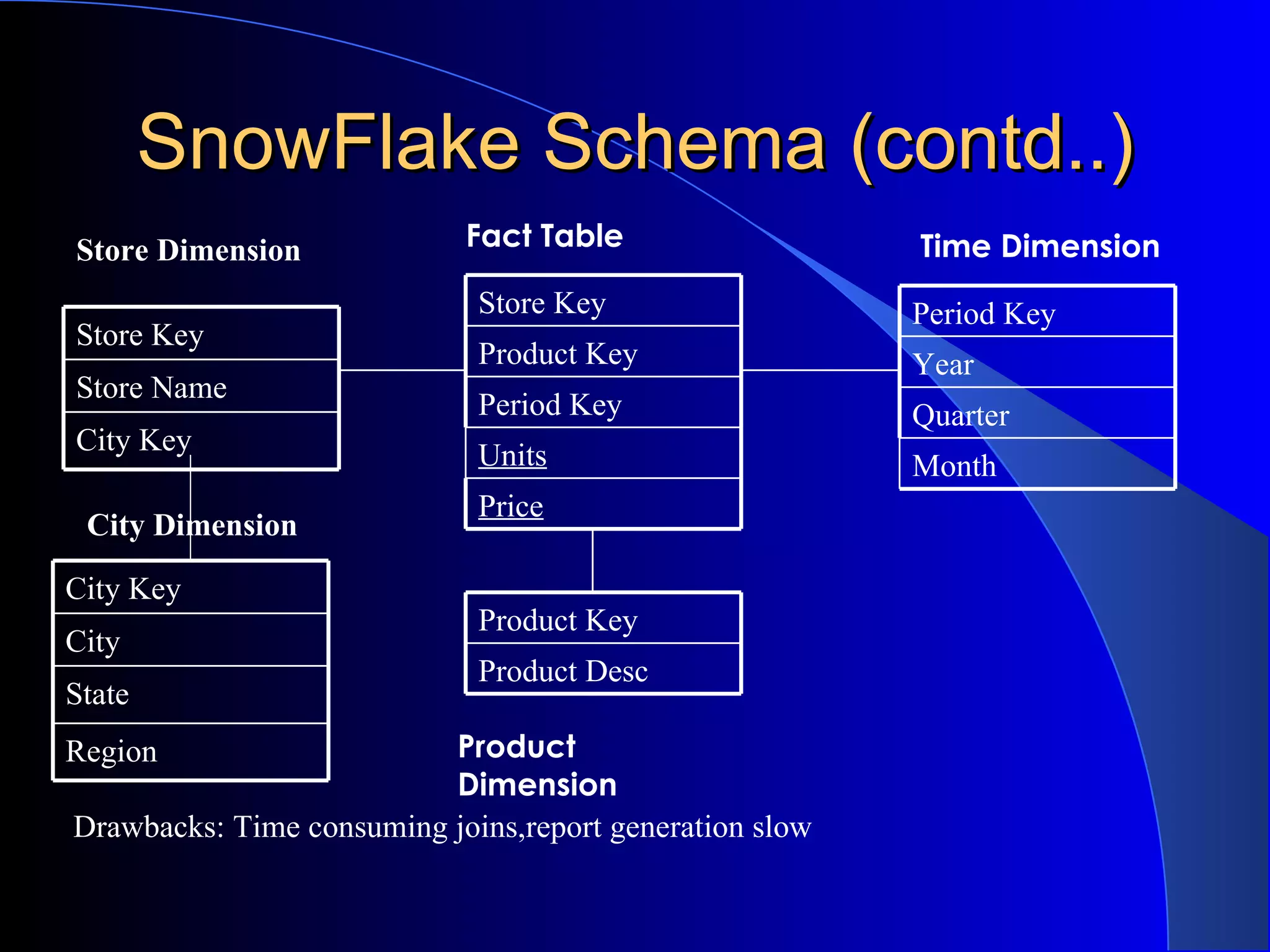
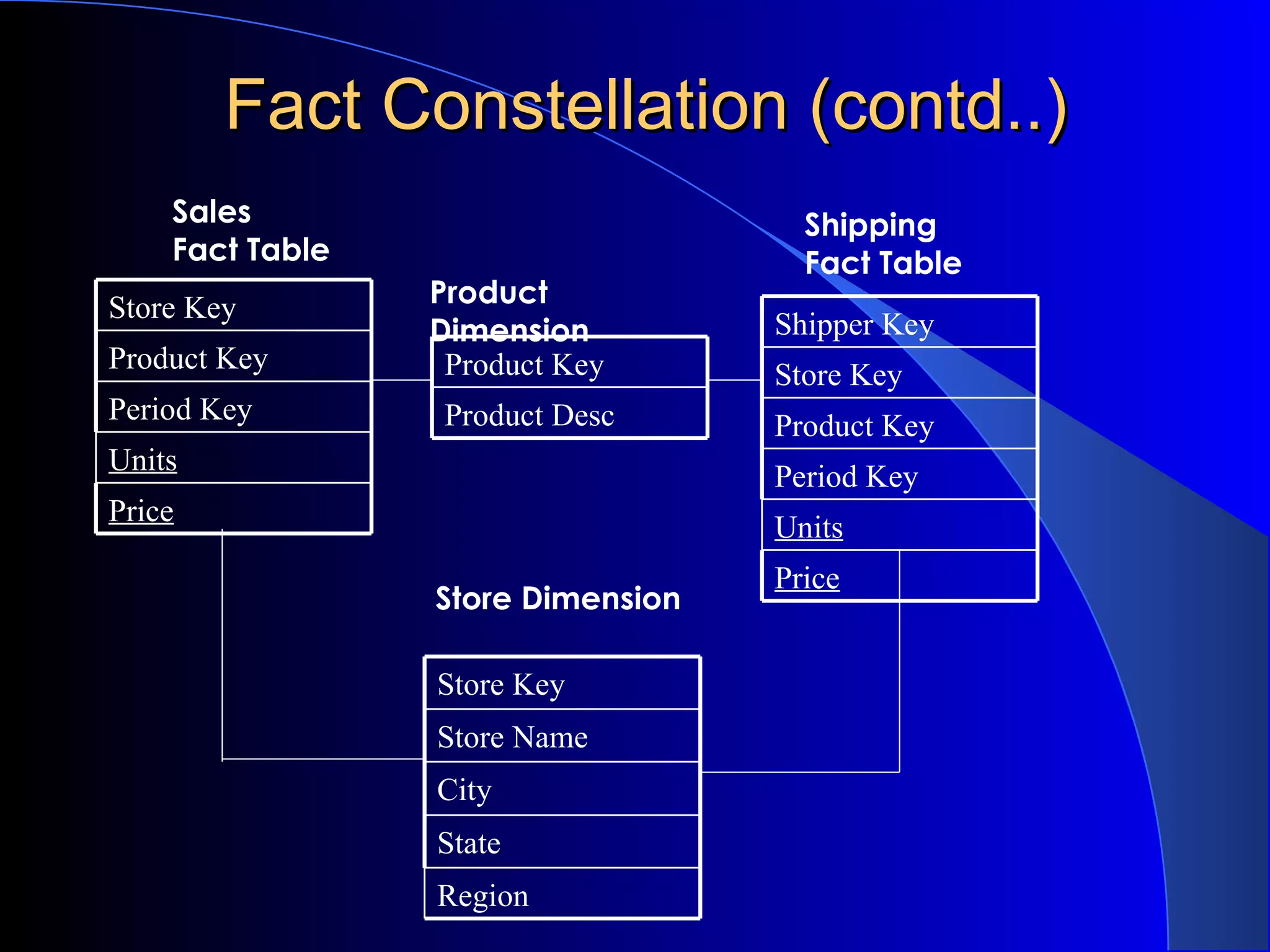
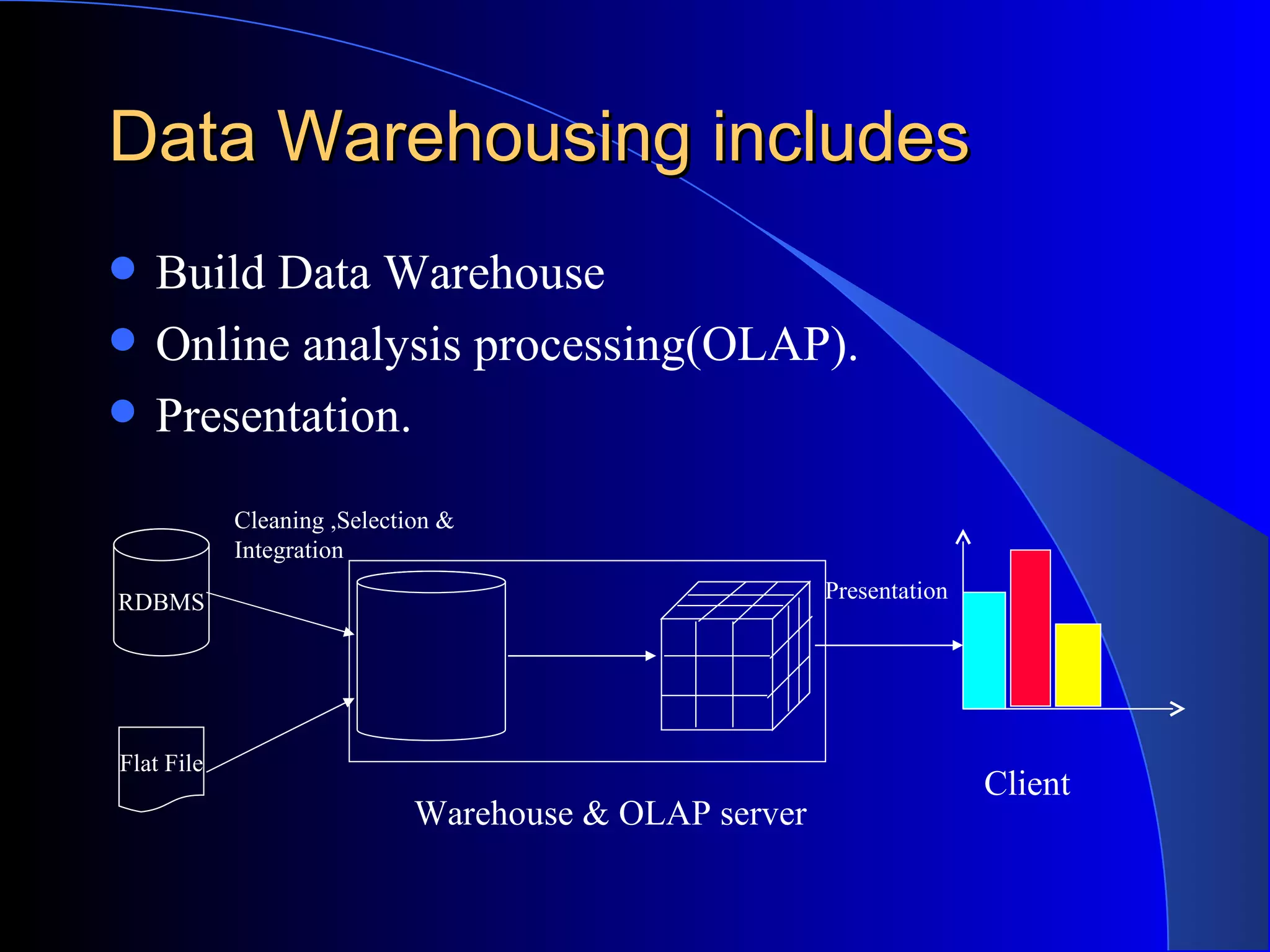
The document discusses the need for data warehousing and provides examples of how data warehousing can help companies analyze data from multiple sources to help with decision making. It describes common data warehouse architectures like star schemas and snowflake schemas. It also outlines the process of building a data warehouse, including data selection, preprocessing, transformation, integration and loading. Finally, it discusses some advantages and disadvantages of data warehousing.