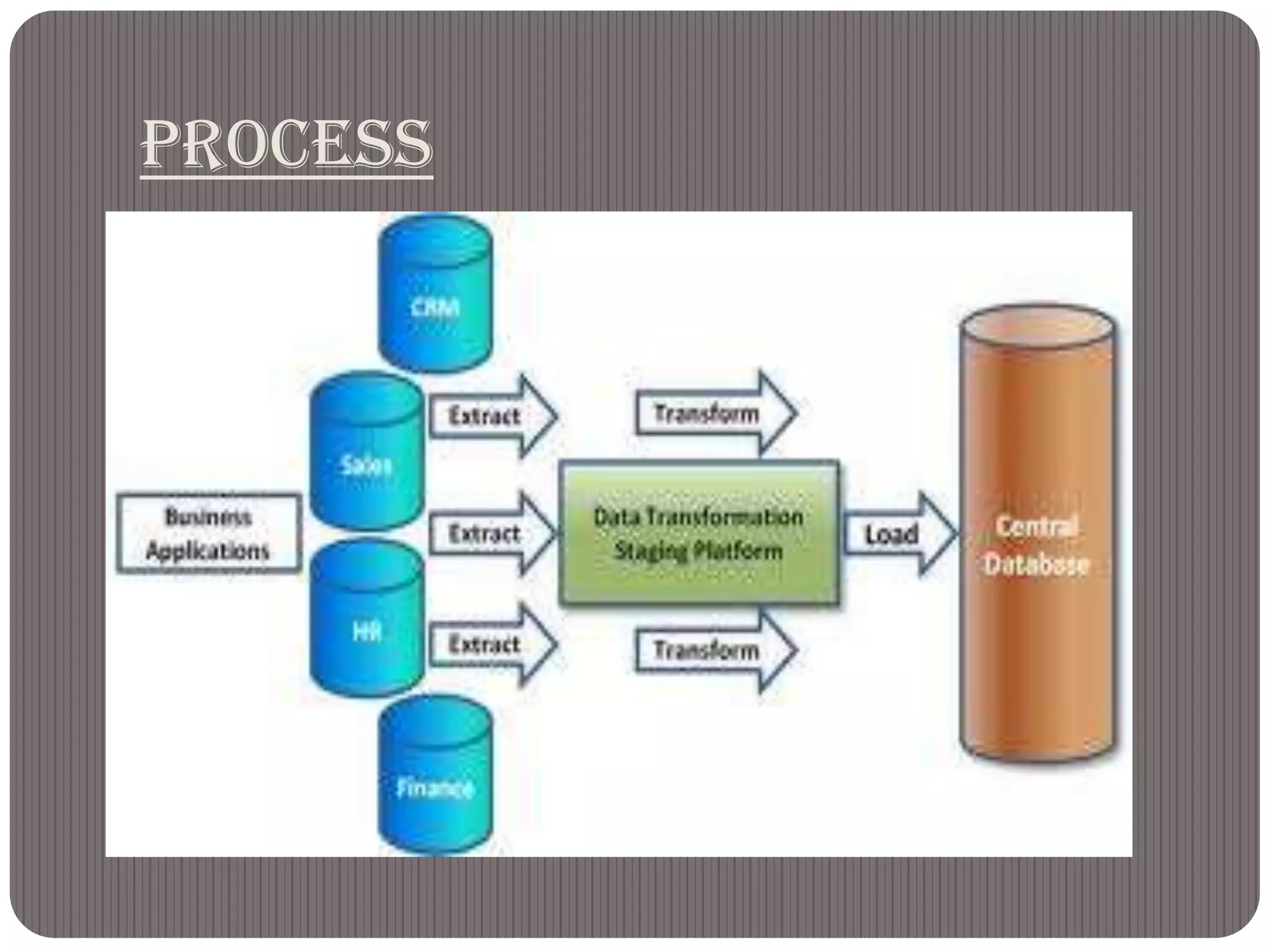
The ETL process in data warehousing involves extraction, transformation, and loading of data. Data is extracted from operational databases, transformed to match the data warehouse schema, and loaded into the data warehouse database. As source data and business needs change, the ETL process must also evolve to maintain the data warehouse's value as a business decision making tool. The ETL process consists of extracting data from sources, transforming it to resolve conflicts and quality issues, and loading it into the target data warehouse structures.