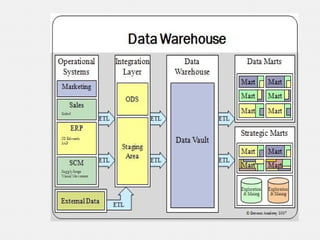
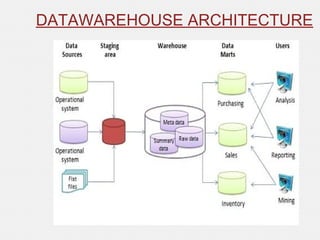
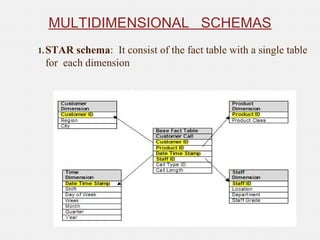
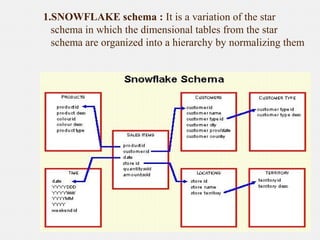
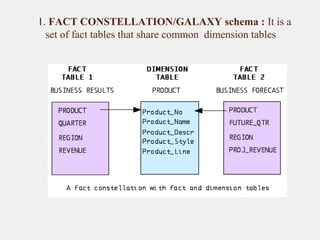
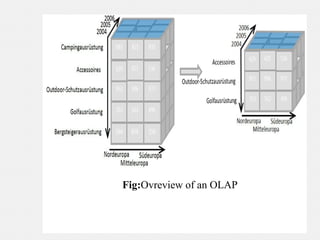
The document provides an overview of data warehousing, defining it as a subject-oriented, integrated, non-volatile, time-variant data collection that supports management decisions. It discusses the architecture and characteristics of data warehouses, compares them with databases, and explains multidimensional schemas, OLAP operations, and the process of building a data warehouse. Additionally, it highlights applications such as query and reporting tools, OLAP, analysis, and data mining, concluding that data warehouses address the need for advanced information analysis beyond operational systems.