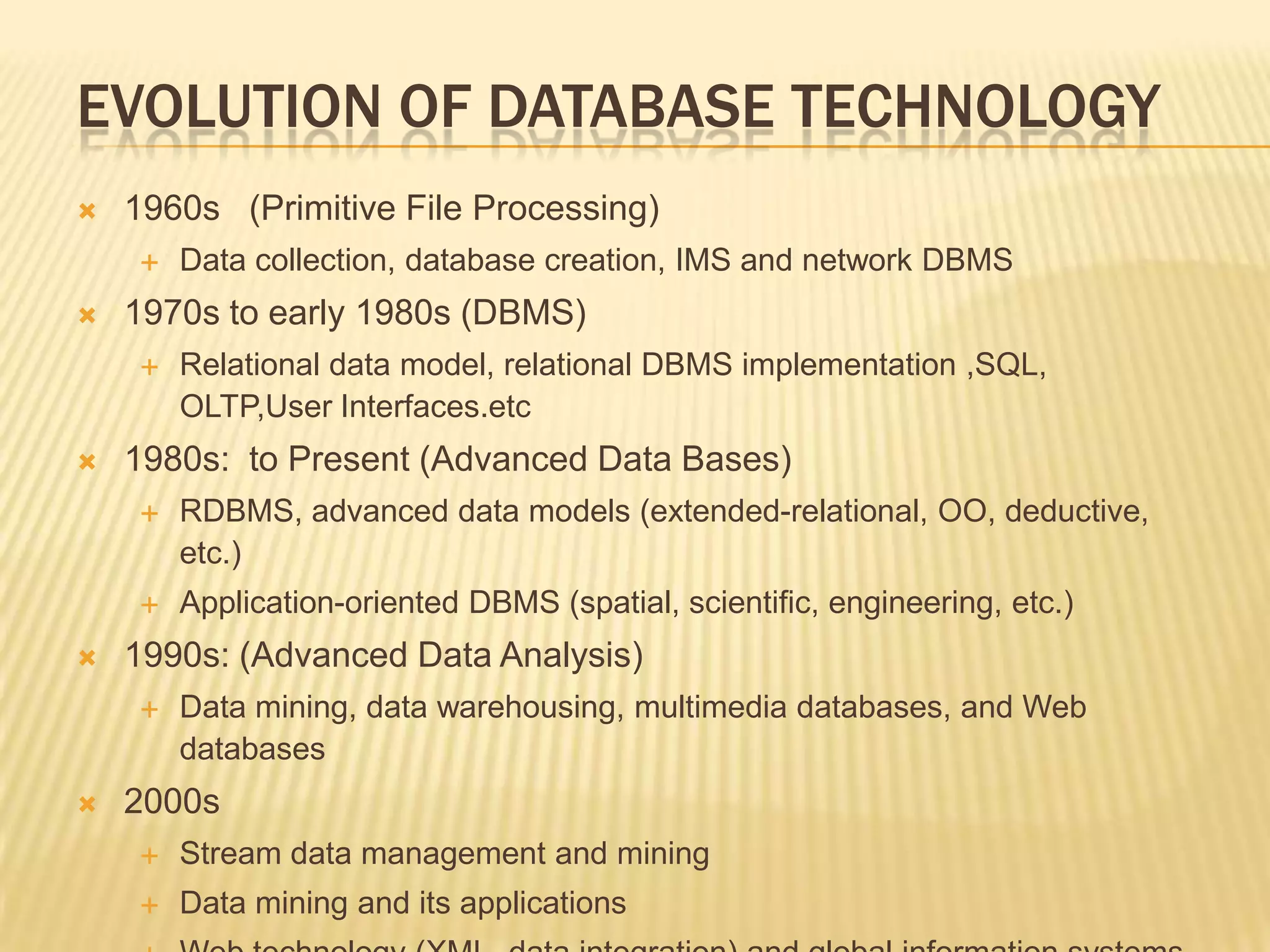
1) The document discusses the evolution of database technology from the 1960s to present, including primitive file processing, DBMS, relational DBMS, advanced data models, and data warehousing and mining.
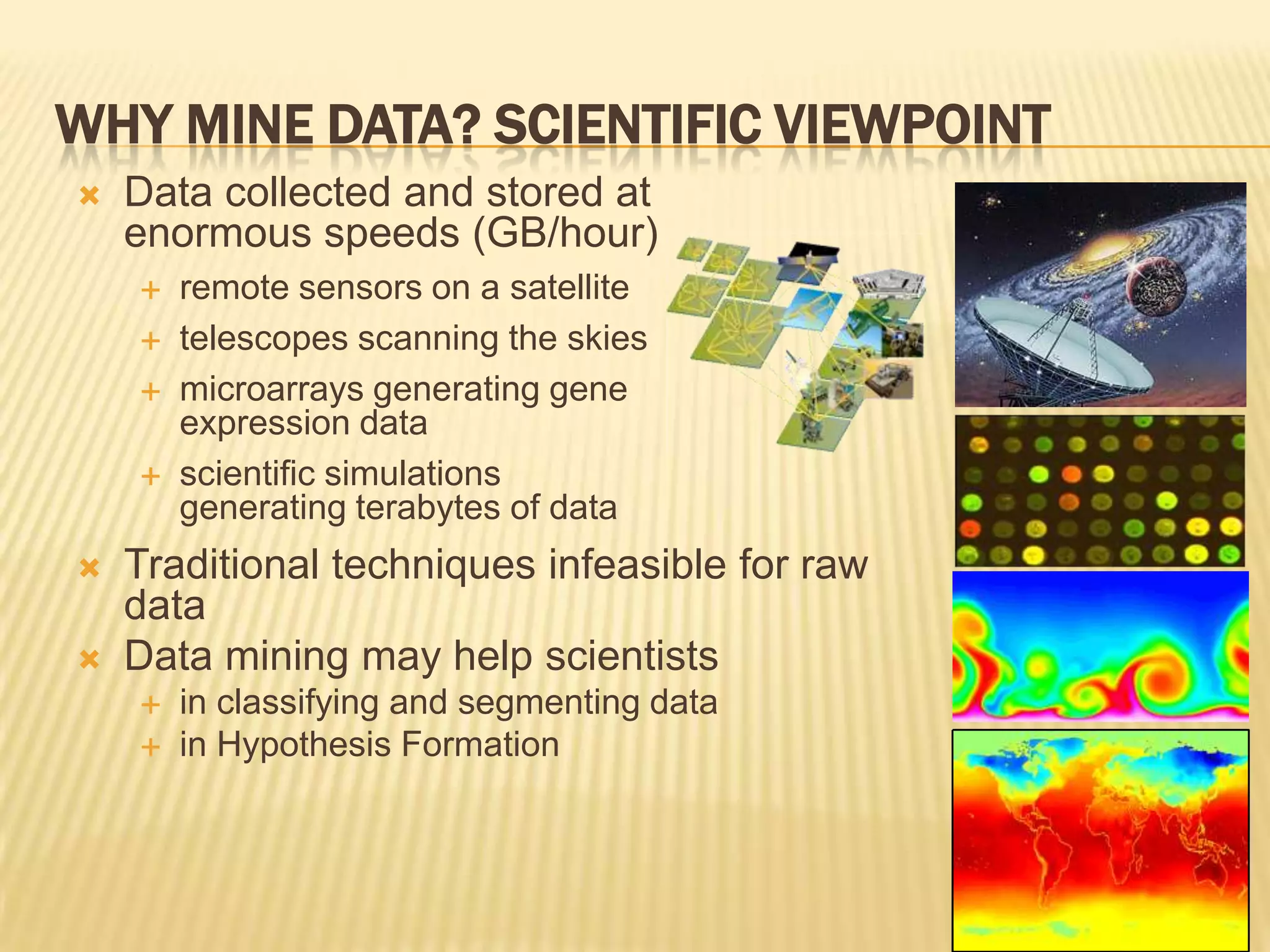
2) It explains why organizations mine data from a commercial viewpoint, to gain competitive advantages through better customized services, and from a scientific viewpoint to make use of large amounts of data being collected.
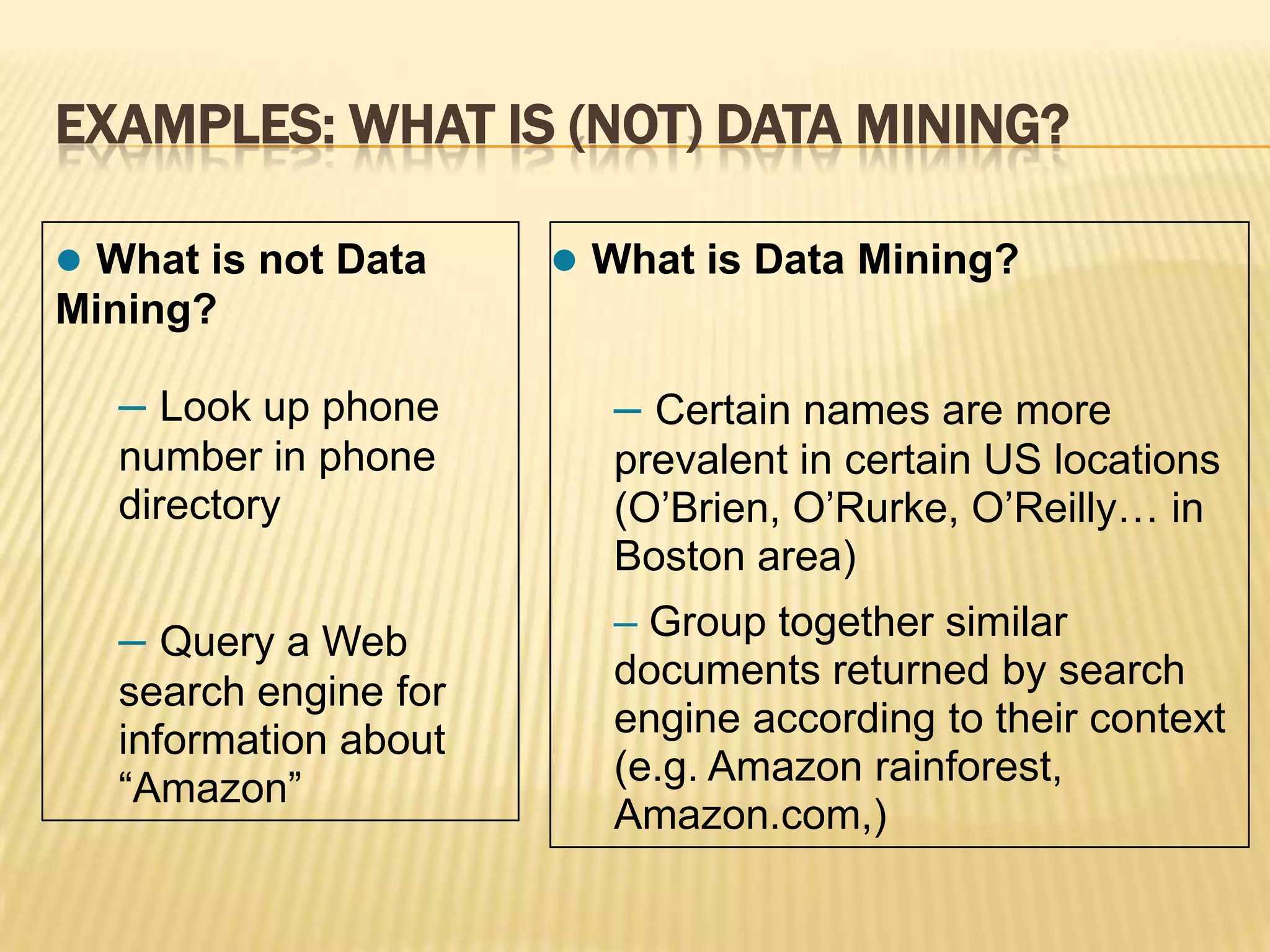
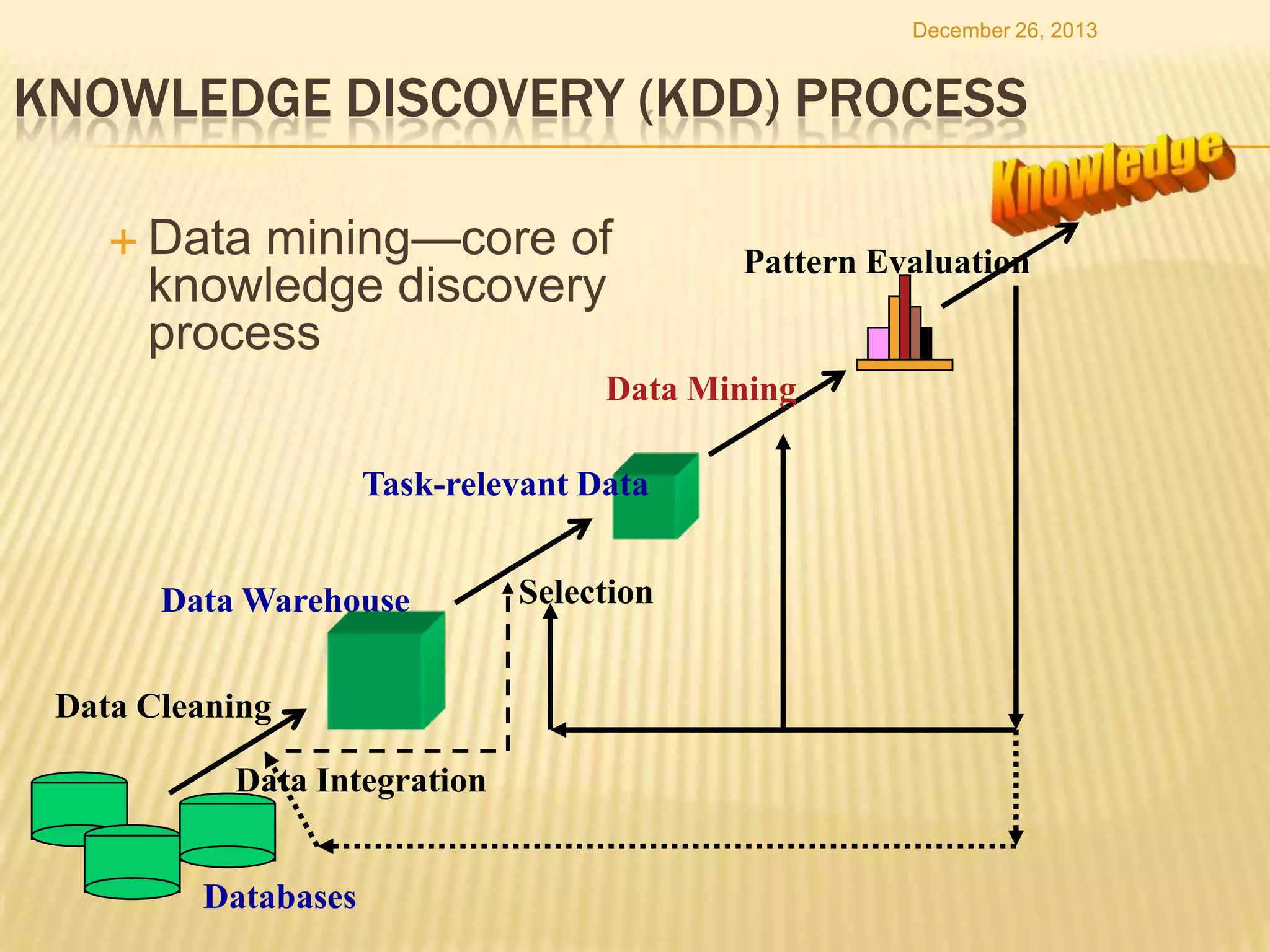
3) Data mining is defined as the process of analyzing data from different perspectives to extract useful patterns and knowledge, and examples are given of what is and is not considered data mining.