The document discusses key concepts in data warehousing including:
1) The distinction between data and information, with data becoming valuable when organized and presented as information for decision making.
2) Characteristics of a data warehouse including being subject-oriented, integrated, non-volatile, time-variant, and accessible to end-users.
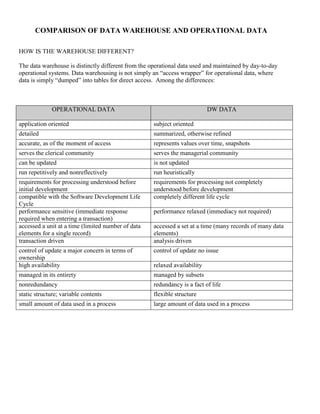
3) Differences between operational data and data warehouse data including the data warehouse being subject-oriented, summarized over time, and serving managerial communities rather than transactional needs.