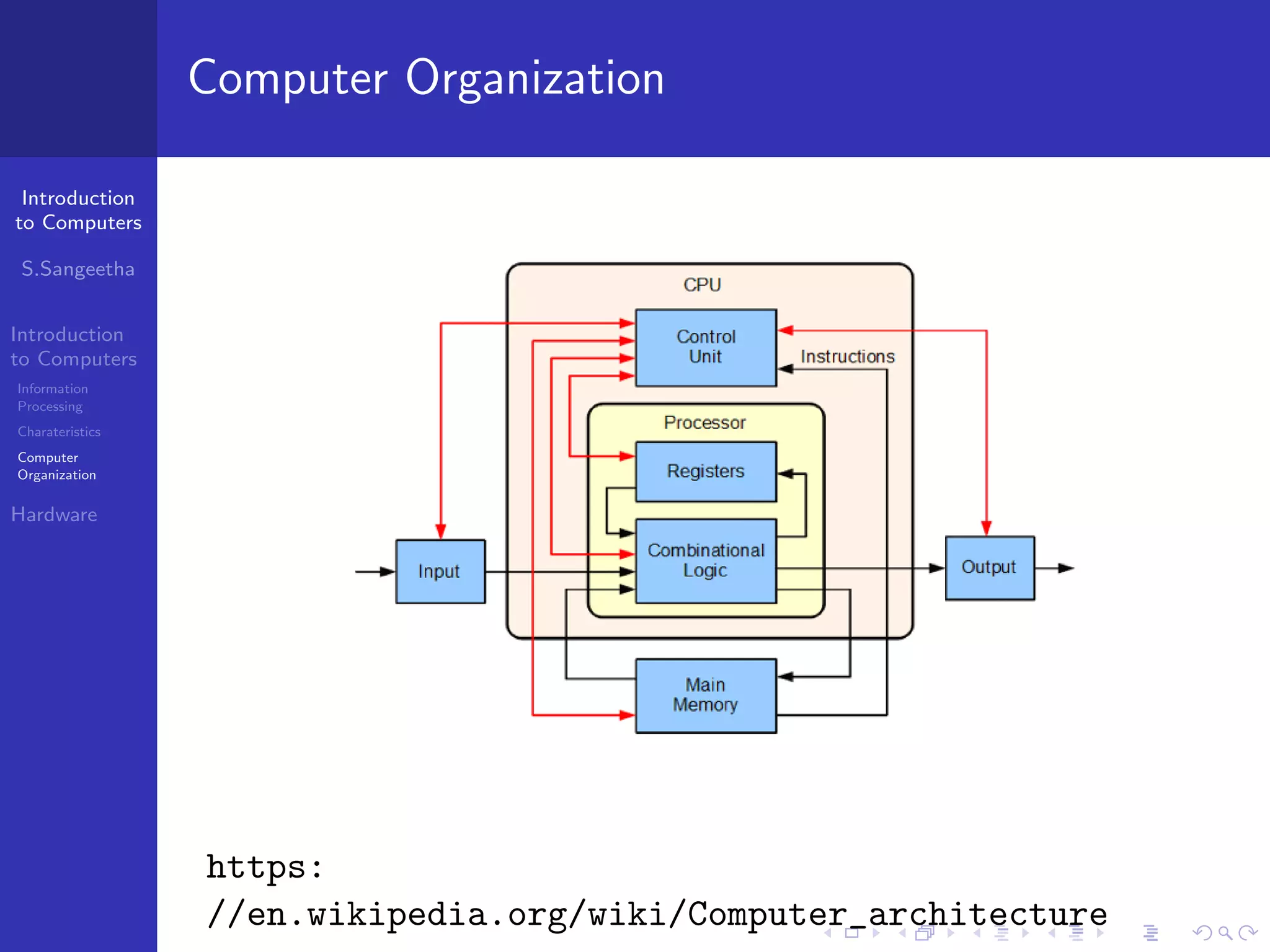
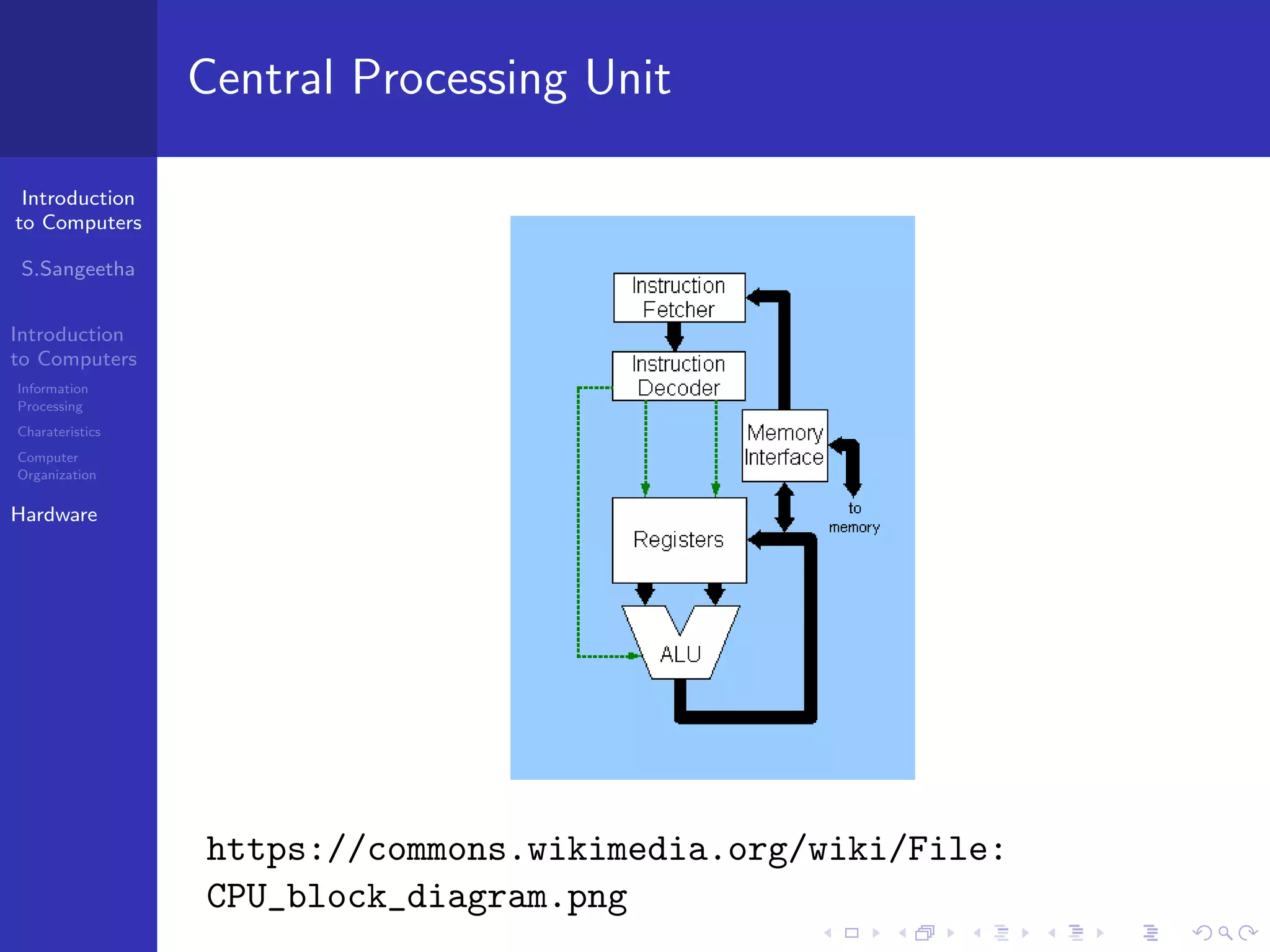
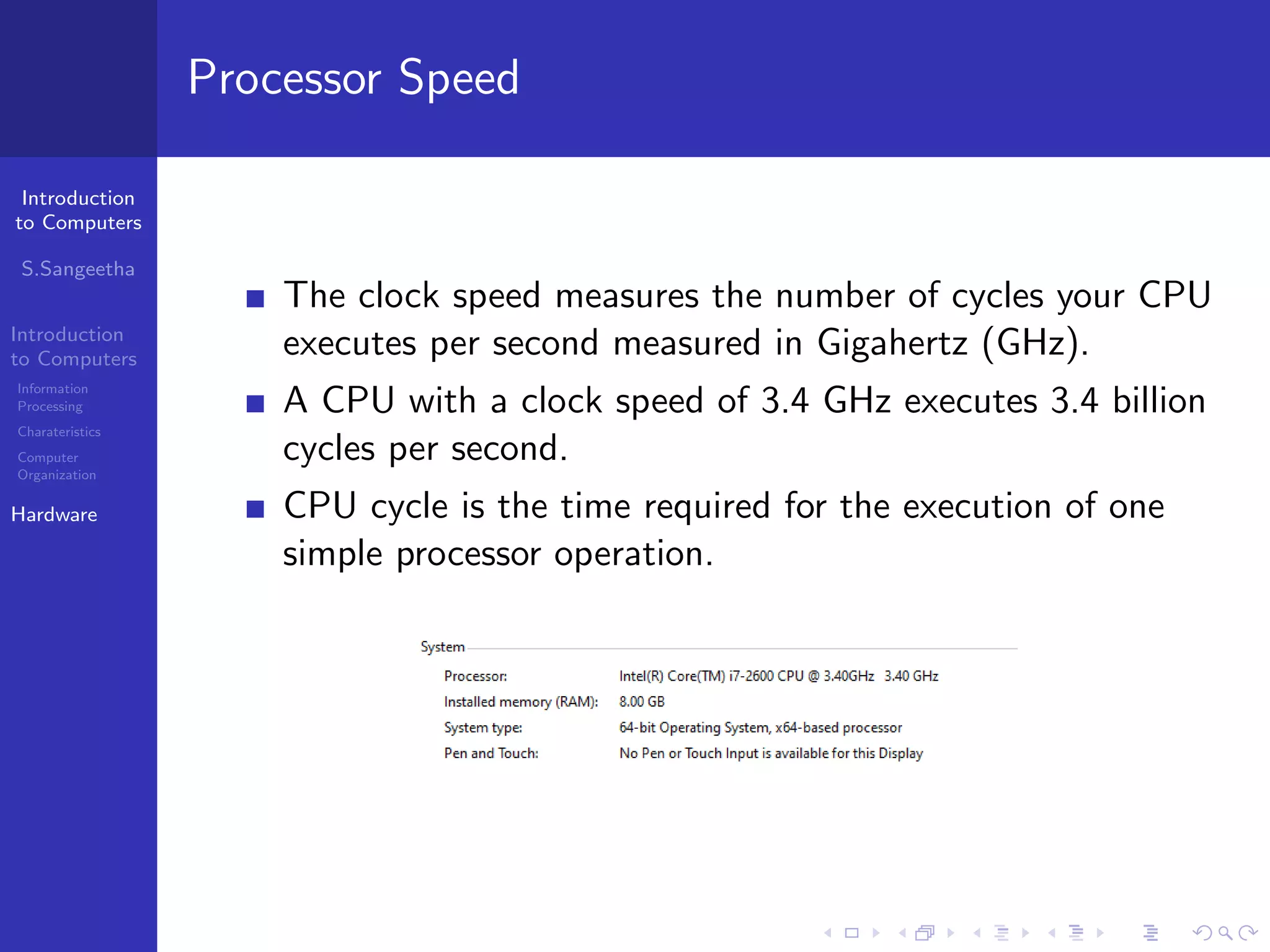
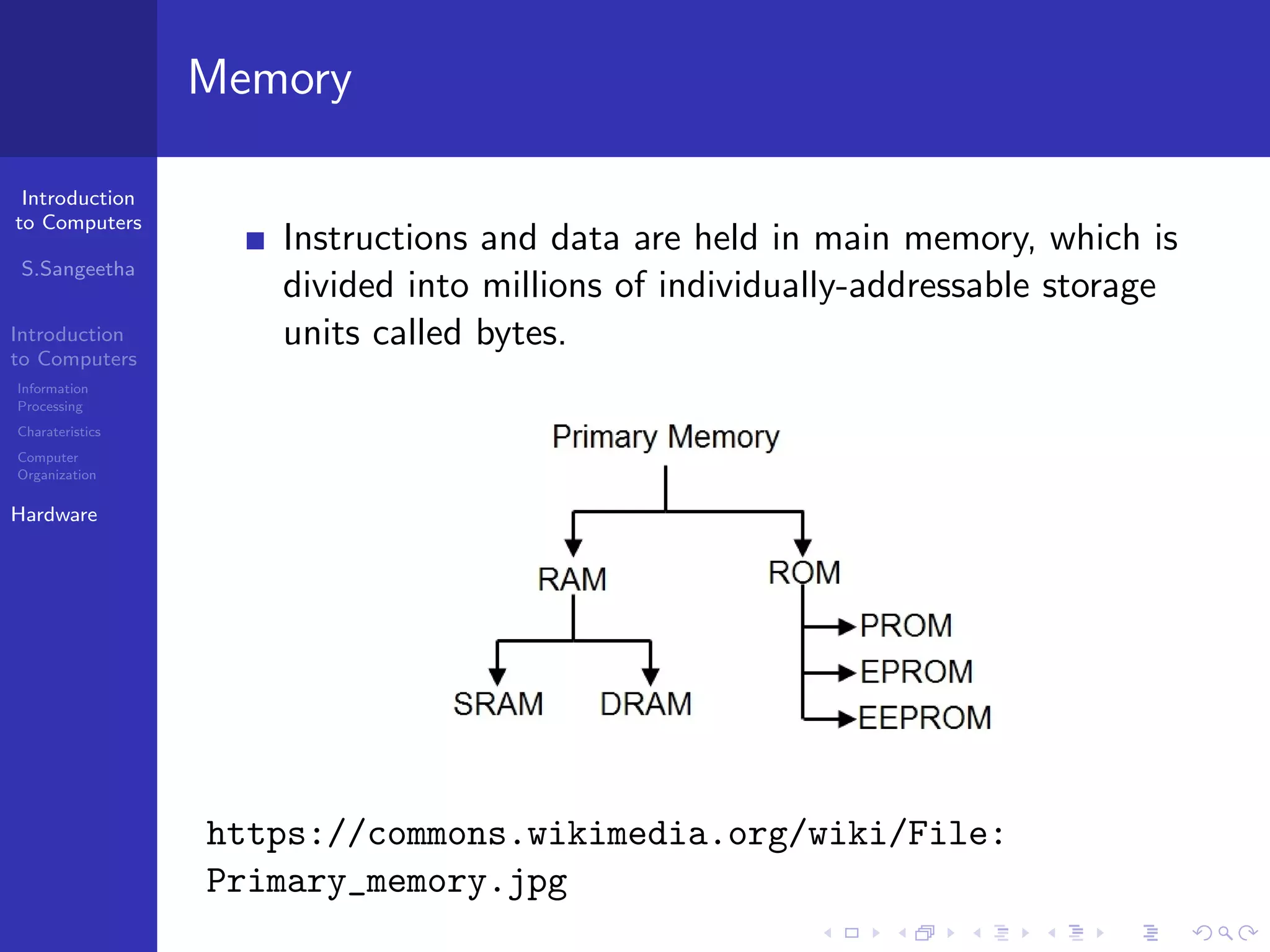
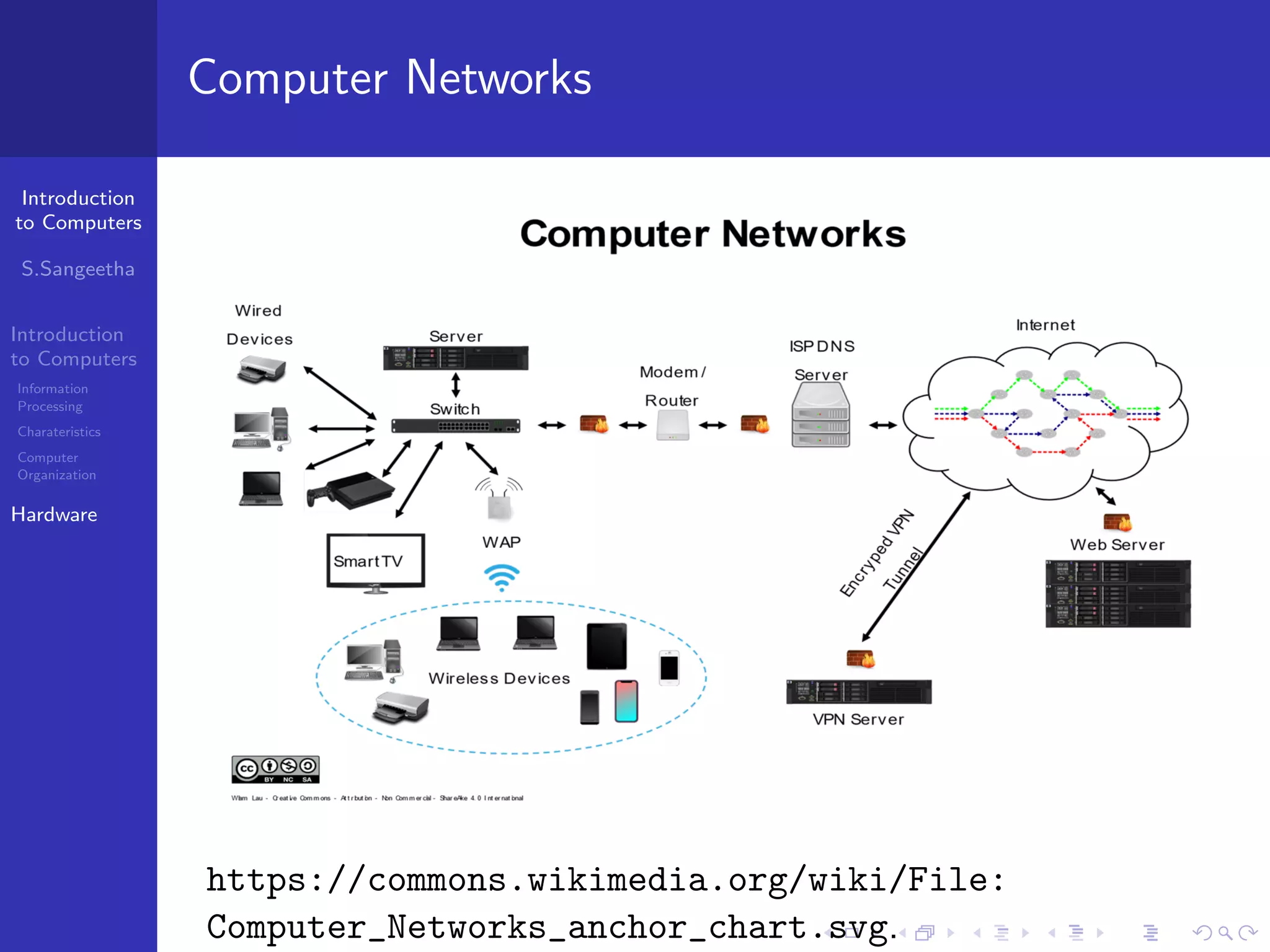
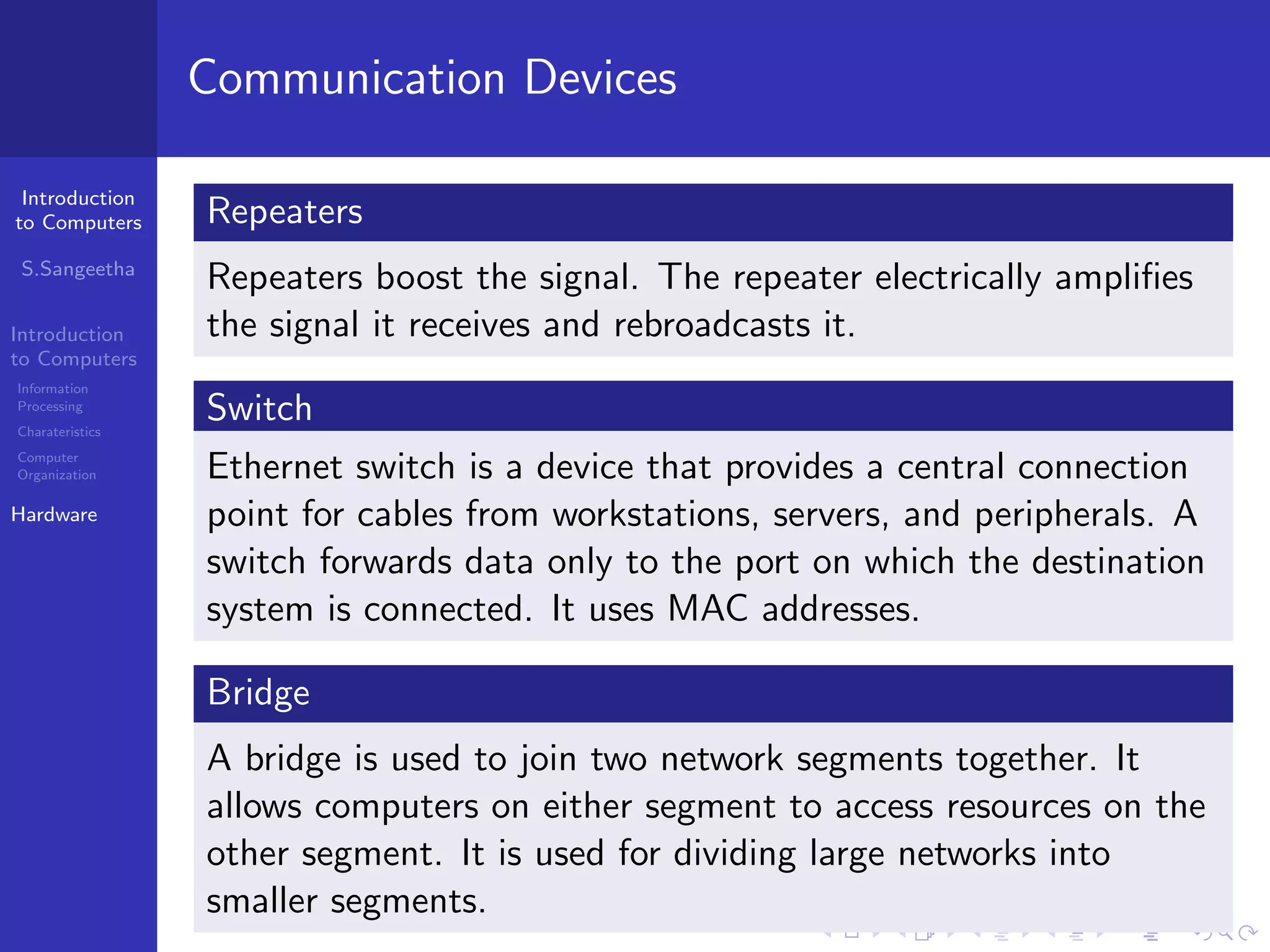
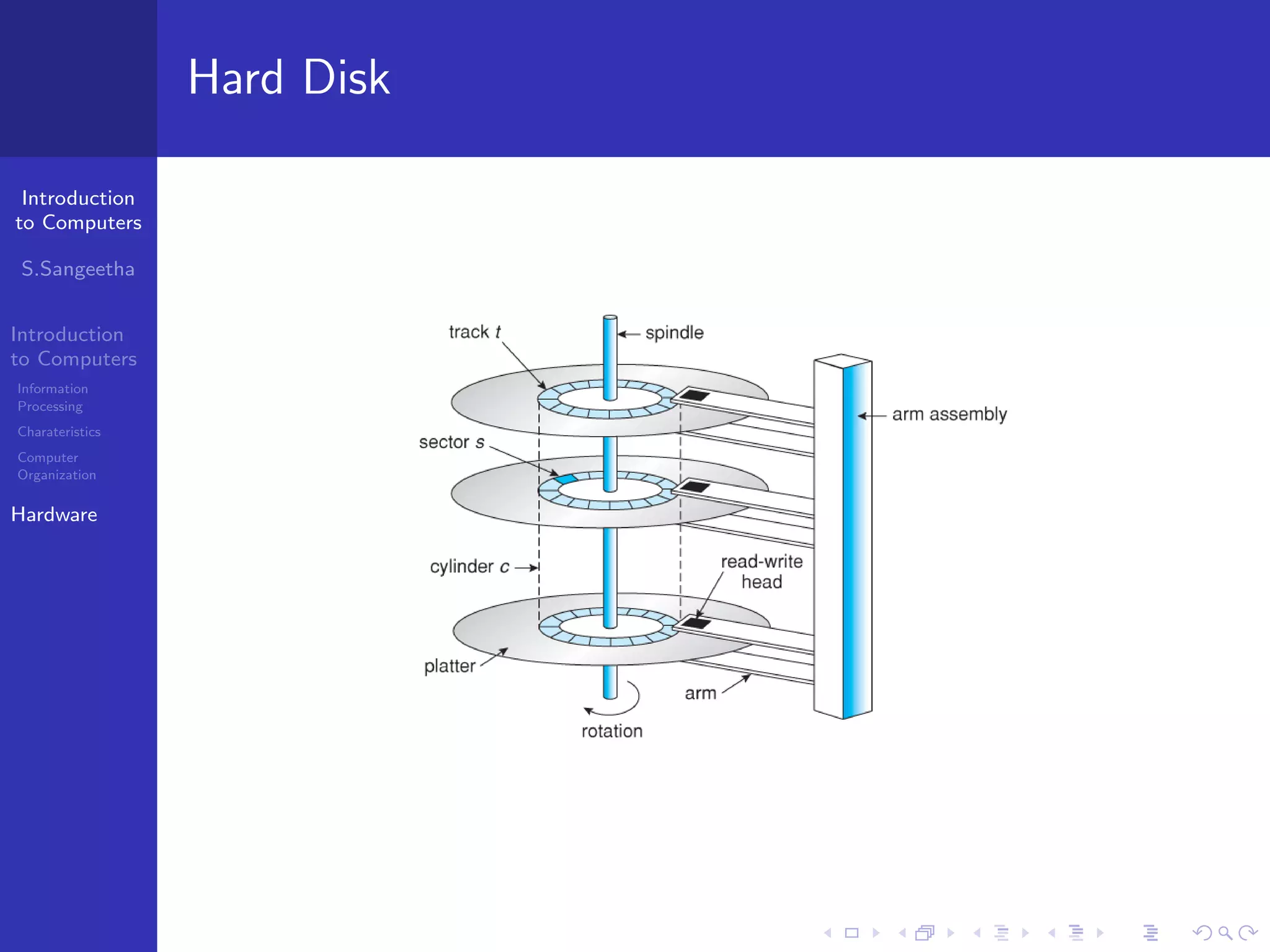
The document provides an introduction to computers, including information processing, characteristics of computers, computer organization, and hardware components. It describes how computers accept data as input, manipulate it, and produce output. It also outlines the basic components of a computer including the central processing unit, memory, storage devices, input/output ports, and communication devices.