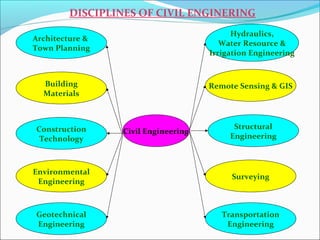
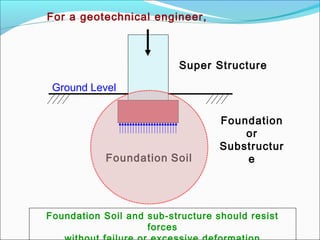
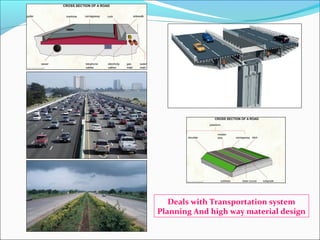
This document provides an introduction and overview of civil engineering. It discusses how civil engineering applies scientific and mathematical principles to improve infrastructure and living standards. It then describes civil engineering as dealing with the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings, bridges, roads, and other infrastructure facilities. The document outlines several disciplines within civil engineering, including structural engineering, transportation engineering, geotechnical engineering, water resources engineering, environmental engineering, construction management, surveying, and others. It provides examples to illustrate concepts within several of these disciplines.