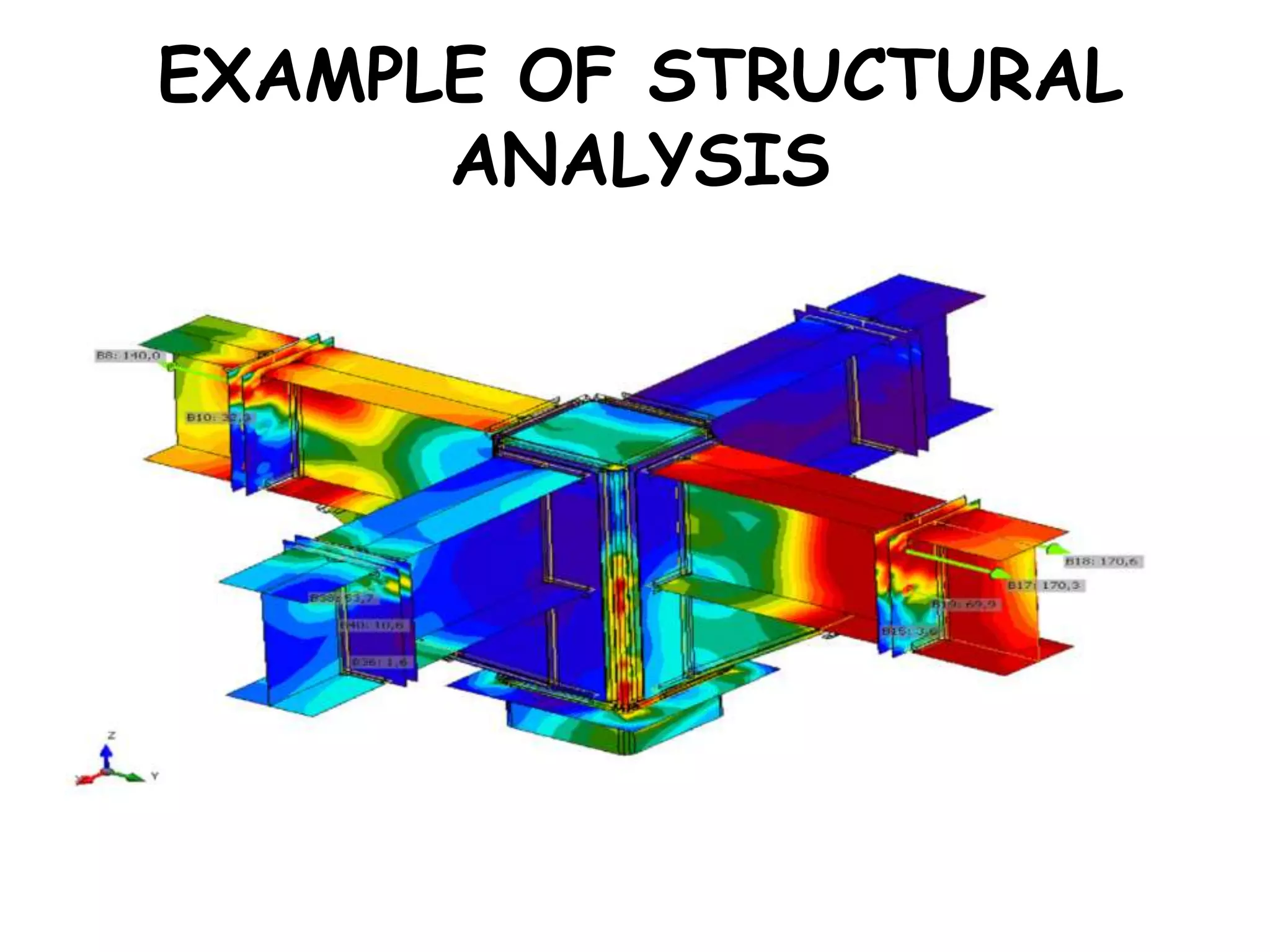
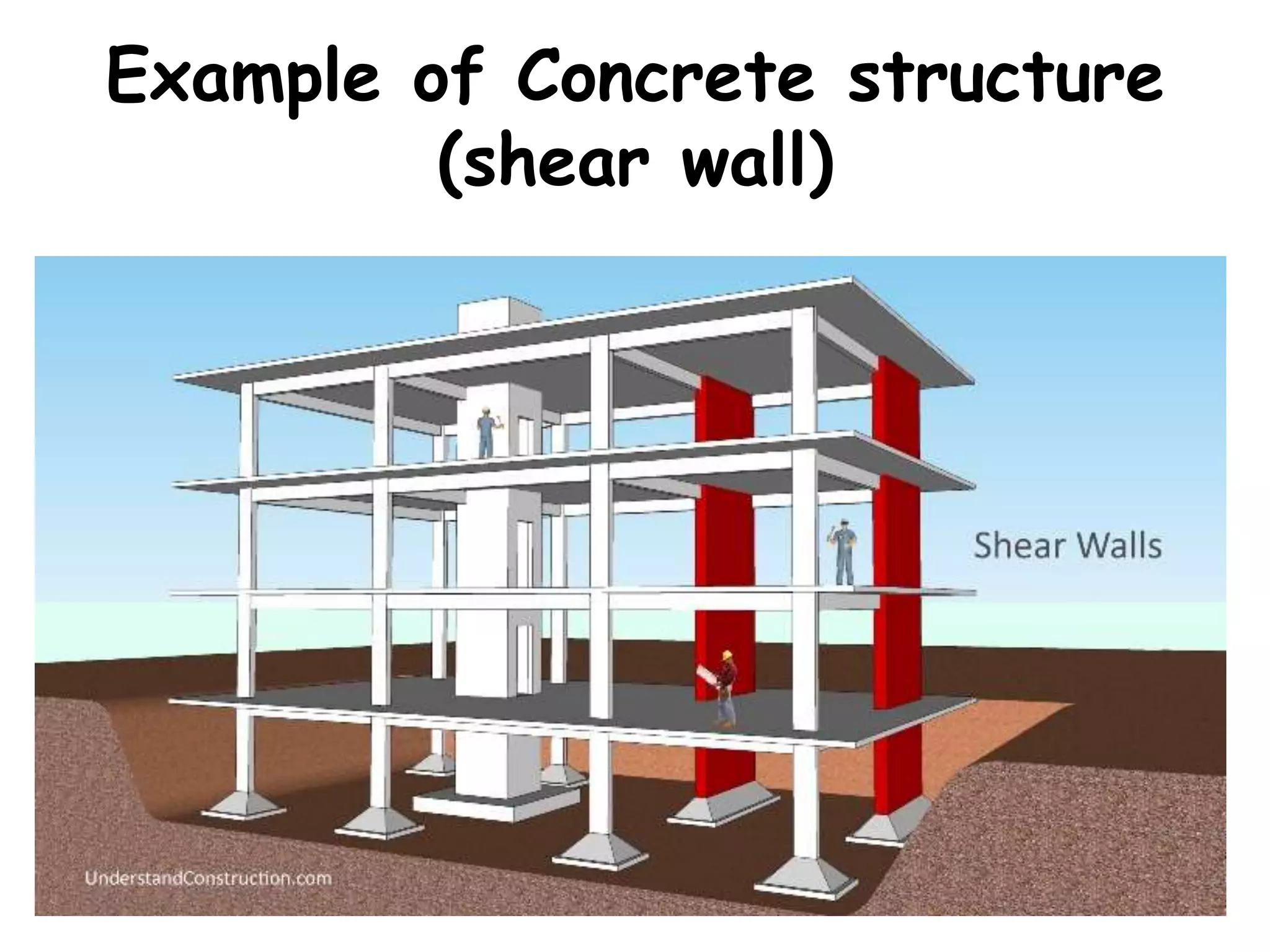
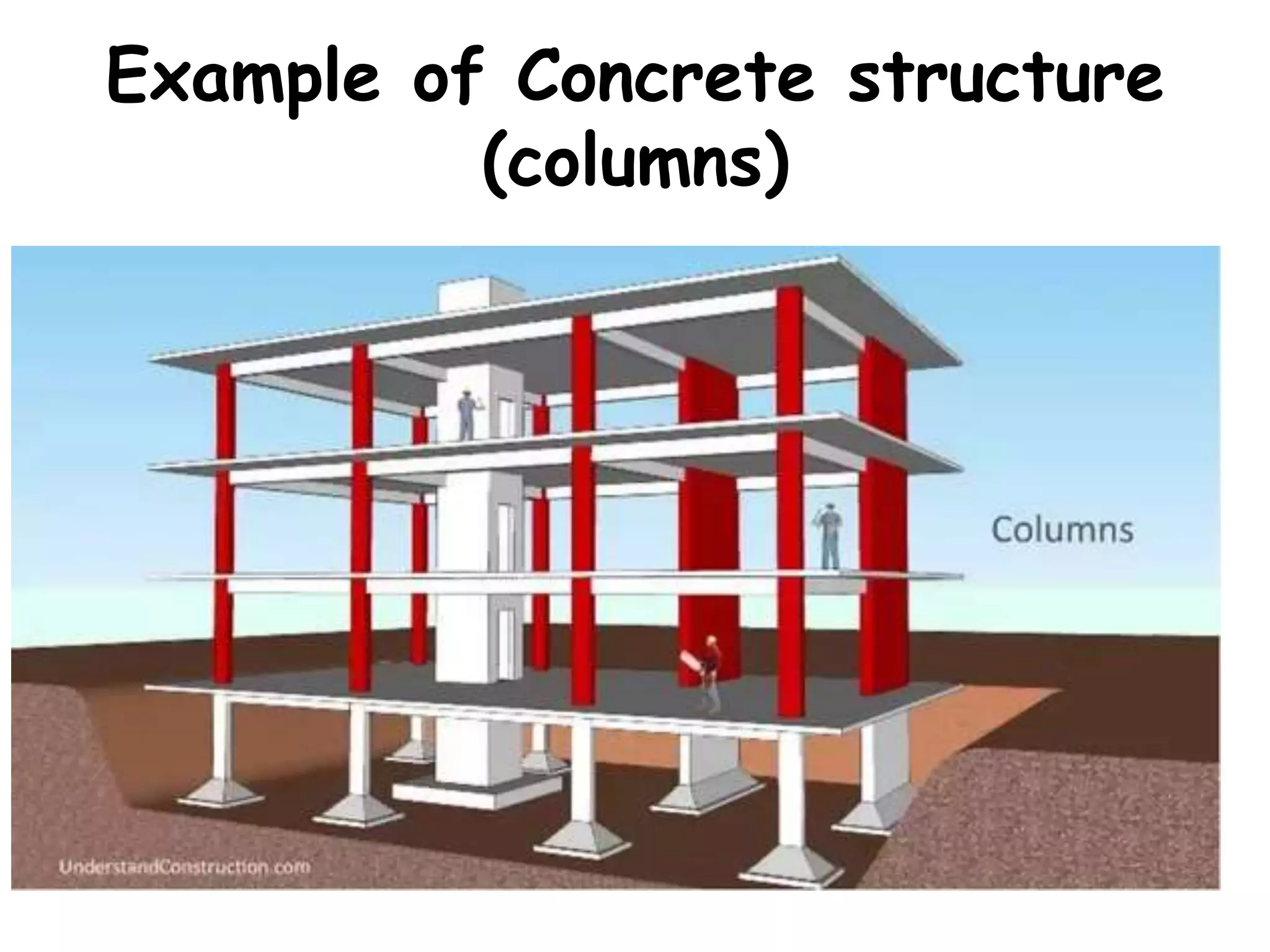
Civil engineering deals with designing, constructing, and maintaining infrastructure like roads, bridges, buildings, and water systems. It involves structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, environmental engineering, transportation engineering, and other areas. Civil engineers play a key role in building infrastructure that is important for society and the economy. Their work ranges from designing foundations and bridges to managing water resources, waste, and pollution control projects.