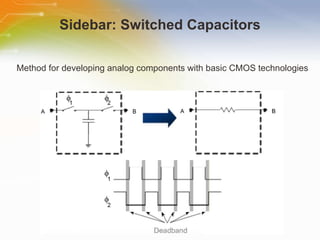
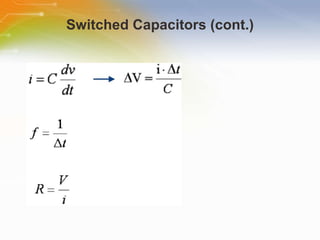
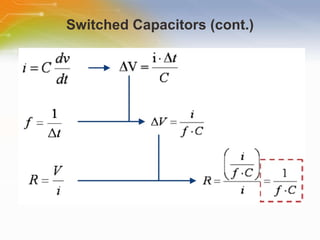
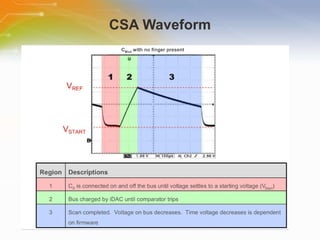
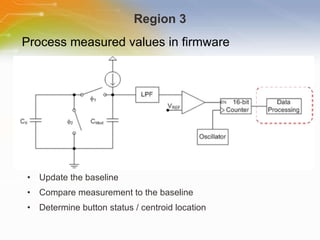
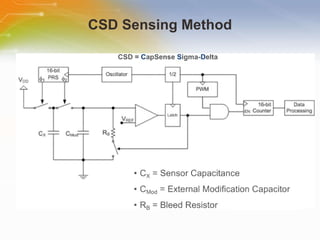
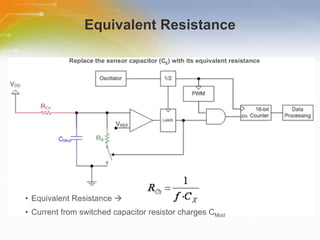
This document introduces the CSA and CSD capacitive sensing methods. CSA uses successive approximation to find the capacitance value by charging and discharging the sensor capacitor until the voltage matches a reference level. CSD uses a sigma-delta modulator to compare the sensor capacitor to a reference and outputs a bit stream. Both methods detect changes in capacitance by measuring how long it takes to charge the sensor capacitor, with increased capacitance resulting in a faster charge time and higher output value. The value is then processed to determine if a touch is present.