Introduction to common essential Drugs
•
1 like•360 views
This document provides information on common essential drugs including benzoic acid, salicylic acid, aspirin, paracetamol, PABA, sulfa drugs, and PASA. It describes the structure, synthesis, properties and uses of each drug. Benzoic acid is used as a germicide and food preservative. Salicylic acid has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Aspirin is used to reduce fever and pain. Paracetamol is an analgesic and antipyretic. PABA acts as a sunscreen and in vitamin synthesis. Sulfa drugs treat bacterial infections. PASA is used to treat tuberculosis.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Anticonvulsant 

This document provides information on various anticonvulsant drugs. It begins by defining anticonvulsants as drugs used for managing and controlling central nervous system disorders manifested by recurrent seizures. It then classifies anticonvulsants based on their chemical structure and discusses several individual drugs, including phenytoin, carbamazepine, ethosuximide, and trimethadione. For each drug, it provides information on their structure, properties, uses, and other details. The document aims to inform readers about different types of anticonvulsant medications.
General anaesthesia By MOHD. AFAQUE

General anaesthetics are drugs that induce unconsciousness and abolish sensations like pain. Some key points:
- Diethyl ether was the first widely used inhalation anaesthetic in 1846. Thiopentone was the first intravenous anaesthetic in 1935.
- Types include volatile/inhalation agents like halothane and cyclopropane, and non-volatile intravenous agents like thiopentone sodium and methohexital sodium.
- Thiopentone sodium is a white powder used as a simple anaesthetic for short procedures, commonly used to induce general anaesthesia. Methohexital sodium is a similar intravenous agent that is 3 times more potent and has a briefer action.
Phytochemistry essential oils terpene hydrocarbons

Myrcene, Ocimene, sesquicitronellene, farnesene, Limonene,
Sylvestrene, a-Pinene, zingiberene, derivatives of azulenes, santalene, Styrene and Cymene
Expectorant and emetics ppt

Expectorants are agents that enhance sputum secretion from the respiratory tract and facilitate removal of bronchopulmonary mucus. They are classified as sedatives like ipecac or stimulants like eucalyptus oil. Potassium iodide is a sedative expectorant prepared by reacting iodine with potassium hydroxide or using iron fillings with potassium carbonate. Ammonium chloride is also a sedative expectorant made by neutralizing hydrochloric acid with ammonia. Emetics induce vomiting by stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone or irritating the GI tract. Copper sulphate is a common emetic that is prepared as blue crystals through a two-
Expectorant and Emetics

This document discusses expectorants and emetics. It describes expectorants as agents that enhance sputum secretion from the respiratory tract and are used to treat cough. Expectorants are classified as sedative or stimulant based on their mechanism of action. Sedative expectorants irritate the stomach to stimulate gastric reflux, while stimulant expectorants directly or indirectly stimulate respiratory secretory cells. Potassium iodide and ammonium chloride are discussed as examples of expectorant drugs. Emetics induce vomiting and act by stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone or irritating the GI tract. Copper sulfate is provided as an example of an emetic drug and its properties and uses are summarized.
Expectorant

This document discusses expectorants and their classification. It covers two main types of expectorants - sedative and stimulant. Sedative expectorants like ipecac and antimony potassium tartarate work through gastric stimulation. Stimulant expectorants like eucalyptus oil directly stimulate respiratory secretions. Two specific expectorants, potassium iodide and ammonium chloride, are then described in detail including their chemical properties, methods of preparation, uses and storage conditions.
Sedatives and Hypnotics

Sedatives and hypnotics are central nervous system drugs that reduce excitement and tension, producing relaxation or sleep. Sedatives have lower drug concentrations and hypnotics have higher concentrations. They are classified based on their chemical structure, including barbiturates, benzodiazepines, alcohol, and others. Barbiturates like phenobarbital are long-acting and used as sedatives and anticonvulsants, while butobarbital and cyclobarbital are also barbiturates used as sedatives and hypnotics. Benzodiazepines such as nitrazepam are used as long-acting hypnotics. Paraldehyde and glutethimide
EXPECTORANT AND EMETICS

DEFINATION
TYPES OF COUGH
CLASSIFICATION OF EXPECTORANT AND MECHANISM OF ACTION
DEFINATION OF EMETICS
MECHANISM OF ACTION OF EMETICS
COMPOUND RELATED TO EXPECTORANT.
Recommended
Anticonvulsant 

This document provides information on various anticonvulsant drugs. It begins by defining anticonvulsants as drugs used for managing and controlling central nervous system disorders manifested by recurrent seizures. It then classifies anticonvulsants based on their chemical structure and discusses several individual drugs, including phenytoin, carbamazepine, ethosuximide, and trimethadione. For each drug, it provides information on their structure, properties, uses, and other details. The document aims to inform readers about different types of anticonvulsant medications.
General anaesthesia By MOHD. AFAQUE

General anaesthetics are drugs that induce unconsciousness and abolish sensations like pain. Some key points:
- Diethyl ether was the first widely used inhalation anaesthetic in 1846. Thiopentone was the first intravenous anaesthetic in 1935.
- Types include volatile/inhalation agents like halothane and cyclopropane, and non-volatile intravenous agents like thiopentone sodium and methohexital sodium.
- Thiopentone sodium is a white powder used as a simple anaesthetic for short procedures, commonly used to induce general anaesthesia. Methohexital sodium is a similar intravenous agent that is 3 times more potent and has a briefer action.
Phytochemistry essential oils terpene hydrocarbons

Myrcene, Ocimene, sesquicitronellene, farnesene, Limonene,
Sylvestrene, a-Pinene, zingiberene, derivatives of azulenes, santalene, Styrene and Cymene
Expectorant and emetics ppt

Expectorants are agents that enhance sputum secretion from the respiratory tract and facilitate removal of bronchopulmonary mucus. They are classified as sedatives like ipecac or stimulants like eucalyptus oil. Potassium iodide is a sedative expectorant prepared by reacting iodine with potassium hydroxide or using iron fillings with potassium carbonate. Ammonium chloride is also a sedative expectorant made by neutralizing hydrochloric acid with ammonia. Emetics induce vomiting by stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone or irritating the GI tract. Copper sulphate is a common emetic that is prepared as blue crystals through a two-
Expectorant and Emetics

This document discusses expectorants and emetics. It describes expectorants as agents that enhance sputum secretion from the respiratory tract and are used to treat cough. Expectorants are classified as sedative or stimulant based on their mechanism of action. Sedative expectorants irritate the stomach to stimulate gastric reflux, while stimulant expectorants directly or indirectly stimulate respiratory secretory cells. Potassium iodide and ammonium chloride are discussed as examples of expectorant drugs. Emetics induce vomiting and act by stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone or irritating the GI tract. Copper sulfate is provided as an example of an emetic drug and its properties and uses are summarized.
Expectorant

This document discusses expectorants and their classification. It covers two main types of expectorants - sedative and stimulant. Sedative expectorants like ipecac and antimony potassium tartarate work through gastric stimulation. Stimulant expectorants like eucalyptus oil directly stimulate respiratory secretions. Two specific expectorants, potassium iodide and ammonium chloride, are then described in detail including their chemical properties, methods of preparation, uses and storage conditions.
Sedatives and Hypnotics

Sedatives and hypnotics are central nervous system drugs that reduce excitement and tension, producing relaxation or sleep. Sedatives have lower drug concentrations and hypnotics have higher concentrations. They are classified based on their chemical structure, including barbiturates, benzodiazepines, alcohol, and others. Barbiturates like phenobarbital are long-acting and used as sedatives and anticonvulsants, while butobarbital and cyclobarbital are also barbiturates used as sedatives and hypnotics. Benzodiazepines such as nitrazepam are used as long-acting hypnotics. Paraldehyde and glutethimide
EXPECTORANT AND EMETICS

DEFINATION
TYPES OF COUGH
CLASSIFICATION OF EXPECTORANT AND MECHANISM OF ACTION
DEFINATION OF EMETICS
MECHANISM OF ACTION OF EMETICS
COMPOUND RELATED TO EXPECTORANT.
8-Quinoline_and_Isoquinoline.pptx

Structural features of Cinchona alkaloids
1- The basic skeleton of Cinchona alkaloids is Ruban-9-Ol.
2- Ruban nucleus is a combined skeleton formed from a quinoline ring attached to a quinuclidine ring (a bicyclic ring contain N) through methylene group.
10-Opium_alkaloids_and_derivatives.pptx

Opium is the air-dried milky exudate, or latex, obtained by incising the unripe capsules of the opium poppy Papaver somniferum (Papaveraceae).
the ripe capsule can contain up to 0.5% total alkaloids
Opium represents a much concentrated form and up to 25% of its mass is composed of alkaloids ( more than 40 alkaloids).
tannins.pptx

Tannins are phenolic compounds found in plants that can precipitate proteins. They are classified as true tannins, pseudotannins, hydrolysable tannins, and condensed tannins. Hydrolysable tannins include gallitannins and ellagitannins that break down into gallic acid or ellagic acid. Condensed tannins are polymeric flavan-3-ols like catechin. Tannins are identified through tests like reaction with iron salts or bromine water. They have industrial uses in tanning leather and making ink, and medicinal uses as astringents and antioxidants in conditions like diarrhea, burns, and inflamed skin. Major commercial sources
Unorganized drugs part_2

Cantharides (Spanish flies)
Origin:
Cantharides is the dried beetles of Cantharis vescicatoria, Meloidae.
Active Constituents:
Cantharidin
Uses:
It is a very irritant poison (10 mg is fatal).
It was formerly used for treatment of skin diseases mainly in veterinary medicine.
Rubefacient.
As tincture in treatment of alopecia areata.
Internally, in too small doses as aphrodisiac (illegal).
Determination of cineole in eucalyptus oil

Determination of Oxides in volatile oils
vapozol sol. for inh., eucal cr. and gel, alveolin syrup and followcease syrup.... etc.
Phytochemistry essential oils esters, oxides and peroxides

Geranyl acetate, Geranyl formate, Geranyl butyrate, Linalyl acetate, Methyl Salicylate, Methyl cinnamate, Ethyl cinnamate, Methyl anthranilate, Benzyl acetate, Benzyl benzoate,1,8-cineole Eucalyptol, Cajuputol and Ascaridole
Presevatives-mass.pptx

This document discusses preservatives used in pharmaceutical products. It defines preservatives as substances added to prevent microbial growth. Ideal preservatives are effective at low concentrations, nontoxic, compatible with other ingredients, and stable over the product's shelf life. Common preservatives discussed include parabens, benzoic acid derivatives, alcohols, phenols, and quaternary ammonium compounds. The document also covers preservative classification, mechanisms of action, analysis, side effects, and uses in different dosage forms like oral, dermal, ophthalmic, and more.
Emetics 

Emetics are drugs that induce vomiting by causing the contents of the stomach to be expelled through the mouth. They are important for treating poisoning cases. Copper sulfate is a common emetic that is blue crystalline powder. It can be assayed through an oxidation-reduction titration with iodine and sodium thiosulfate. Sodium potassium tartrate, also known as Rochelle salt, is a crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It has uses as a laxative, diuretic, and food additive.
Glycosides Note 

lycosides and glycoside containing drugs.
Biosynthesis of glycosides: The details of the followings:
i) Cyanogenic: Wild Cherry
ii)Isothiocyanate-Mustard (Black mustard and white mustard).
iii) Cardiac: Digitalis, strophanthus, squill.
B.Pharm Syllabus
Northern University Bangladesh
De ve loped b y: Ma hab ur R a hma n She i kh & M ahm ud ur R ahman
Assistant Professors, Department of Pharmacy, Northern University Bangladesh
30
iv) Saponins: Sarsaparilla, glycyrrhiza, dioscorea.
v)
Anthraquinone glycosides: Cascara sagrada, aloe, senna, rhubarb.
vi) Other glycosides and neutral principles: Gentian, quassia, saffron.
Meat flavour

This presentation highlights the flavor developed during cooking of meat. Meat flavor development is a complex process which involves formation of multiple kinds of chemical compounds. So check out this presentation to know more about those savory, mouth watering flavors of meat that you can't resist!
Bnzoic acid ppt

Benzoic acid is a colorless crystalline solid that occurs naturally in many plants. It can be produced commercially through the partial oxidation of toluene or synthesized in the laboratory through various methods like the hydrolysis of benzonitrile. Its main use is in the production of phenol, and it is also used to make plasticizers and in some medicinal ointments. Benzoic acid is metabolized in the body and excreted as hippuric acid in urine. Reactions can occur on the aromatic ring or carboxyl group, with electrophilic aromatic substitutions favoring the meta position.
Phytochemistry essential oils organo-nitrogen and organo-sulphur compounds

This document discusses organo-nitrogen and organo-sulfur compounds found in volatile oils. It describes their occurrence in plants through steam distillation and provides examples such as hydrogen sulfide in anise and caraway oils and diallyl disulfide in onion and garlic oils. Methods for isolating and identifying compounds like allyl isothiocyanate from mustard seeds and hydrocyanic acid using Prussian blue and Guignard's paper tests are also summarized. Potential uses of these compounds as flavorings, irritants, or fixatives in perfumes are mentioned.
Topical agents: Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry

Protectives, Local anti-infectives, Astringents
Classification, Ideal properties, and
Talc, Zinc oxide, Calamine, Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2). Potassium permangnate (KMnO4)
Anti oxidants

This document discusses antioxidants and other food additives. It defines antioxidants as substances added to food to prevent oxidative spoilage and notes their objectives are to prevent rancidity in fatty foods and browning in fruits and vegetables. It describes oxidation and the two types that occur, and explains how antioxidants work by consuming free radicals produced. The document outlines natural antioxidants like ascorbic acid and tocopherols, and synthetic antioxidants like BHA, BHT and TBHQ. It notes health concerns about consuming too much of these additives and provides FSSAI standards. Finally, it briefly mentions other additives used as bulking agents, anti-caking agents, humectants and glazing agents
Antidote (PCI Syllabus, B.Pharm)

poison, antidote, symptoms of poisoning, sodium thiosulphate, Assay of sodium thiosulphate, iodimetry, Medicinal uses of sodium thiosulphate, activated charcoal, medicinal uses of activated charcoal, Sodium nitrite, Medicinal uses of sodium nitrite
Phytochemistry essential oils aromatic constituents from animal origin

This document discusses aromatic constituents derived from animal sources, including ambergris and musk. It provides details on ambergris, which comes from sperm whale intestinal tracts, and its constituents including ambrein. Natural musk is obtained from the rump glands of musk deer and other animals. Harvesting involves removing the gland and allowing it to dry. Synthetic musks are also discussed as perfume fixatives. The document is authored by Dr. Mostafa Mahmoud Hegazy and provides additional educational resources.
Pharmaceutical aids-and-necessities

This document discusses pharmaceutical aids and necessities. It begins by outlining the objectives and providing an overview. It then classifies various aids such as acids, bases, buffers, antioxidants, water and glass. The document goes on to describe specific acids, bases, buffers and antioxidants in detail, outlining their properties, production methods and uses in pharmaceutical preparations and storage.
Protectives & adsorbents 

Protectives and adsorbents are drugs that adsorb intestinal toxins, bacteria, and form a protective coating on the inflamed gastrointestinal tract. They are chemically inert substances such as bismuth subcarbonate, kaolin, and activated charcoal that are used to treat diarrhea and dysentery by adsorbing gases, toxins, and bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
Flavor enhancers

This document provides information on flavor enhancers and stabilizers used in foods. It discusses flavor, common flavor enhancers like monosodium glutamate, and techniques for analyzing flavors like gas chromatography. It also defines food stabilizers, provides examples like alginates and agar, describes general confirmatory tests, and discusses applications such as preventing emulsions from separating.
Pharmaceutical Solvents 

Pharmaceutical solvents
coloring agents
flavoring AGENTS
SWEETING AGENTS
DILUTING AGENTS
ANTIOXIDANTS
PRESERVATIVES
Sulphonamides

Sulphonamides are a class of antibacterial drugs that act as competitive inhibitors of dihydropteroate synthetase, blocking the biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolate needed by bacteria. Prontosil, an early sulphonamide prodrug, was found to metabolize into sulphanilamide, the active antibacterial agent. Key features of sulphonamides include their aromatic ring and sulphonamide group, which must be directly attached. While effective, sulphonamides can cause toxicity issues related to solubility, which structural modifications have aimed to address. Resistance can develop through enhanced enzyme activity or mutations impacting enzyme binding.
Reproduction and growth of bacteria by Tanzir

Reproduction and growth of Bacteria
Modes of cell divisions
Normal growth cycle
Synchronous growth
Measurement of Growth
More Related Content
What's hot
8-Quinoline_and_Isoquinoline.pptx

Structural features of Cinchona alkaloids
1- The basic skeleton of Cinchona alkaloids is Ruban-9-Ol.
2- Ruban nucleus is a combined skeleton formed from a quinoline ring attached to a quinuclidine ring (a bicyclic ring contain N) through methylene group.
10-Opium_alkaloids_and_derivatives.pptx

Opium is the air-dried milky exudate, or latex, obtained by incising the unripe capsules of the opium poppy Papaver somniferum (Papaveraceae).
the ripe capsule can contain up to 0.5% total alkaloids
Opium represents a much concentrated form and up to 25% of its mass is composed of alkaloids ( more than 40 alkaloids).
tannins.pptx

Tannins are phenolic compounds found in plants that can precipitate proteins. They are classified as true tannins, pseudotannins, hydrolysable tannins, and condensed tannins. Hydrolysable tannins include gallitannins and ellagitannins that break down into gallic acid or ellagic acid. Condensed tannins are polymeric flavan-3-ols like catechin. Tannins are identified through tests like reaction with iron salts or bromine water. They have industrial uses in tanning leather and making ink, and medicinal uses as astringents and antioxidants in conditions like diarrhea, burns, and inflamed skin. Major commercial sources
Unorganized drugs part_2

Cantharides (Spanish flies)
Origin:
Cantharides is the dried beetles of Cantharis vescicatoria, Meloidae.
Active Constituents:
Cantharidin
Uses:
It is a very irritant poison (10 mg is fatal).
It was formerly used for treatment of skin diseases mainly in veterinary medicine.
Rubefacient.
As tincture in treatment of alopecia areata.
Internally, in too small doses as aphrodisiac (illegal).
Determination of cineole in eucalyptus oil

Determination of Oxides in volatile oils
vapozol sol. for inh., eucal cr. and gel, alveolin syrup and followcease syrup.... etc.
Phytochemistry essential oils esters, oxides and peroxides

Geranyl acetate, Geranyl formate, Geranyl butyrate, Linalyl acetate, Methyl Salicylate, Methyl cinnamate, Ethyl cinnamate, Methyl anthranilate, Benzyl acetate, Benzyl benzoate,1,8-cineole Eucalyptol, Cajuputol and Ascaridole
Presevatives-mass.pptx

This document discusses preservatives used in pharmaceutical products. It defines preservatives as substances added to prevent microbial growth. Ideal preservatives are effective at low concentrations, nontoxic, compatible with other ingredients, and stable over the product's shelf life. Common preservatives discussed include parabens, benzoic acid derivatives, alcohols, phenols, and quaternary ammonium compounds. The document also covers preservative classification, mechanisms of action, analysis, side effects, and uses in different dosage forms like oral, dermal, ophthalmic, and more.
Emetics 

Emetics are drugs that induce vomiting by causing the contents of the stomach to be expelled through the mouth. They are important for treating poisoning cases. Copper sulfate is a common emetic that is blue crystalline powder. It can be assayed through an oxidation-reduction titration with iodine and sodium thiosulfate. Sodium potassium tartrate, also known as Rochelle salt, is a crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It has uses as a laxative, diuretic, and food additive.
Glycosides Note 

lycosides and glycoside containing drugs.
Biosynthesis of glycosides: The details of the followings:
i) Cyanogenic: Wild Cherry
ii)Isothiocyanate-Mustard (Black mustard and white mustard).
iii) Cardiac: Digitalis, strophanthus, squill.
B.Pharm Syllabus
Northern University Bangladesh
De ve loped b y: Ma hab ur R a hma n She i kh & M ahm ud ur R ahman
Assistant Professors, Department of Pharmacy, Northern University Bangladesh
30
iv) Saponins: Sarsaparilla, glycyrrhiza, dioscorea.
v)
Anthraquinone glycosides: Cascara sagrada, aloe, senna, rhubarb.
vi) Other glycosides and neutral principles: Gentian, quassia, saffron.
Meat flavour

This presentation highlights the flavor developed during cooking of meat. Meat flavor development is a complex process which involves formation of multiple kinds of chemical compounds. So check out this presentation to know more about those savory, mouth watering flavors of meat that you can't resist!
Bnzoic acid ppt

Benzoic acid is a colorless crystalline solid that occurs naturally in many plants. It can be produced commercially through the partial oxidation of toluene or synthesized in the laboratory through various methods like the hydrolysis of benzonitrile. Its main use is in the production of phenol, and it is also used to make plasticizers and in some medicinal ointments. Benzoic acid is metabolized in the body and excreted as hippuric acid in urine. Reactions can occur on the aromatic ring or carboxyl group, with electrophilic aromatic substitutions favoring the meta position.
Phytochemistry essential oils organo-nitrogen and organo-sulphur compounds

This document discusses organo-nitrogen and organo-sulfur compounds found in volatile oils. It describes their occurrence in plants through steam distillation and provides examples such as hydrogen sulfide in anise and caraway oils and diallyl disulfide in onion and garlic oils. Methods for isolating and identifying compounds like allyl isothiocyanate from mustard seeds and hydrocyanic acid using Prussian blue and Guignard's paper tests are also summarized. Potential uses of these compounds as flavorings, irritants, or fixatives in perfumes are mentioned.
Topical agents: Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry

Protectives, Local anti-infectives, Astringents
Classification, Ideal properties, and
Talc, Zinc oxide, Calamine, Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2). Potassium permangnate (KMnO4)
Anti oxidants

This document discusses antioxidants and other food additives. It defines antioxidants as substances added to food to prevent oxidative spoilage and notes their objectives are to prevent rancidity in fatty foods and browning in fruits and vegetables. It describes oxidation and the two types that occur, and explains how antioxidants work by consuming free radicals produced. The document outlines natural antioxidants like ascorbic acid and tocopherols, and synthetic antioxidants like BHA, BHT and TBHQ. It notes health concerns about consuming too much of these additives and provides FSSAI standards. Finally, it briefly mentions other additives used as bulking agents, anti-caking agents, humectants and glazing agents
Antidote (PCI Syllabus, B.Pharm)

poison, antidote, symptoms of poisoning, sodium thiosulphate, Assay of sodium thiosulphate, iodimetry, Medicinal uses of sodium thiosulphate, activated charcoal, medicinal uses of activated charcoal, Sodium nitrite, Medicinal uses of sodium nitrite
Phytochemistry essential oils aromatic constituents from animal origin

This document discusses aromatic constituents derived from animal sources, including ambergris and musk. It provides details on ambergris, which comes from sperm whale intestinal tracts, and its constituents including ambrein. Natural musk is obtained from the rump glands of musk deer and other animals. Harvesting involves removing the gland and allowing it to dry. Synthetic musks are also discussed as perfume fixatives. The document is authored by Dr. Mostafa Mahmoud Hegazy and provides additional educational resources.
Pharmaceutical aids-and-necessities

This document discusses pharmaceutical aids and necessities. It begins by outlining the objectives and providing an overview. It then classifies various aids such as acids, bases, buffers, antioxidants, water and glass. The document goes on to describe specific acids, bases, buffers and antioxidants in detail, outlining their properties, production methods and uses in pharmaceutical preparations and storage.
Protectives & adsorbents 

Protectives and adsorbents are drugs that adsorb intestinal toxins, bacteria, and form a protective coating on the inflamed gastrointestinal tract. They are chemically inert substances such as bismuth subcarbonate, kaolin, and activated charcoal that are used to treat diarrhea and dysentery by adsorbing gases, toxins, and bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
Flavor enhancers

This document provides information on flavor enhancers and stabilizers used in foods. It discusses flavor, common flavor enhancers like monosodium glutamate, and techniques for analyzing flavors like gas chromatography. It also defines food stabilizers, provides examples like alginates and agar, describes general confirmatory tests, and discusses applications such as preventing emulsions from separating.
Pharmaceutical Solvents 

Pharmaceutical solvents
coloring agents
flavoring AGENTS
SWEETING AGENTS
DILUTING AGENTS
ANTIOXIDANTS
PRESERVATIVES
What's hot (20)
Phytochemistry essential oils esters, oxides and peroxides

Phytochemistry essential oils esters, oxides and peroxides
Phytochemistry essential oils organo-nitrogen and organo-sulphur compounds

Phytochemistry essential oils organo-nitrogen and organo-sulphur compounds
Topical agents: Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry

Topical agents: Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Phytochemistry essential oils aromatic constituents from animal origin

Phytochemistry essential oils aromatic constituents from animal origin
Viewers also liked
Sulphonamides

Sulphonamides are a class of antibacterial drugs that act as competitive inhibitors of dihydropteroate synthetase, blocking the biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolate needed by bacteria. Prontosil, an early sulphonamide prodrug, was found to metabolize into sulphanilamide, the active antibacterial agent. Key features of sulphonamides include their aromatic ring and sulphonamide group, which must be directly attached. While effective, sulphonamides can cause toxicity issues related to solubility, which structural modifications have aimed to address. Resistance can develop through enhanced enzyme activity or mutations impacting enzyme binding.
Reproduction and growth of bacteria by Tanzir

Reproduction and growth of Bacteria
Modes of cell divisions
Normal growth cycle
Synchronous growth
Measurement of Growth
Organic Synthesis

The document discusses retrosynthetic analysis, which is a problem-solving technique used in organic synthesis. It involves working backwards from the target molecule and breaking it down into simpler structures through the reverse of known reactions. This allows chemists to plan a synthesis by tracing the target back to commercially available starting materials. The document outlines common disconnections, reactions, and strategies used in retrosynthetic analysis and organic synthesis planning.
Lecture 1

This document provides an overview of the key concepts in medicinal chemistry that will be covered in the class. It discusses the history and evolution of medicinal chemistry, defining drugs and their properties, drug discovery and design processes, and the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic phases of drug action. The goal of medicinal chemistry is to design and synthesize new drug molecules through understanding their interactions with biological targets and structure-activity relationships.
Med.chem sulfonamides

Sulphonamides are among the oldest antibacterial agents used to treat infections. They work by competitively inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, blocking folic acid synthesis in bacteria. This makes them bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal. Chemical modifications of the sulphonamide structure have led to important drug classes like diuretics, hypoglycemics, and anti-mycobacterials. Sulphonamides are commonly used to treat urinary tract, respiratory, and other bacterial infections. When combined with trimethoprim, they have broad-spectrum activity against many pathogens and are used as co-trimoxazole. Adverse effects can include allergic reactions and bone marrow suppression.
Chapter 6 antimicrobial drugs

This document discusses antimicrobial drugs, including antibiotics. It defines antibiotics as substances produced by microorganisms that inhibit other microbes. It lists several antibiotic-producing microbes such as Bacillus, Penicillium, Streptomyces, and Micromonospora. The document also discusses the mechanisms of action of antimicrobials including inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, and nucleic acid synthesis. It provides examples of antimicrobials that act through these mechanisms like penicillin, tetracyclines, and rifampin. Finally, it notes some safety concerns with antimicrobial use like toxicity, interactions, resistance, and effects on normal flora.
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim

Sulfonamides and trimethoprim are antibacterial drugs that work by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Sulfonamides were the first antibacterial sulfone drugs discovered in the 1930s. Trimethoprim inhibits a different enzyme in the folic acid pathway. The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is highly synergistic and known as cotrimoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract, respiratory, and other infections. Both drugs can cause side effects like rash, nausea, and bone marrow suppression if not used carefully, especially in pregnancy, renal impairment, or the elderly.
Anemia And Its Classification

The document discusses different types and causes of anemia. It classifies anemia into etiologic categories including impaired red blood cell production, excessive destruction of RBCs, and blood loss. It further describes morphologic classifications such as macrocytic, microcytic hypochromic, and normocytic normochromic anemia. Specific causes are provided for each category including deficiencies, diseases, and genetic disorders. Hemolytic anemia is discussed in more detail including hereditary and acquired causes. Laboratory findings associated with different types of anemia are also summarized.
Fatty acid synthesis

The document discusses fatty acid synthesis. It begins by describing fatty acids and their roles in the body. It then covers the three main ways fatty acids are produced: diet, adipolysis, and de novo synthesis. The process of de novo synthesis occurs primarily in the liver, adipose tissue, and lactating mammary glands. It involves acetyl-CoA being carboxylated to malonyl-CoA by acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Fatty acid synthase then catalyzes the repeating cycles of condensation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction to elongate the fatty acid chain until a 16-carbon palmitate is produced. NADPH provides reducing equivalents for the reactions.
Sulphonamide

Sulfonamide (also called sulphonamide, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs) is the basis of several groups of drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group.
Viewers also liked (10)
Similar to Introduction to common essential Drugs
ANALEPTICS Mrs Namrata Sanjay Mane Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry...

ANALEPTICS
Mrs Namrata Sanjay Mane
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Nagpur College of Pharmacy, Wanadongri, Hingna Road, Nagpur-441110,Maharashtra, India.
Sulphonamides 191117134235

Sulfonamides are among the oldest antibacterial agents. They work by inhibiting the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, blocking the synthesis of folic acid and acting bacteriostatically. Gerhard Domagk discovered the first sulfonamide drug, Prontosil, in 1932, which was effective in treating streptococcal infections. Common sulfonamide drugs discussed in the document include sulfadiazine, sulfaguanidine, phthalylsulfathiazole, succinylsulfathiazole, sulfamethoxypyridazine, and cotrimoxazole.
ALKALOIDS sayee.pptx

This document discusses alkaloids, which are basic nitrogenous compounds found in plants. It defines alkaloids and describes their forms and classification. True alkaloids are derived from amino acids and contain nitrogen in a heterocyclic ring. They are toxic and show physiological activity. Examples of alkaloids discussed include ephedrine, quinine, and strychnine. The biosynthesis, isolation, and uses of these three specific alkaloids are summarized.
ALKALOIDS sayee.pptx

This document provides information about alkaloids. It defines alkaloids as basic nitrogenous compounds derived from plants that are toxic and have physiological effects. The document classifies alkaloids into true, proto and pseudo alkaloids. It then discusses the biosynthesis, isolation and uses of three specific alkaloids: ephedrine, quinine and strychnine. Ephedrine is used as a decongestant and stimulant. Quinine is a key antimalarial compound. Strychnine is a highly toxic pesticide.
3rd SEM Alkaloids- Structure _ Properties_ Applications _.pptx

1) Alkaloids are often classified based on their chemical structure, such as indole alkaloids containing an indole ring system, or alternatively based on the biological system where they occur.
2) Morphine, nicotine, and atropine are discussed. Morphine is isolated from opium and used as a powerful narcotic for pain relief. Nicotine is the active compound in tobacco. Atropine is isolated from belladonna.
3) The document provides methods for isolating morphine from opium and atropine from belladonna, and discusses their biological significance - morphine as a pain reliever and atropine as an antidote and pupil dilator.
3rd SEM Alkaloids. structure , isolation and their applicationspptx

This document discusses alkaloids, including their classification, isolation, structure, and biological functions. It focuses on the alkaloids morphine, nicotine, and atropine. Morphine is isolated from opium through an extraction process using hydrochloric acid and ether. It is a powerful narcotic analgesic but is highly addictive. Atropine is isolated from belladonna through extraction with sodium carbonate and precipitation. It is used as an antidote and as a pupil dilator. The document provides methods for isolating these important alkaloids.
04. Introduction to Common Essential Drugs.pptx

The document discusses essential drugs including salicylic acid, aspirin, paracetamol, benzoic acid, benzyl benzoate, and sulfa-drugs. It provides details on their preparation, properties, uses, and reactions. Essential medicines are selected based on disease prevalence, public health relevance, efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness. The WHO publishes a Model List of Essential Medicines that contains over 1200 drug recommendations.
Alkaloids (full)

1. Alkaloids are nitrogenous organic compounds that are derived from plants and have pharmacological effects in humans. They have diverse chemical structures and properties.
2. Alkaloids can be detected using various chemical tests like Mayer's reagent, Hager's reagent, and Dragendorff's reagent which cause precipitation or color changes.
3. Alkaloids have many pharmacological uses including as sedatives, anticholinergics, narcotics, local anesthetics, and to treat conditions like asthma, ulcers, and malaria. Some key alkaloid-containing plants discussed are belladonna, coca, and cinchona.
miss_compund.pptx

This document provides information about expectorants, astringents, and antidotes for cyanide poisoning. It discusses the mechanisms and examples of expectorants like ammonium chloride and potassium iodide. It also covers the properties and uses of astringents like potash alum. Finally, it explains the mechanisms and administration of sodium nitrite and sodium thiosulfate as antidotes for cyanide poisoning through their effects on hemoglobin and endogenous detoxification pathways.
Antioxidants

Introduction ,Classification of antioxidants, Ideal properties of antioxidants ,Commonly used antioxidants , Hypo phosphorous acid , Sulphur dioxide, Sodium bisulphate ,Sodium metabisulphite, Sodium thiosulphate, Nitrogen, Sodium nitrite, Questions
Alkaloids.pdf

Alkaloids are organic compounds found in plants that contain nitrogen and have physiological effects in humans and animals. They are usually colorless solids that are bitter tasting and have pronounced biological activity. Alkaloids are classified into groups based on their origin and structure, with true alkaloids originating from amino acids and containing nitrogen in a heterocyclic ring. Common extraction methods involve soxhlet extraction using organic solvents. Purification methods include precipitation, crystallization, and chromatography.
Chapter 9 tanins

This document discusses various types of tannins, including their definitions, classifications, properties, tests, sources, and uses. It describes hydrolysable tannins such as gallotannins and ellagitannins which are esters of sugars and phenolic acids. Condensed tannins are polymers of flavan-3-ol units linked by carbon-carbon bonds. Pseudotannins are lower molecular weight compounds that do not respond to the goldbeater's skin test. Examples of plant sources of tannins discussed include kino, myrobalan, catechu, nutgall, chestnut, and krameria.
Anticholinergics D.Pharm PC II

This document discusses various cholinesterase antagonists (anticholinergics). It begins by explaining their mechanism of action in blocking acetylcholine and classifies them as natural alkaloids or synthetic drugs. Key drugs discussed include atropine, hyoscine, homatropine, benztropine, propantheline, and tropicamide. Their structures, properties, uses, formulations, and brand names are summarized for each drug. Common uses include treatment of Parkinson's disease, ulcers, and as antispasmodics and antisecretory agents.
Medicinal Chemistry of NSAIDS

- NSAIDs work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are mediators of inflammation. Traditional NSAIDs block both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, reducing inflammation but also the protective stomach lining. Selective COX-2 inhibitors block only COX-2, reducing inflammation without affecting the stomach.
- NSAIDs include salicylate derivatives like aspirin, para-aminophenol derivatives like paracetamol, and classes derived from pyrazolones, fenamates, arylalkanoic acids, propionic acids, and heteroaryl acetic acids. Each class has different structures and mechanisms of action.
Alkaloids

The document discusses four plant sources of alkaloids - Vinca, Rauwolfia, Belladonna, and Opium. It provides details on the biological source of each plant, their major alkaloids, uses, and marketed products containing the plants or their alkaloids. Vinca contains the anticancer alkaloids vinblastine and vincristine. Rauwolfia contains the antihypertensive reserpine. Belladonna contains the anticholinergic alkaloids atropine, hyoscyamine, and scopolamine. Opium is the source of the analgesic alkaloids morphine, codeine, and noscapine.
3. Penicillin compounds.pptx

The document discusses 6 compounds that will be studied under penicillin: benzyl penicillin, benzathine penicillin, phenoxymethyl penicillin, ampicillin, carbenicillin, and cloxacillin. For each compound, the document provides information on chemical and physical properties, stability and storage requirements, uses for treating various infections, and available pharmaceutical formulations. The compounds are antibacterial drugs used to treat infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Drugs acting Center Nervous system Diploma pharmacy 

Diploma pharmacy drug acting on central nervous system
It includes tranquilizers, sedative and hypnotics, antidepressant, general anesthetics
Antioxidants, Solvents, Pharmaceutically Acceptable Glass & Glass Wires,Manik,

This document discusses antioxidants, solvents, pharmaceutically acceptable glass and glass wires. It defines antioxidants and describes their mechanisms of action and cautions in selection. It discusses official inorganic antioxidants including hypophosphorus acid and sodium metabisulfite. It also discusses pharmaceutical waters such as water for injection, purified water, and bacteriostatic water. Finally, it provides an introduction to glass, describing its composition and components.
Alkaloids

The document discusses alkaloids, which are basic organic compounds found in plants that contain at least one nitrogen atom. It defines alkaloids and describes their properties, occurrence in plants, and functions. The document then covers various topics related to alkaloids including their classification into heterocyclic and non-heterocyclic types based on their ring structure, general extraction methods, and in-depth examinations of specific alkaloid-containing plants and their active constituents like cocaine from coca leaves and colchicine from autumn crocus.
The Dangers Of Inhalants Among Adolescents

This document discusses a lab experiment involving the Grignard reaction. The purpose was to prepare a Grignard reagent using bromobenzene and magnesium, and then react it with benzophenone. After workup, this produced triphenylmethanol. Anhydrous conditions were required. The Grignard reagent inserted magnesium into the carbon-bromine bond of bromobenzene. After reacting with benzophenone and acidic workup, the product was isolated using liquid-liquid extraction and identified through melting point and titration.
Similar to Introduction to common essential Drugs (20)
ANALEPTICS Mrs Namrata Sanjay Mane Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry...

ANALEPTICS Mrs Namrata Sanjay Mane Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry...
3rd SEM Alkaloids- Structure _ Properties_ Applications _.pptx

3rd SEM Alkaloids- Structure _ Properties_ Applications _.pptx
3rd SEM Alkaloids. structure , isolation and their applicationspptx

3rd SEM Alkaloids. structure , isolation and their applicationspptx
Drugs acting Center Nervous system Diploma pharmacy 

Drugs acting Center Nervous system Diploma pharmacy
Antioxidants, Solvents, Pharmaceutically Acceptable Glass & Glass Wires,Manik,

Antioxidants, Solvents, Pharmaceutically Acceptable Glass & Glass Wires,Manik,
Introduction to common essential Drugs
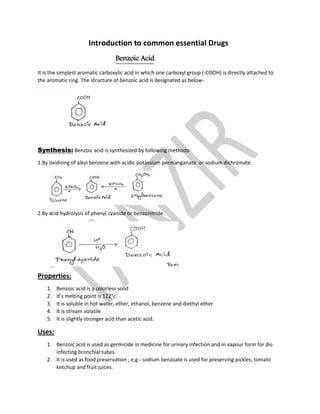
- 1. Introduction to common essential Drugs Benzoic Acid It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid in which one carboxyl group (-COOH) is directly attached to the aromatic ring. The structure of benzoic acid is designated as below- Synthesis: Benzoic acid is synthesized by following methods- 1.By oxidizing of alkyl benzene with acidic potassium permanganate or sodium dichromate. 2.By acid hydrolysis of phenyl cyanide or benzonitride. Properties: 1. Benzoic acid is a colorless solid 2. It’s melting point is 122°c 3. It is soluble in hot water, ether, ethanol, benzene and diethyl ether 4. It is stream volatile 5. It is slightly stronger acid than acetic acid. Uses: 1. Benzoic acid is used as germicide in medicine for urinary infection and in vapour form for dis- infecting bronchial tubes. 2. It is used as food preservation ; e.g.- sodium benzoate is used for preserving pickles, tomato ketchup and fruit juices.
- 2. 3. In dye industry, it is used for preparing anile blue. 4. The combination of benzoic acid alcohol and water is used as cleaning agent in pharmacy. 5. It is used as an antibacterial and antifungal agent. Salicylic Acid Salicylic acid is a hydrobenzoic acid on which the carboxyl group(-COOH) is attached to the benzene ring at “ortho” position. It’s structure is designated as below- Synthesis: Salicylic acid is obtained by following process- 1. By heating sodium phenoxide and carbon dioxide at 125°C under pressure This process is known as Kolbe reaction. Properties: 1. Salicylic acid is colorless solid 2. It’s melting point is 159°C 3. It is insoluble in cold water but soluble in hot water, ethanol and ether. 4. It is steam volatile 5. It is stronger acid than benzoic acid. Uses: 1. Prodrug of salicylic acid is aspirin that is an OTC drug. 2. It has analgesic or painkiller properties. 3. It is used as skin care to remove dead skin cells 4. Inflammation and skin irritation caused by burns, insect bite, fungal infection and eczema are treated by it. 5. It is used as antidandruff, antiseptic and antibacterial agent. 6. It is used for food preservation.
- 3. Prodrug: It is the drug that is individually insert and becomes active after entering into body and converts into main drug that shows biological action.Example— Prodrug—Aspirin; Main drug-Salicylic acid. Salicylic acid is not used directly because it causes stomach irritation and gastric problem. For these reasons, it is used as the form of prodrug. Acetyl-Salicylate Or Aspirin Acetyl-Salicylic acid is an important derivation of salicylic acid. It is called Aspirin as trade name. It’s structure is designated as- Synthesis: It is prepared by heating salicylic acid with acetyl chloride or acetyl anhydride in the presence of phosphoric acid. Properties: 1. It is a colorless solid 2. It’s melting point is 135°c 3. It is odorless. Uses: 1. It is used to reduce fever without lowering body temperature. 2. It is also a painkiller and used to treat headache, muscle & joint ache. 3. It reduces swelling and treats inflammation. 4. It is used to the treatment of rheumatic fever and rheumatic arthritis. 5. It is also used as additive in food, animal feed, drug and cosmetic 6. It is used to treat common cold.
- 4. Paracetamol Paracetamol is para acetyl amino phenol. It’s structure is designated as below- Synthesis: It is prepared by the reduction of para nitrophenol by NaBH4.And then the product para amino phenol reacts with acetic anhydride to produce paracetamol. Properties: 1. It is a white crystalline powder 2. It’s melting point is 170°c 3. It is odorless and has slightly bitter taste. 4. It is slightly soluble in water and soluble in most of the organic solvents Uses: 1. It is an analgesic and used to relieve pain. 2. It has antipyretic property and so it reduces fever. 3. It can treat cold. PABA The full form of PABA is para amino benzoic acid. The structure of PABA is designated as- PABA is considered to be in the B-complex vitamin family. It is not a vitamin; our body can make PABA from folic acid at the time of special need.
- 5. Synthesis: When toluene gives nitration reaction at p-position; para nitro toluene is formed by oxidizing the para nitro toluene; para nitro benzoic acid is obtained. When the p-nitro benzoic acid is gone reduction by H2 & Pd-C catalyst; PABA is formed. Properties: 1. It is white-grey crystal. 2. It’s melting point is 188°c 3. It is slightly soluble in water 4. It can block UV rays. Uses: 1. It is used as UV screening and sun screening agent. It prevents skin cancer. 2. It helps in the formation of RBC & formely used as anti rickeltsial agent. 3. It is useful for the bacteria that synthesizes folic acid in human 4. It acts as co-enzyme for the metabolism of protein and it’s utilization 5. It is an anti oxidant 6. It helps to restore color of grey hair of human. Sulfa Drug Sulfa drugs are the group of drugs derived from sulfonamide compounds that inhibit the activity of bacteria and are used in medicine to treat bacterial infection. The structure of sulfonamide/ sulfanilamide is designated as- Hydrogen of Sulfo amide group
- 6. When the NH2 SO2NH H is substituted by various groups; the derivation of sulfa drugs are formed such as- Synthesis: It is prepared from acetanilide by following steps— Properties: 1. It is a white crystalline solid 2. It’s melting point is 166.5°c 3. It has anti microbial properties Uses: 1. Sulfa drugs are used to treat pneumonia gonorrhea etc caused by microorganisms 2. It is used to treat eye infection 3. Sulfa drugs- sulfadiazine is used to treat meningitis & urinary tract disorders 4. Sulfa drugs are used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease 5. It also helps to reduce allergies Kernicterus: it is brain damage due to excess bilirubin; is the effect of sulfa drugs.
- 7. PASA The full form of PASA is para- amino salicylic acid. The structure is Synthesis:( Kolbe synthesis reaction) Amino phenol reacts with alkyl magnesium bromide and then CO2 and at the end in acidic medium reaction with water reacts para amino salicylic acid. Properties: 1. PASA is a white crystalline solid 2. It’s melting point is 150°c 3. It is soluble in water and polar organic solvent Uses: 1. It is used to treat tuberculosis 2. It is used to the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease 3. It is also used in pregnancy category 4. It is used in manganese chelation therapy. Tanzir Ahmed 141021