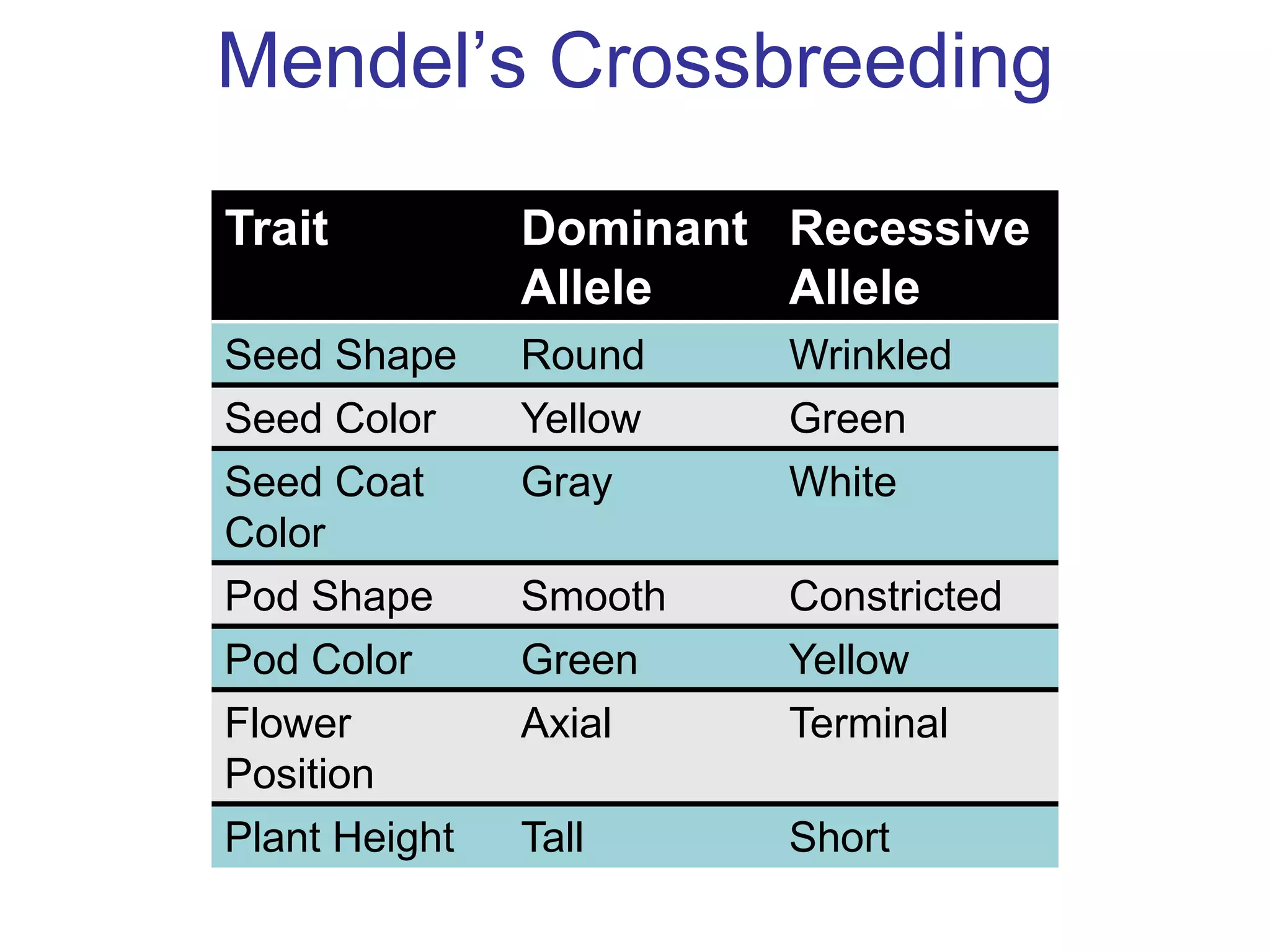
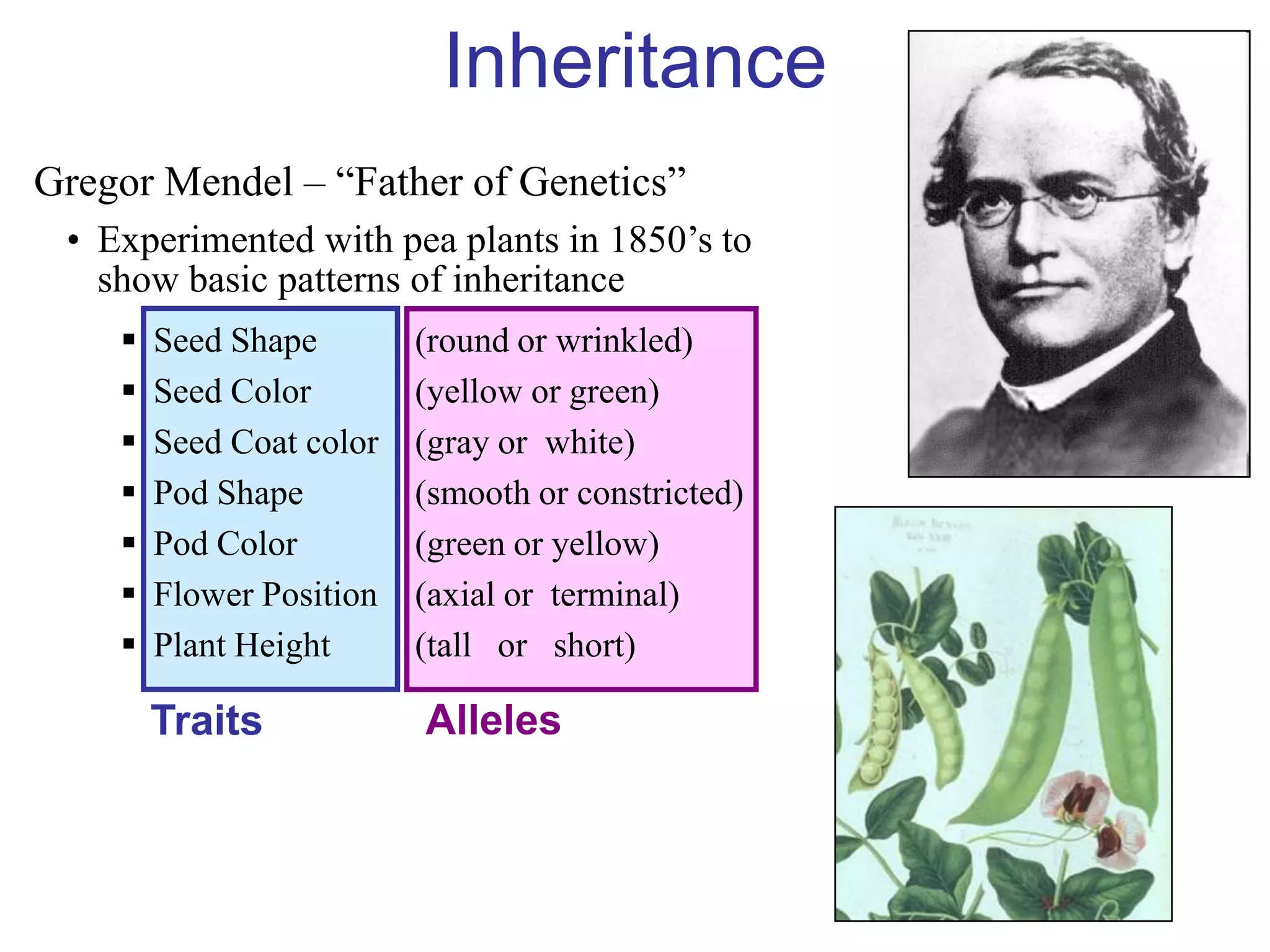
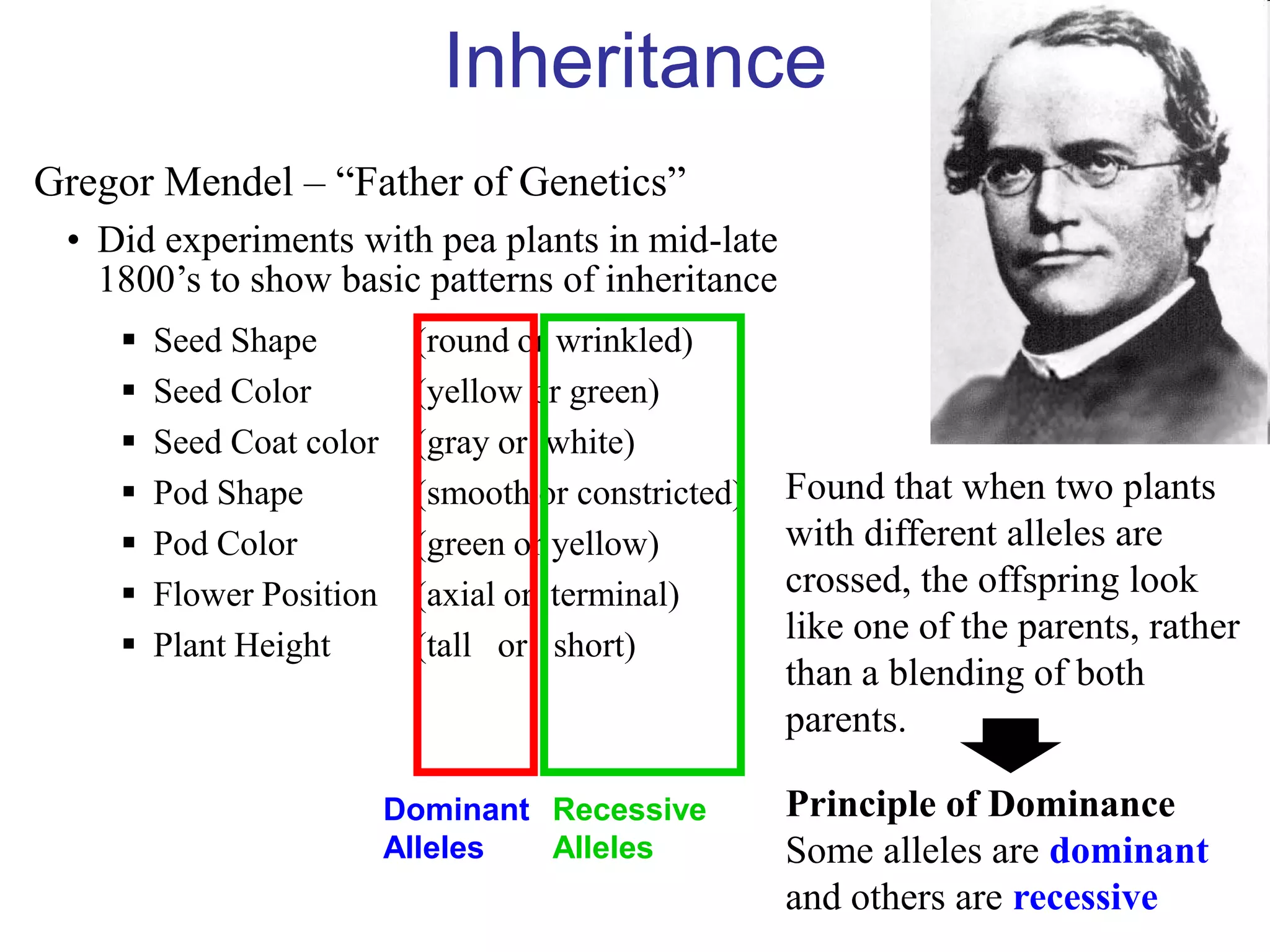
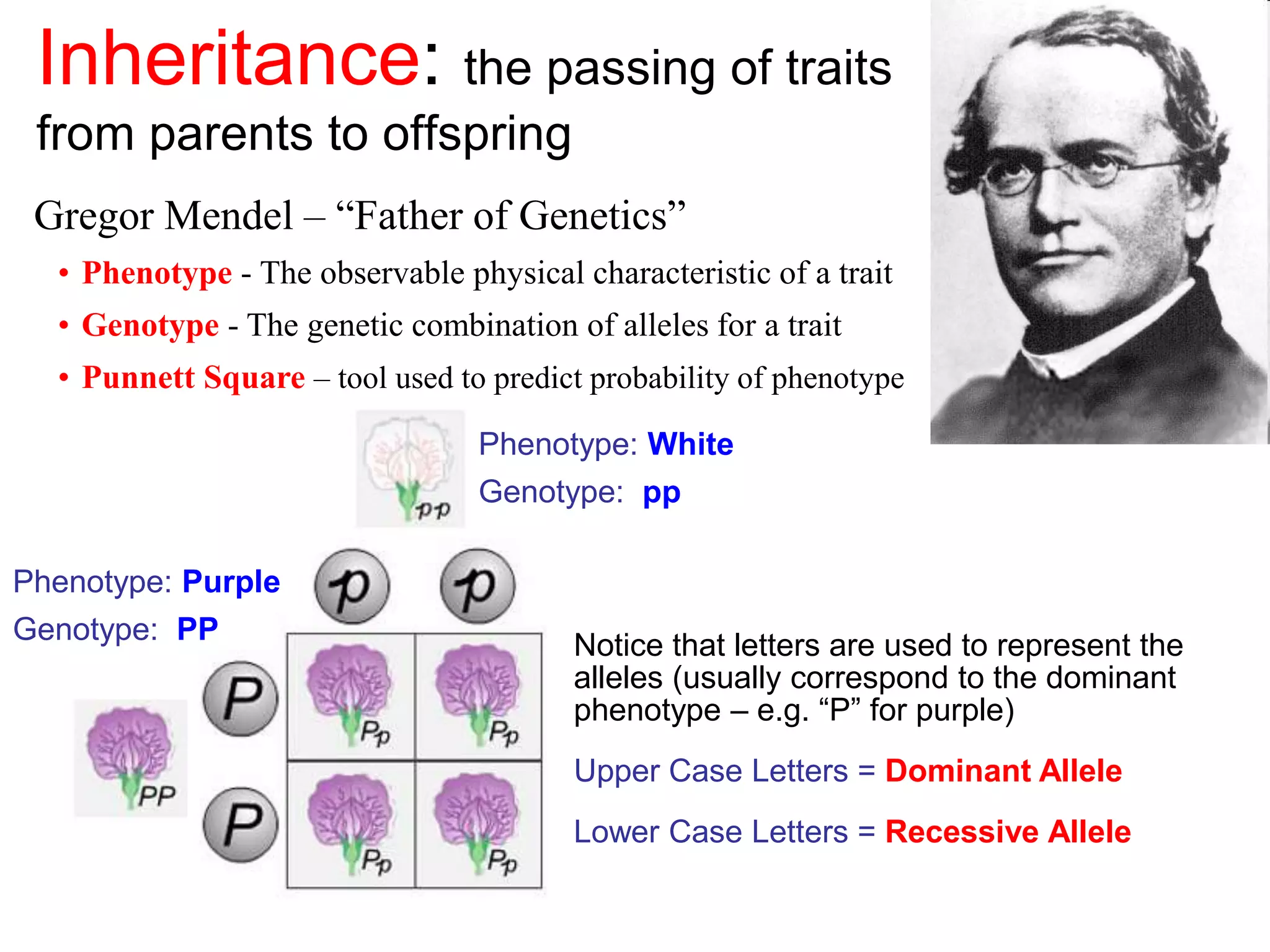
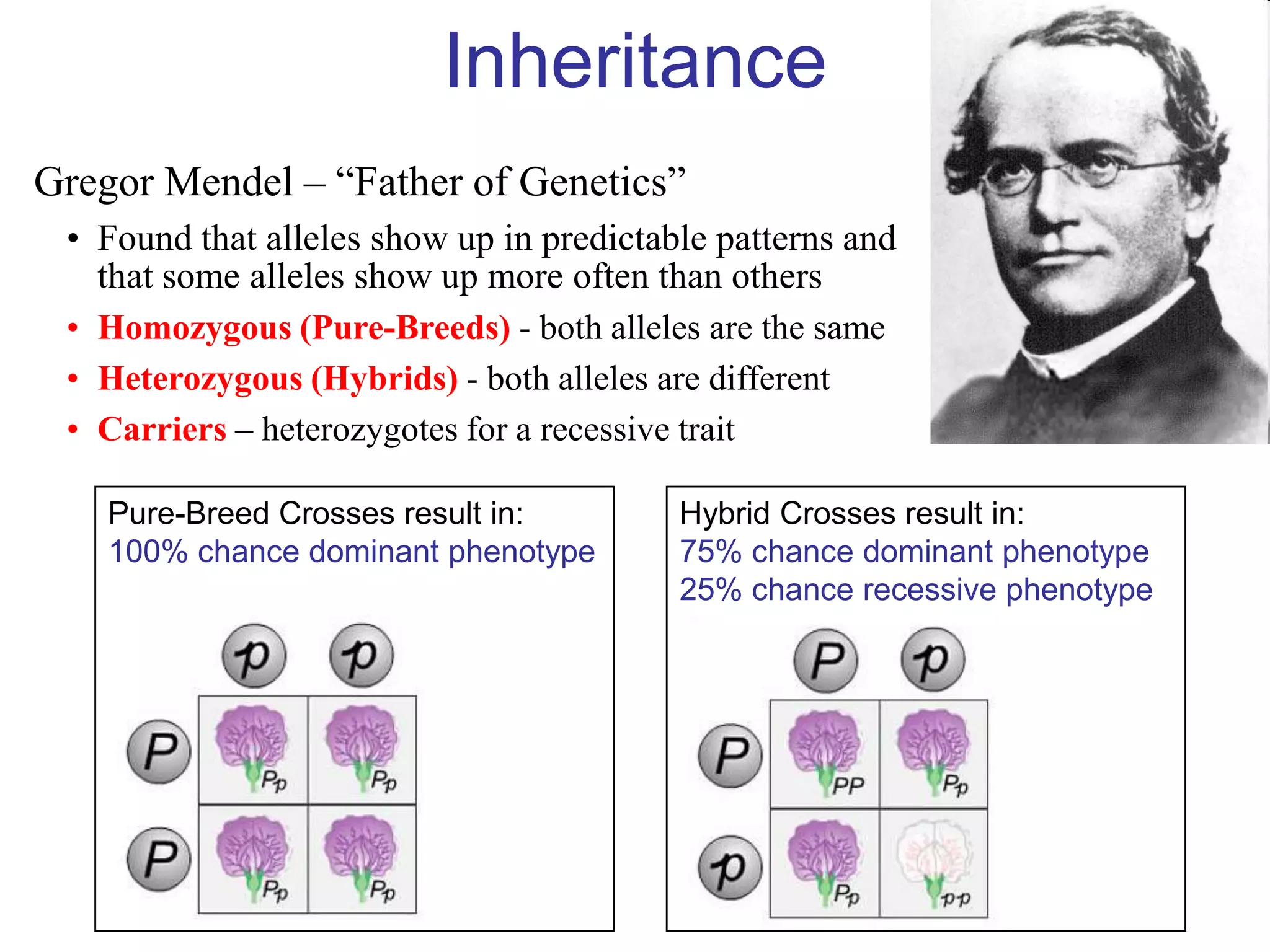
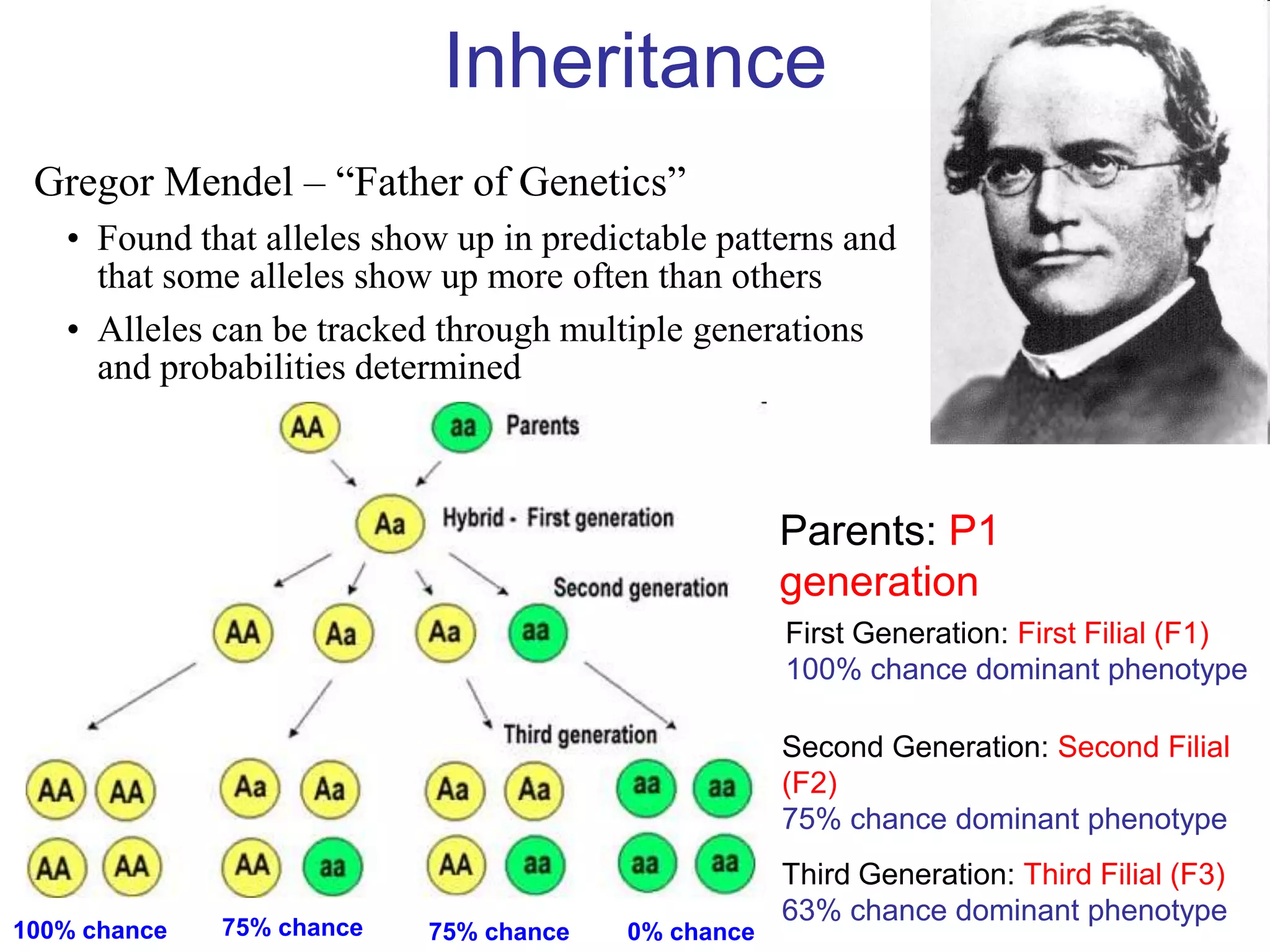
Gregor Mendel studied inheritance through pea plant experiments in the mid-1800s. He found that alleles (versions of genes) show up in predictable patterns, with some alleles being dominant over others. Mendel also discovered that alleles segregate and assort independently during reproduction, laying the foundations for modern genetics.