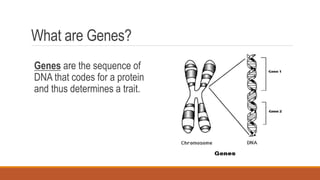
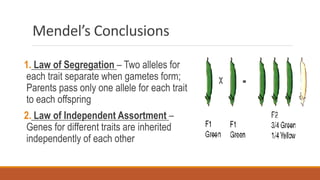
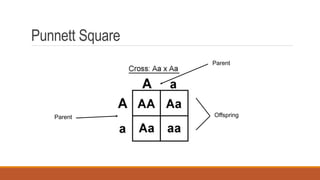
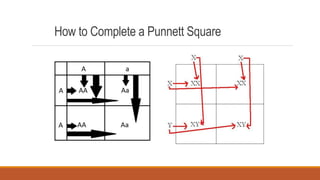
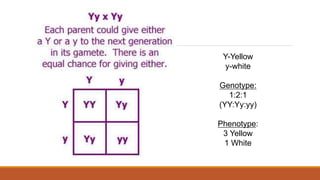
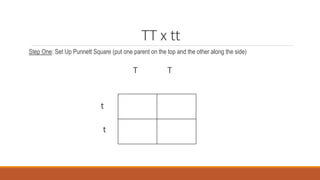
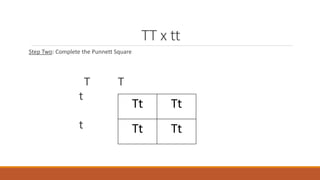
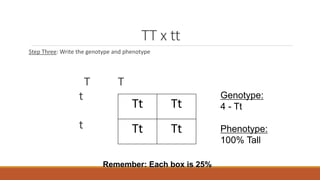
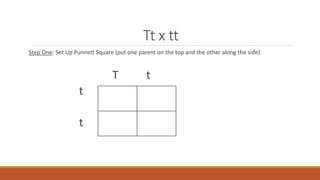
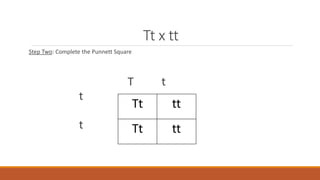
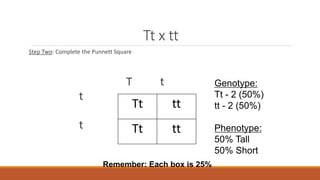
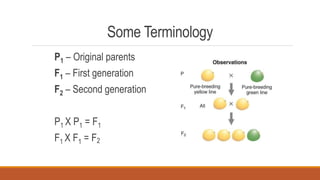
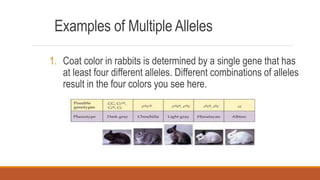
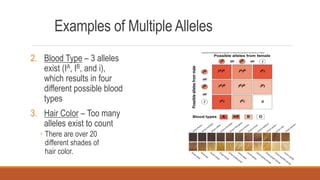
Gregor Mendel conducted early experiments in genetics using pea plants. He identified two laws of inheritance: the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment. The law of segregation states that alleles separate during gamete formation such that offspring receive one allele from each parent for each trait. The law of independent assortment states that genes assort independently, so the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of others. Mendel also described dominant and recessive alleles and used Punnett squares to predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes.