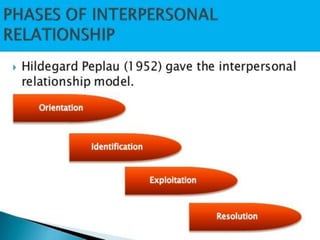
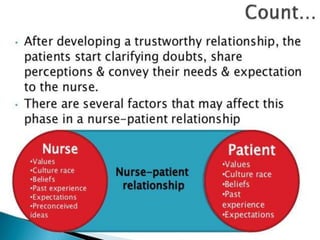
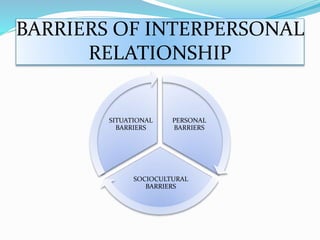
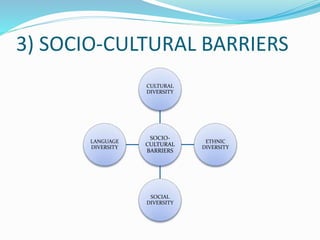
Interpersonal relationships involve close associations between individuals sharing common interests and goals, characterized by trust, loyalty, and commitment. They go through five stages: acquaintance, build-up, continuation, deterioration, and termination, with various types including friendship, family, professional, and romantic relationships. Barriers to these relationships can be personal, situational, or socio-cultural, but can be improved through techniques like appreciation, active listening, and understanding others' views.