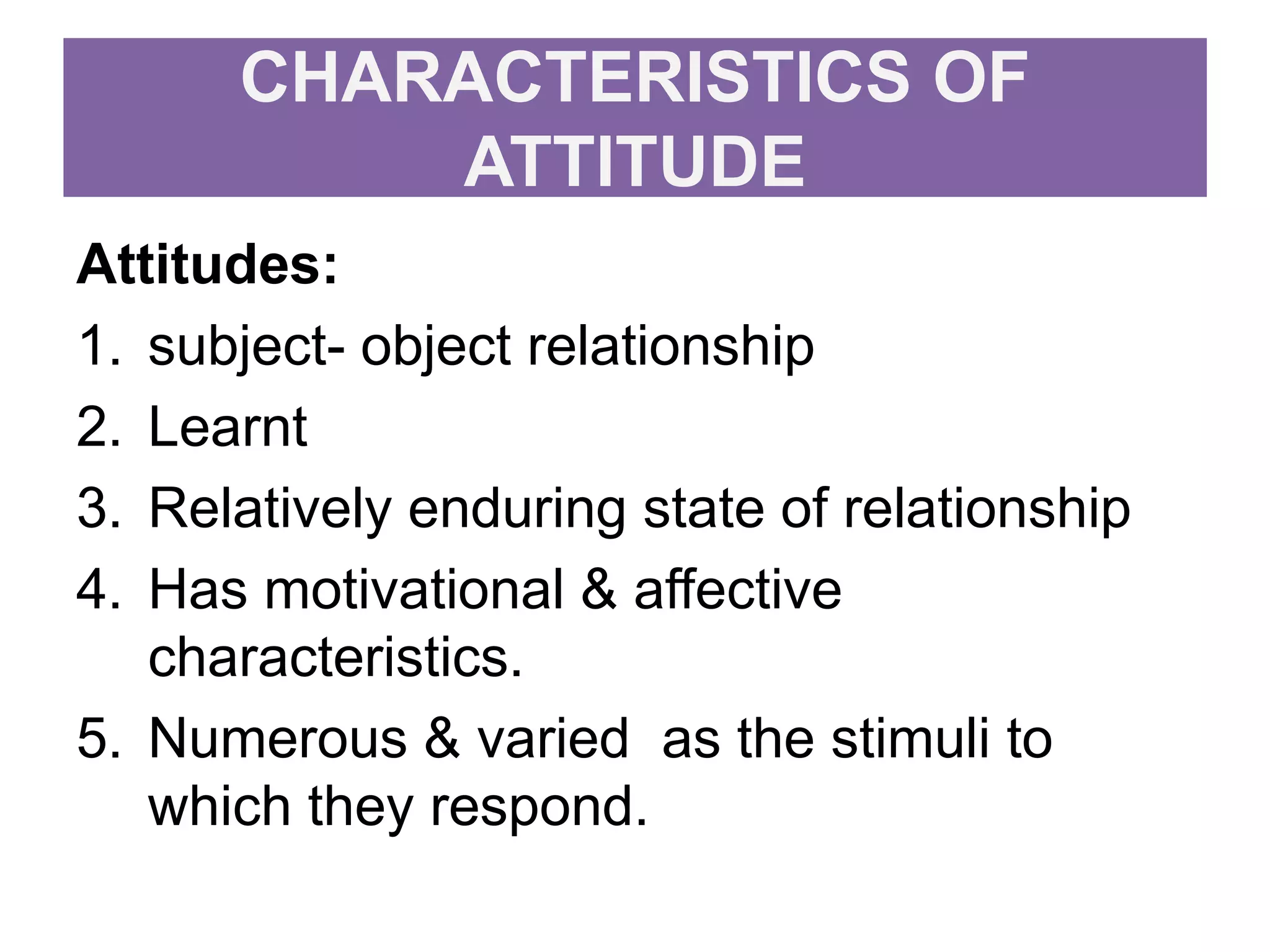
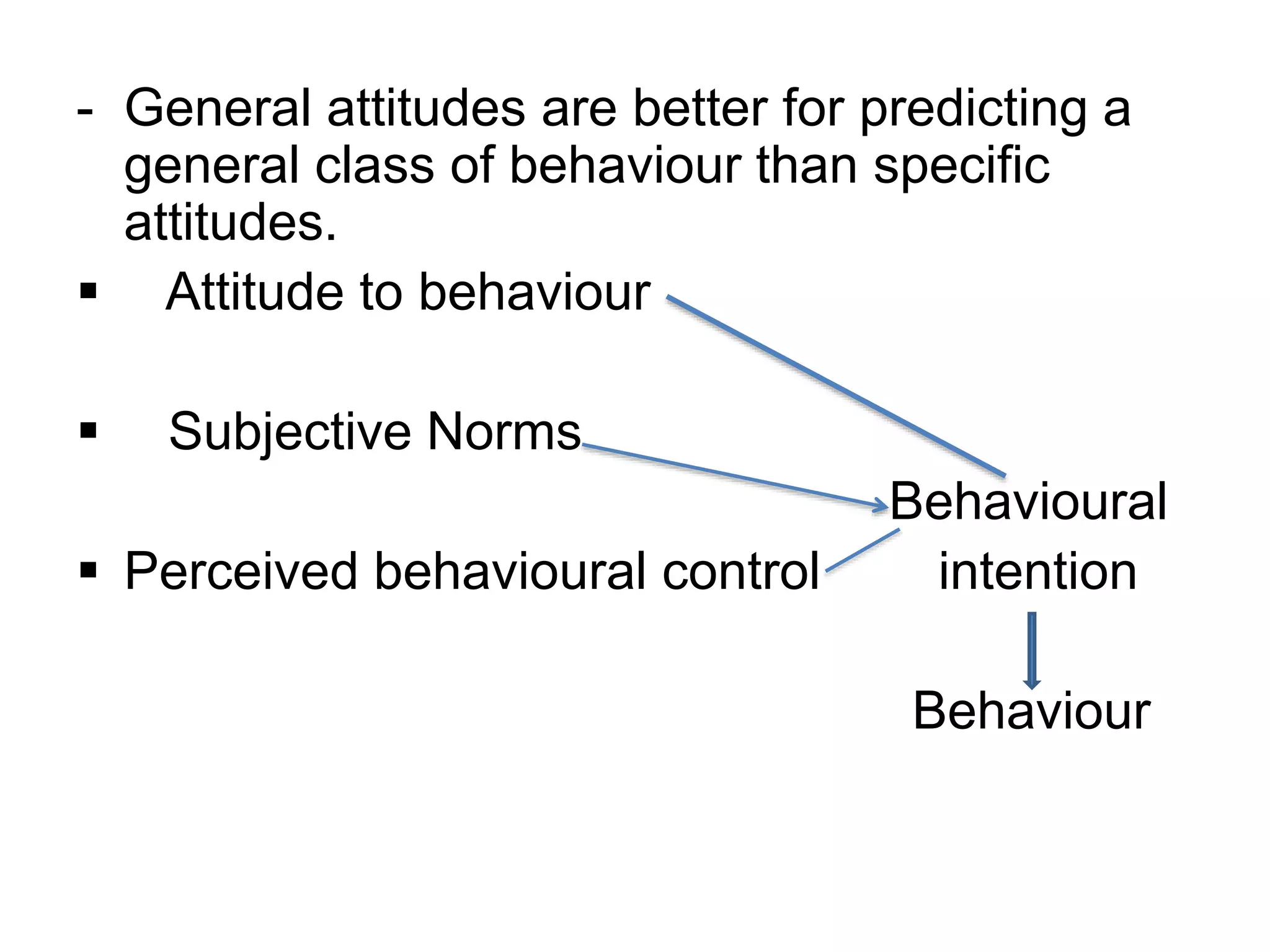
This document discusses attitudes, including definitions, characteristics, formation, factors influencing formation, and implications for nursing. It defines attitude as an enduring organization of processes regarding an aspect of one's world. Attitudes are learned and range from positive to negative, consisting of affective, behavioral, and cognitive components. They serve knowledge, self-expression, adaptation, and ego-defensive functions. Attitudes are formed through family, social norms, peers, school, experiences, and media, and can be changed through education, propaganda, fear, modeling, experiences, and changing beliefs/values. Nursing implications include avoiding prejudiced attitudes, understanding patient attitudes, and cultivating a professional attitude.