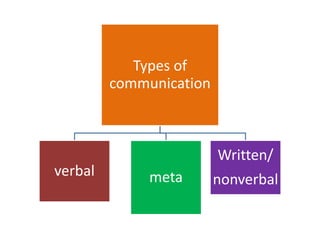
This document discusses therapeutic communication and interpersonal relationships in nursing. It outlines the goals and functions of nurse-patient communication, including allowing patients to express themselves, clarifying issues, and modifying behaviors. It describes different types of communication like verbal, nonverbal, written and meta communication. Elements of the communication process and characteristics of therapeutic communication are explained. The document also covers dynamics of the nurse-patient relationship and techniques to facilitate therapeutic communication.