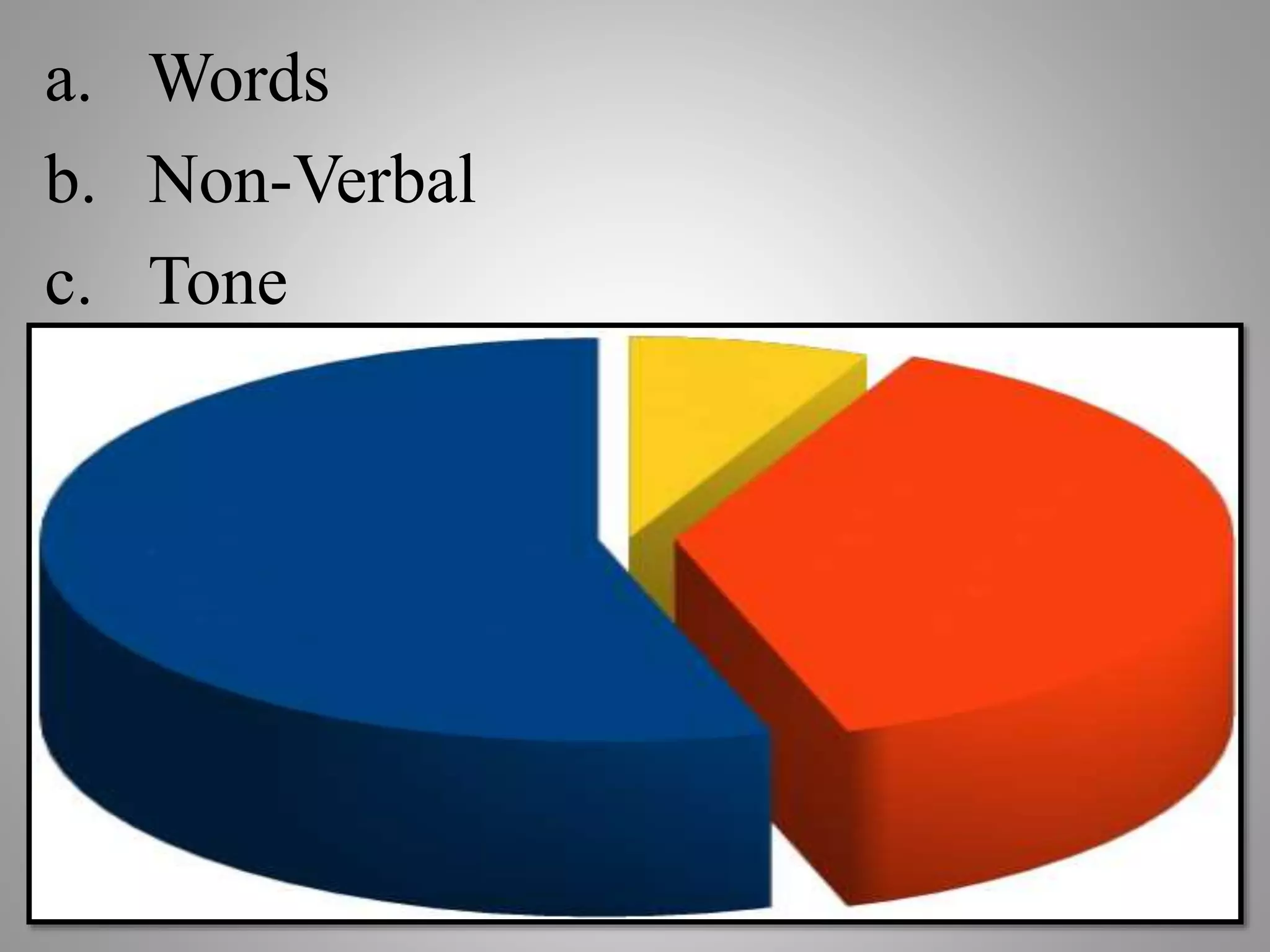
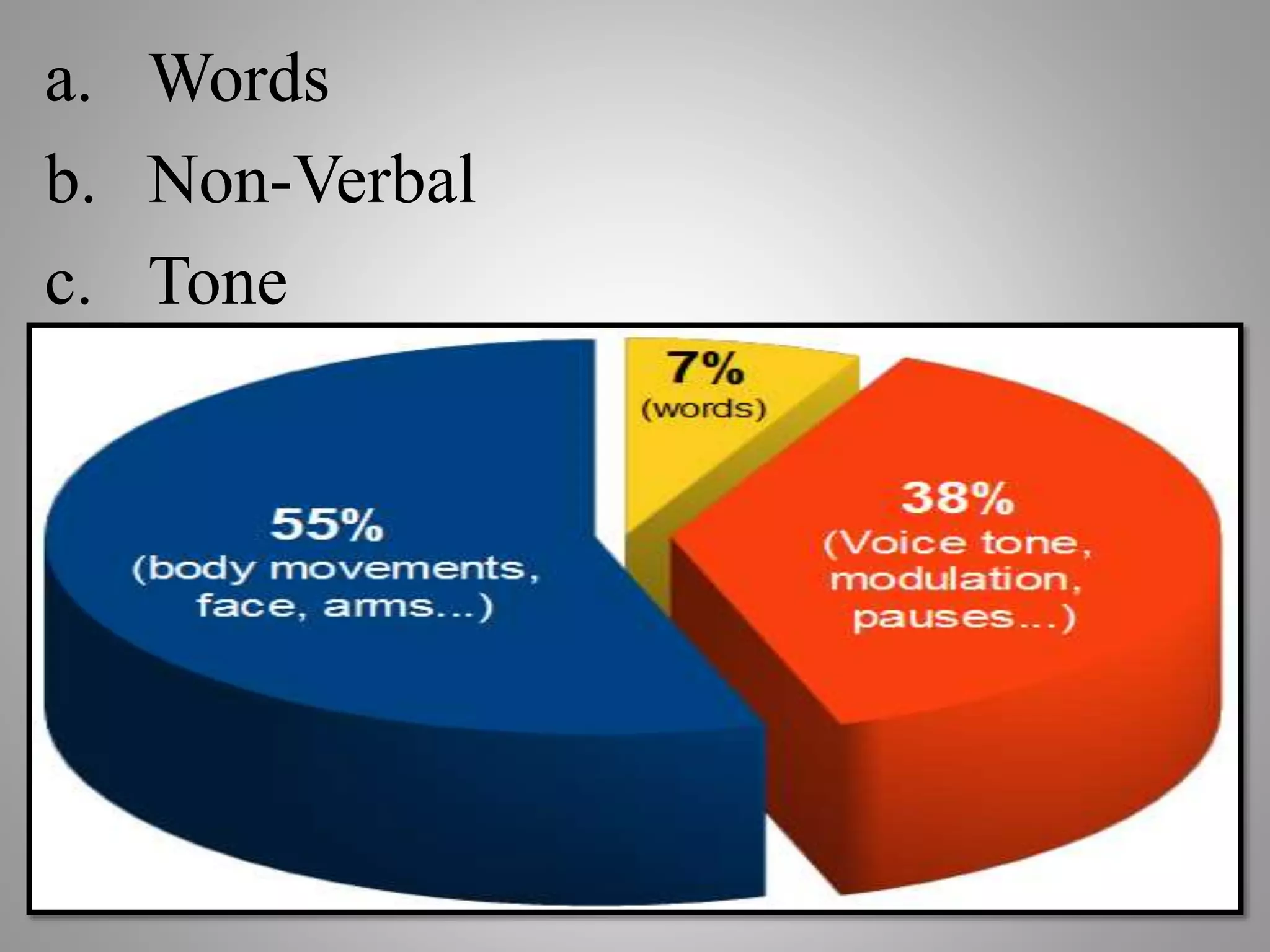
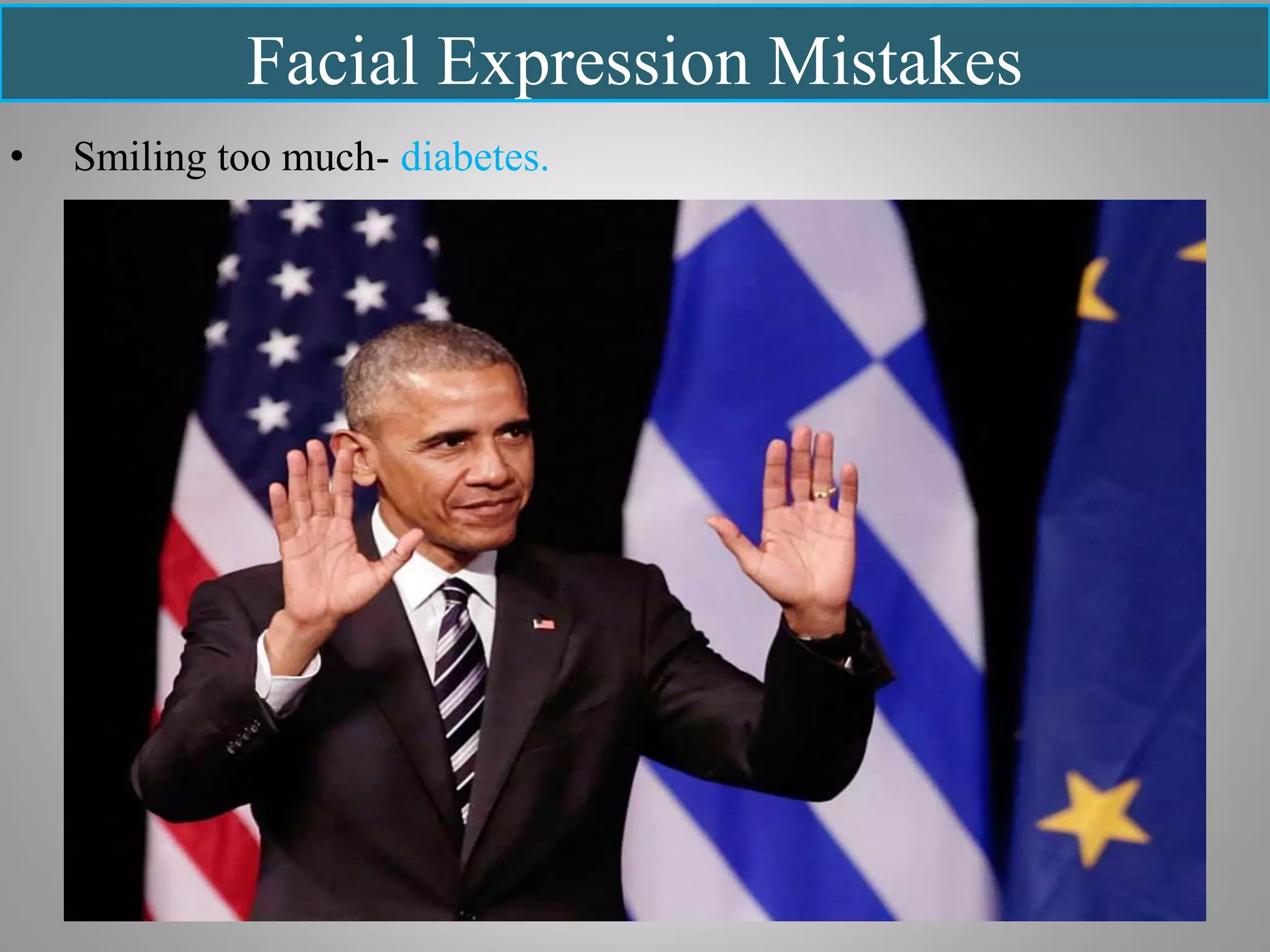
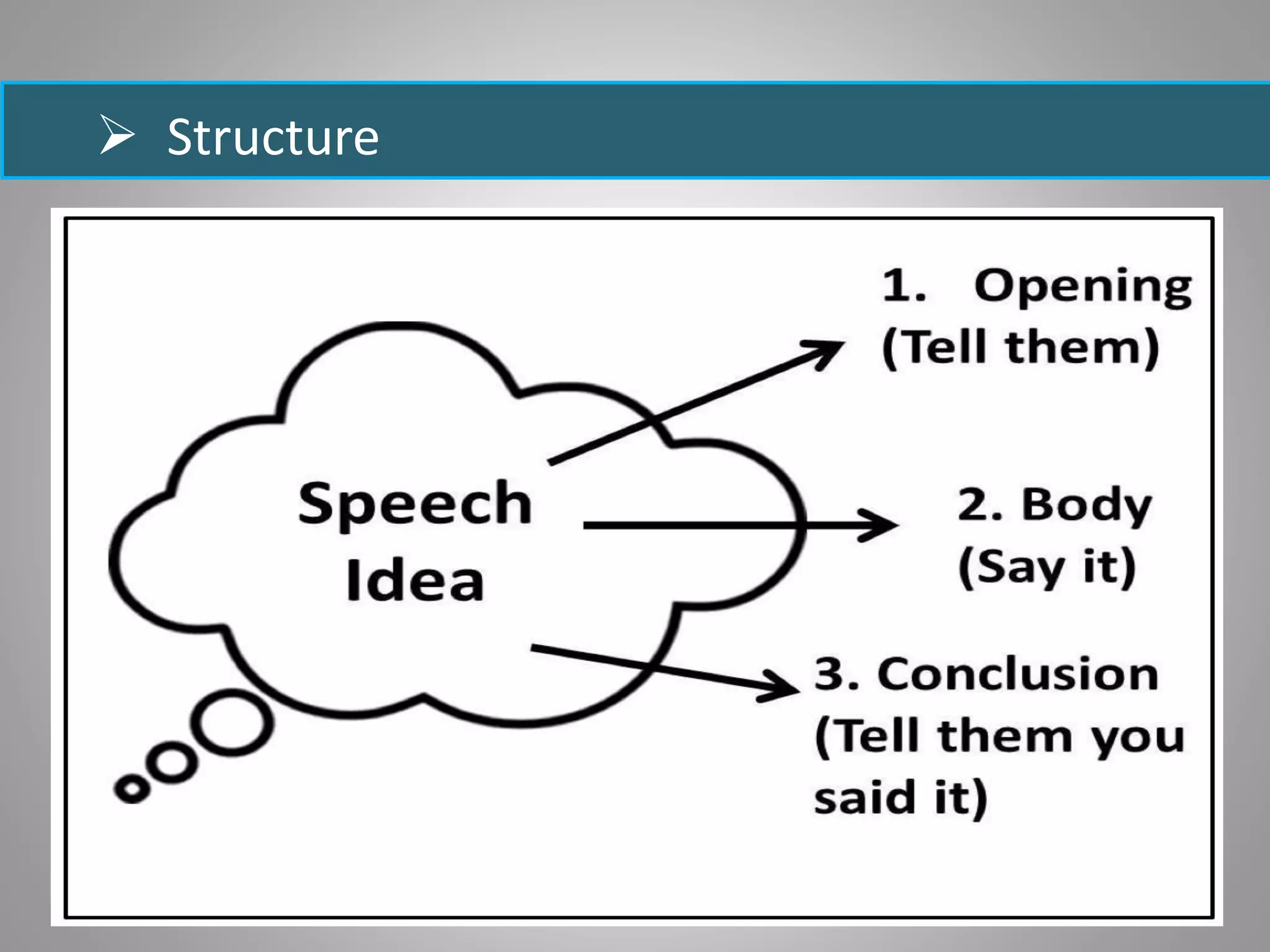
The document discusses various types of oral presentations and techniques for effective public speaking. It outlines five types of presentations: informative, instructional, arousing, persuasive, and decision-making. It also provides tips on first impressions, body language, gestures, movement, posture, facial expressions, vocal techniques, word choice, and managing speech anxiety. Specific mistakes to avoid regarding gestures, movement, posture, and facial expressions are highlighted. Overall, the document serves as a practical guide for delivering successful oral presentations.