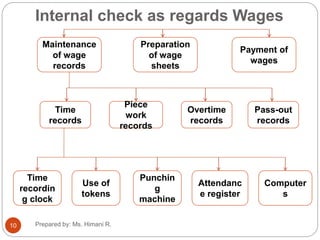
The document discusses internal control, internal check, internal audit, and the differences between internal check and internal audit. It defines internal control as the system established by management to carry out business operations in an orderly manner. The objectives of internal control are to avoid inefficiency, waste, and fraud, and ensure accuracy of records. Internal check is a part of internal control that divides work so no single person can carry out a whole transaction alone. Internal audit involves examining procedures, records, and operations to evaluate management controls and ensure goals are met. It differs from internal check in that internal check mechanically checks work as it is performed while internal audit examines work after it is completed.