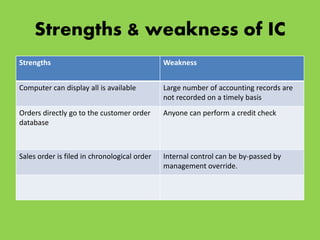
The document discusses internal control as a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding fair financial reporting, compliance with laws, and efficient operations. It outlines the objectives, components, limitations, and importance of internal control, emphasizing the relationship between internal control and audit evidence. Additionally, it highlights the role of management in establishing effective controls and includes considerations for evaluating internal control effectiveness.