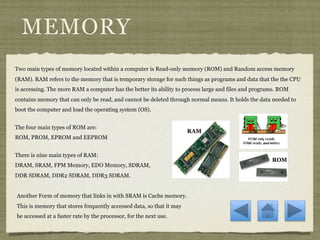
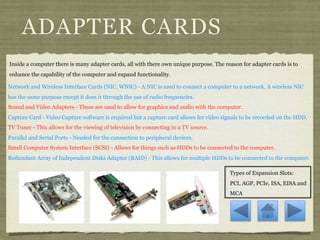
The document discusses the internal components of a computer. It describes the motherboard as the central communications component that connects the CPU and other parts. It also outlines the functions of the hard drive for data storage, memory for temporary storage and programs, and additional drives like solid state drives. The presentation concludes by noting the value of understanding how all the internal components work together within the computer system.