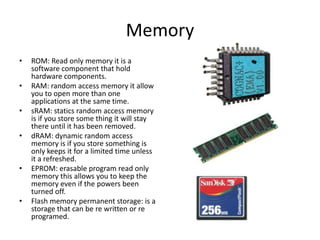
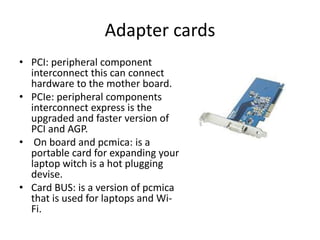
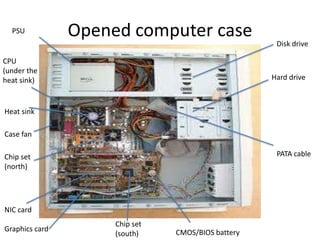
The document discusses several key components of internet and computer systems. The CPU controls the operating system and has processors ranging from 2.1-3.1 GHz depending on whether it's a laptop or normal computer. Memory comes in various types like ROM, RAM, SRAM, and DRAM that allow storage and retrieval of data. Adapter cards like PCI and PCIe connect hardware to the motherboard. Storage devices include hard drives connected via PATA, SATA, or SCSI interfaces, and solid state drives. Input devices provide input to computers while output devices like monitors provide output.