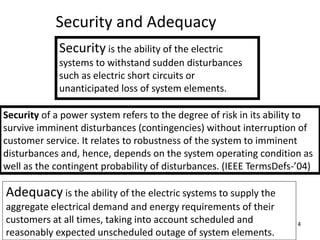
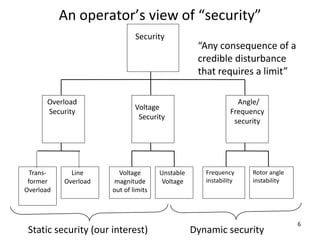
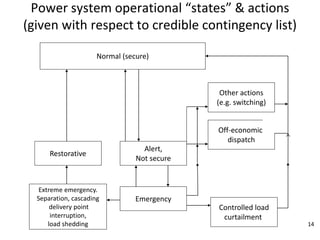
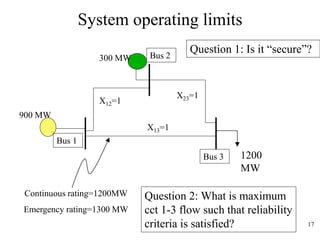
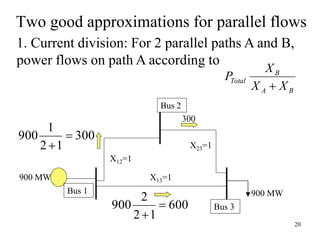
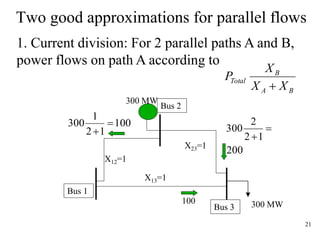
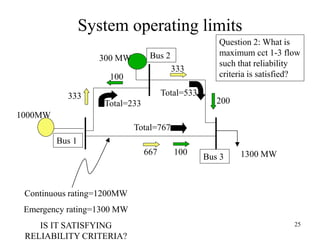
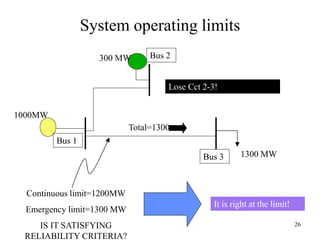
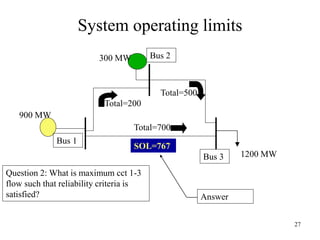
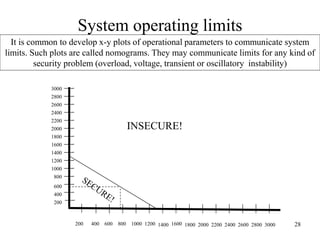
The document discusses reliability criteria for bulk power supply systems. It defines key terms like reliability, security, adequacy, and discusses how reliability criteria are used in system planning and operation. Specifically, it establishes the most economic operating conditions under normal conditions and ensures the system can withstand disturbances without violating criteria. The document uses examples of system operating limits and disturbance-performance tables to illustrate how limits are determined and assessed using reliability criteria.