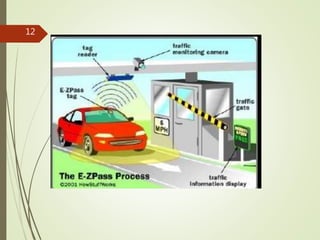
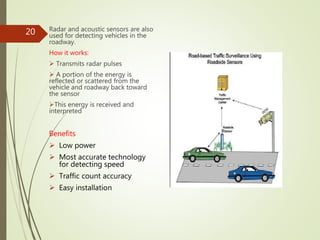
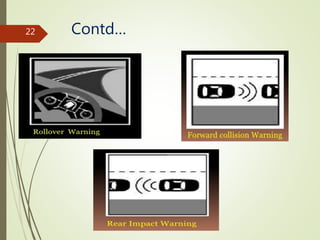
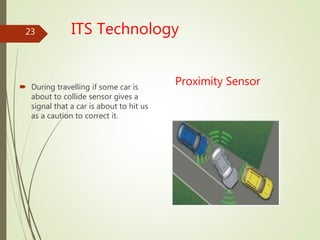
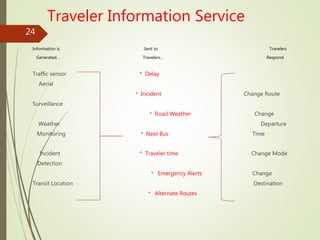
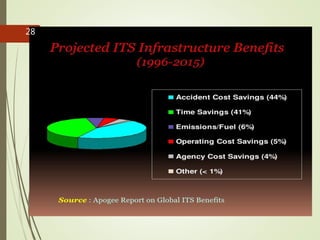
This document presents an overview of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) by Thakkar Jayshiv M. It discusses problems with current transportation systems like traffic congestion and accidents. ITS uses technologies like GPS, electronic toll collection, and vehicle sensors to provide real-time traffic information and improve safety. The presentation covers various ITS applications, benefits like reduced congestion and costs, and challenges including high equipment costs. It concludes that implementing ITS can help solve India's growing transportation problems.