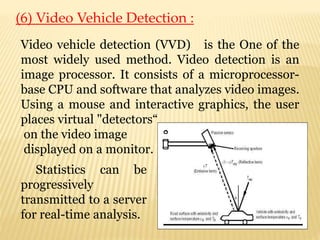
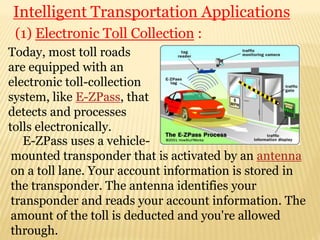
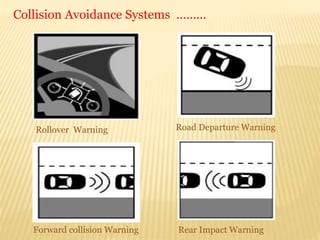
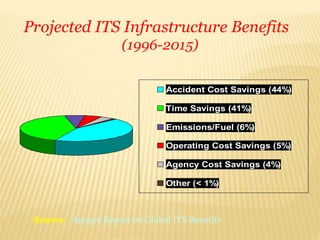
The seminar on 'Intelligent Transportation Systems' at Government Polytechnic Amravati discusses the integration of advanced technologies in transportation to enhance safety and efficiency. It highlights various intelligent technologies, applications, and the benefits they provide, including reduced congestion and improved economic performance. Key features include electronic toll collection, emergency vehicle notifications, and collision avoidance systems, aimed at advancing transportation infrastructure and addressing social issues.