The document discusses a proposed process for project management and solution delivery. It provides an overview of the benefits of using standardized processes, including consistency, productivity, and risk reduction. It then describes the key phases in the solution delivery and project management processes, and provides examples of document templates used in each phase.


























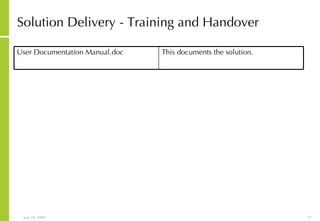


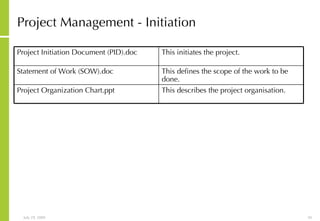


































![More Information Alan McSweeney [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/integratedprojectmanagementandsolutiondeliveryprocess-090729030907-phpapp01/85/Integrated-Project-Management-And-Solution-Delivery-Process-65-320.jpg)