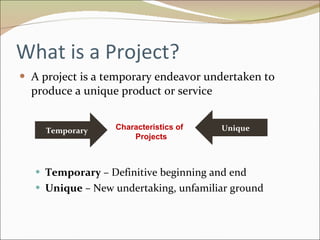
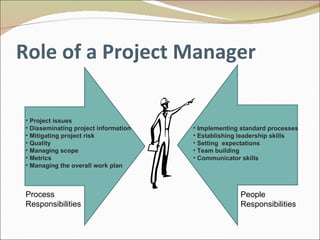
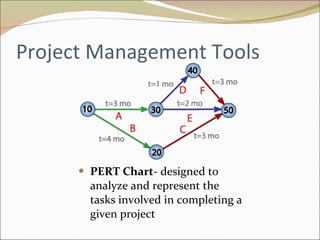
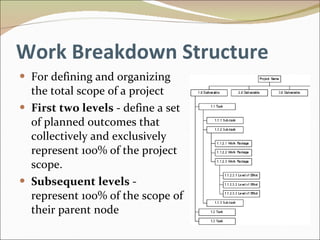
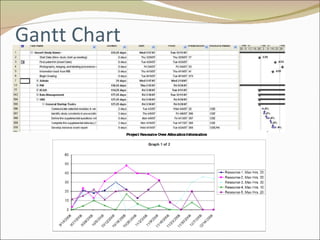
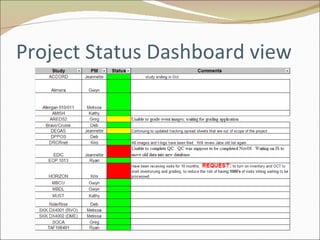
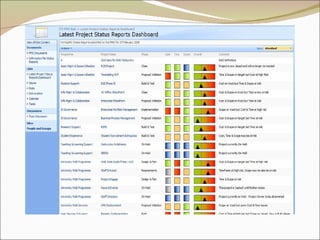
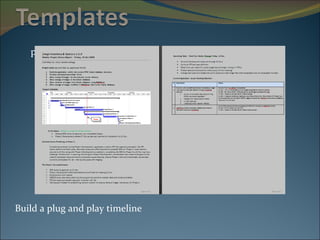
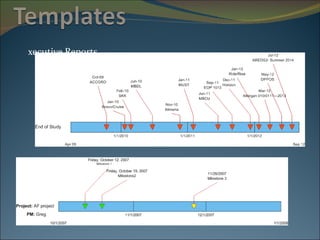
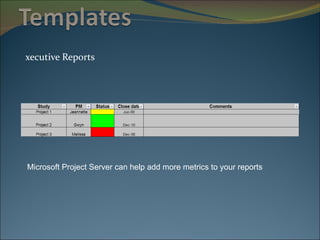
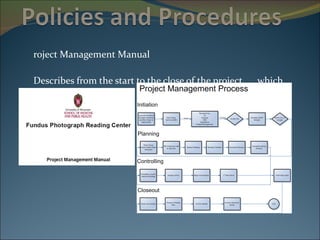
The document discusses project management and summarizes key aspects of the role of a project manager. It outlines that a project manager is responsible for overseeing the project scope, timeline, budget, quality, and team. A project manager must manage communications, risks, and changes, and guide the project through typical phases from initiation to planning, execution, monitoring, and closing. Project management involves using tools like Gantt charts, dashboards, and templates to help define the project plan and track progress.