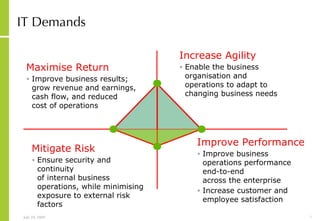
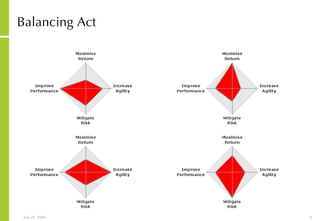
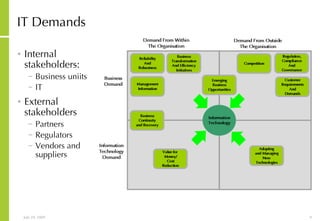
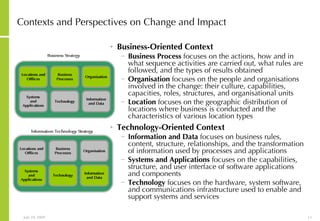
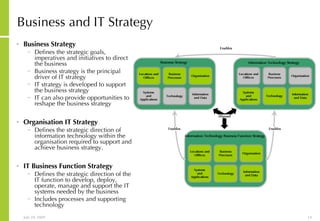
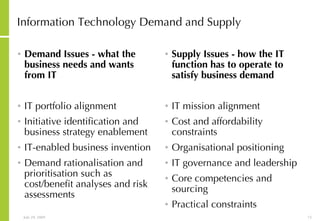
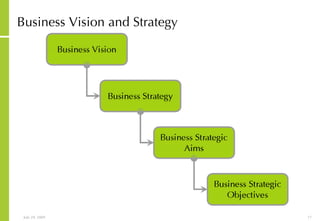
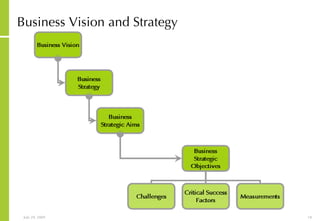
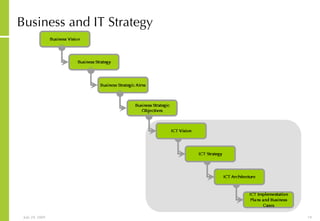
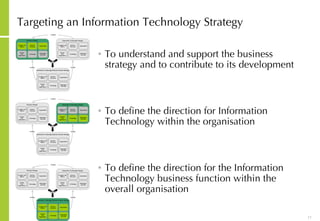
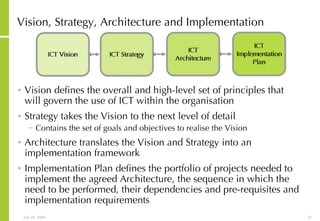
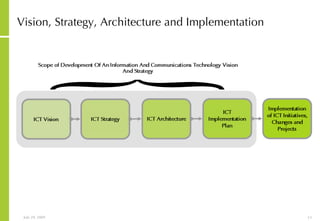
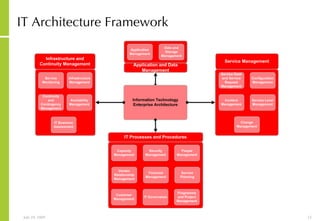
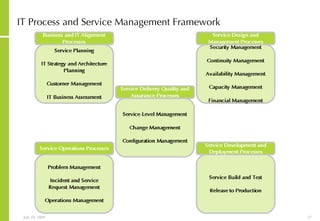
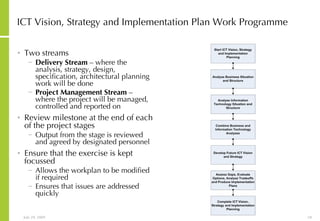
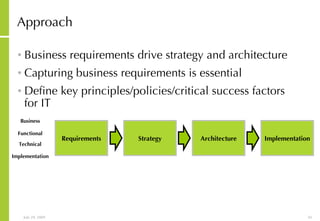
This document discusses developing an ICT vision and strategy. It describes key objectives of defining an IT vision aligned with business needs and challenges, and an approach to developing an IT strategy that considers IT demands, principles, trends and controls. The strategy aims to balance stakeholder needs and support business goals through effective information management, security and service delivery.















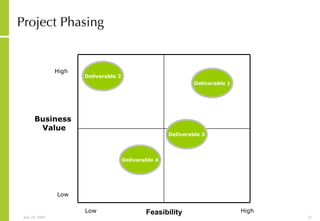
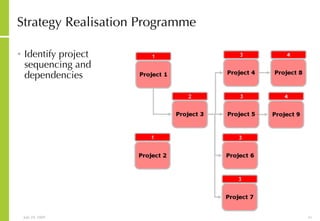
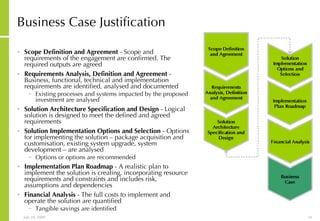
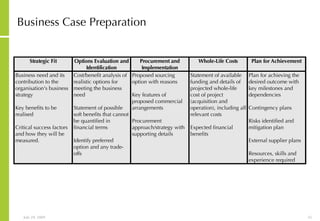

![More Information Alan McSweeney [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictvisionandstrategydevelopment-090729030704-phpapp02/85/Ict-Vision-And-Strategy-Development-37-320.jpg)