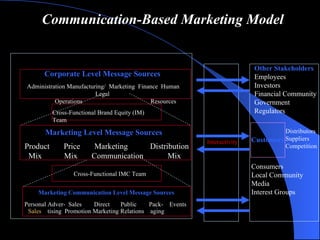
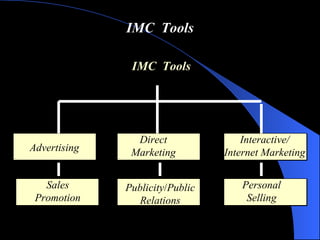
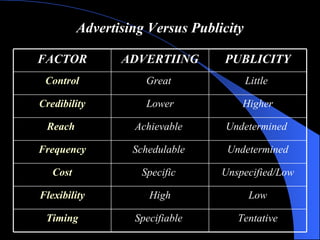
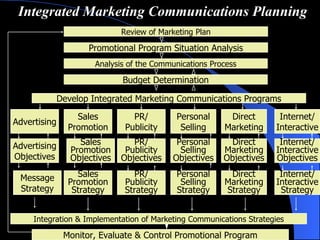
The document provides an overview of integrated marketing communications (IMC), defining it as a planning concept that evaluates various communication disciplines including advertising, direct marketing, interactive marketing, sales promotion, and public relations to provide clarity, consistency and maximum impact. It discusses the reasons for the growing importance of IMC and describes various IMC tools and how they are used, including different types of advertising, direct marketing, interactive marketing, sales promotion, publicity and public relations.