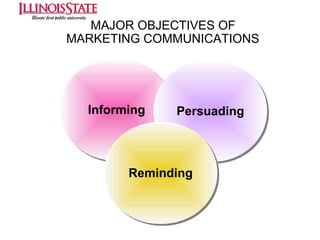
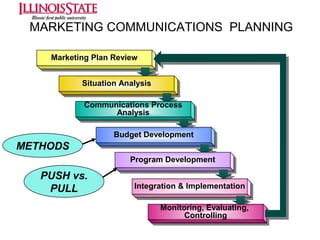
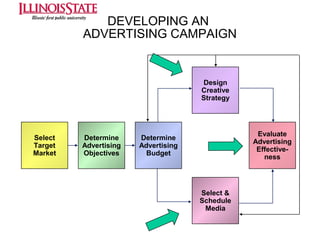
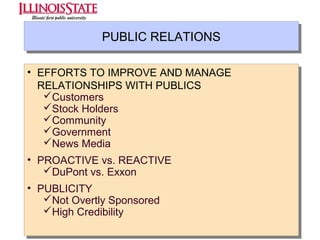
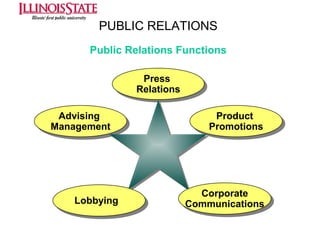
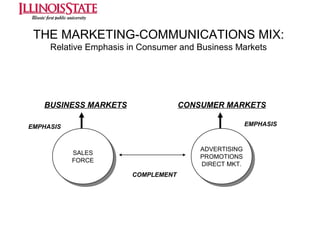
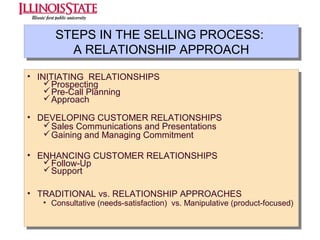
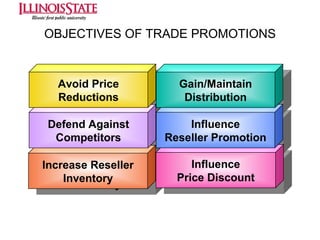
This document provides an overview of marketing communications, including advertising, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and direct marketing. It discusses the objectives of marketing communications programs as well as strategies for developing integrated marketing communication plans and selecting an optimal promotional mix. Key aspects covered include developing advertising campaigns, evaluating advertising effectiveness, conducting public relations, and managing personal selling and sales. The document presents frameworks for conceptualizing these various promotional techniques and their application in consumer and business markets.