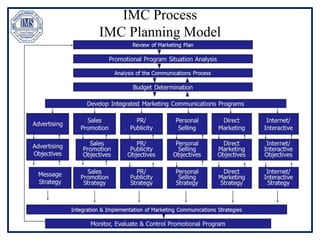
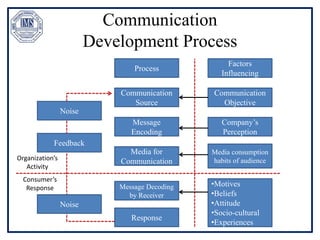
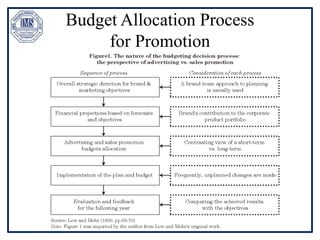
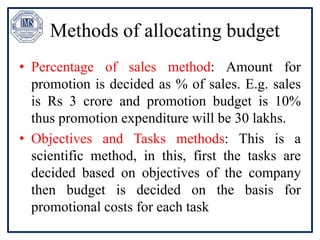
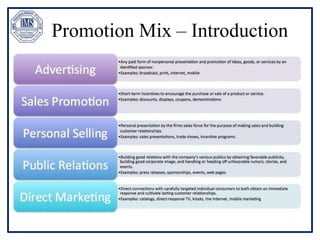
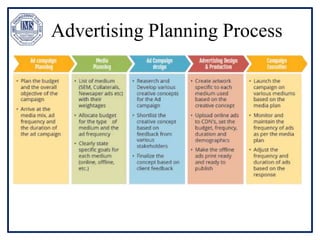
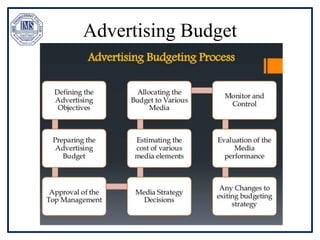
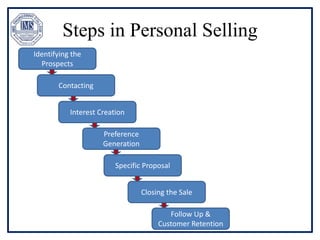
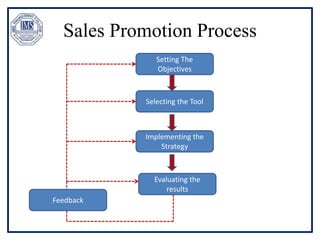
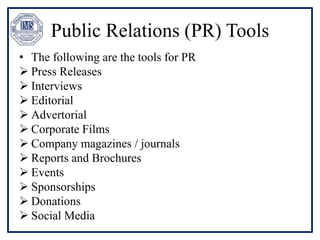
The document discusses promotion management in marketing, highlighting the significance of integrated marketing communication (IMC) to deliver consistent brand messages across various channels. It details the objectives of promotion, methods of budgeting for promotional activities, and various techniques including advertising, personal selling, and public relations. The document also examines the importance of sales promotion and direct marketing, outlining their characteristics and tools.