This document outlines an instructional design support model for developing competency-based education courses. Key points include:
- Faculty are compensated for developing courses through a stipend system. Courses are developed based on defined competencies and include flexible, distance learning components.
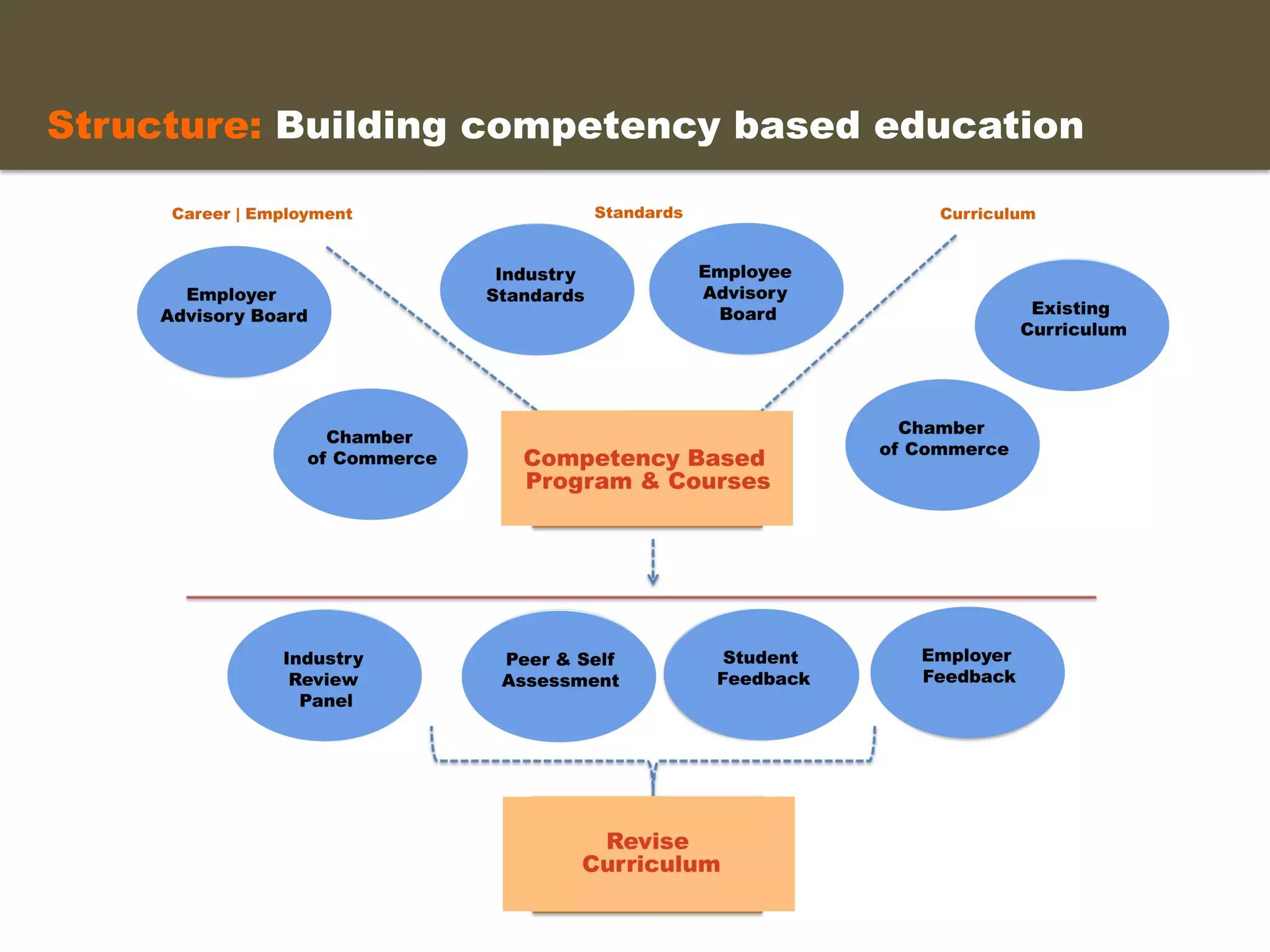
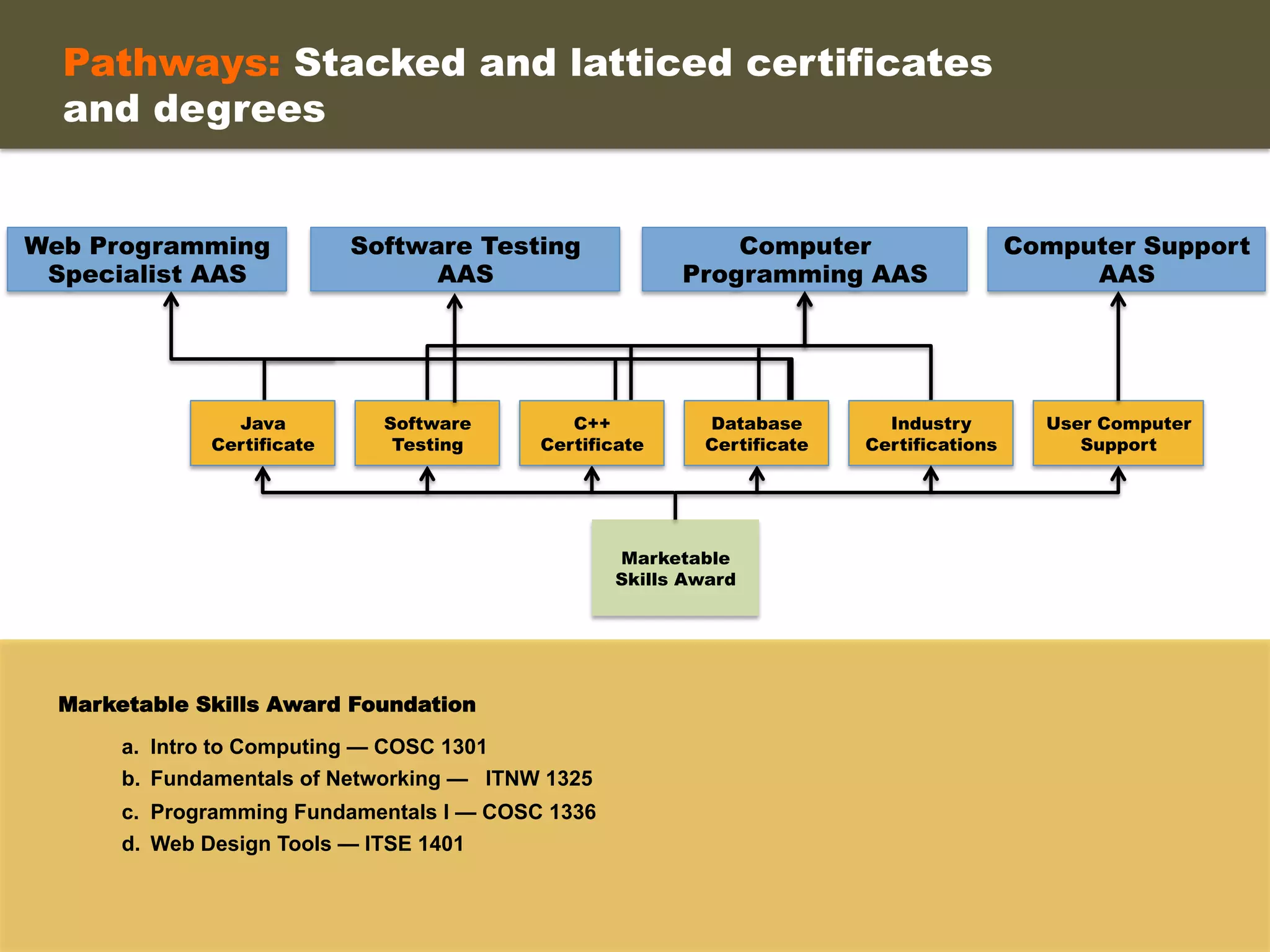
- The proposed structure includes stacking certificates and degrees through marketable skills awards and industry certifications. Student support is provided through specialists who advocate for students and monitor their progress.
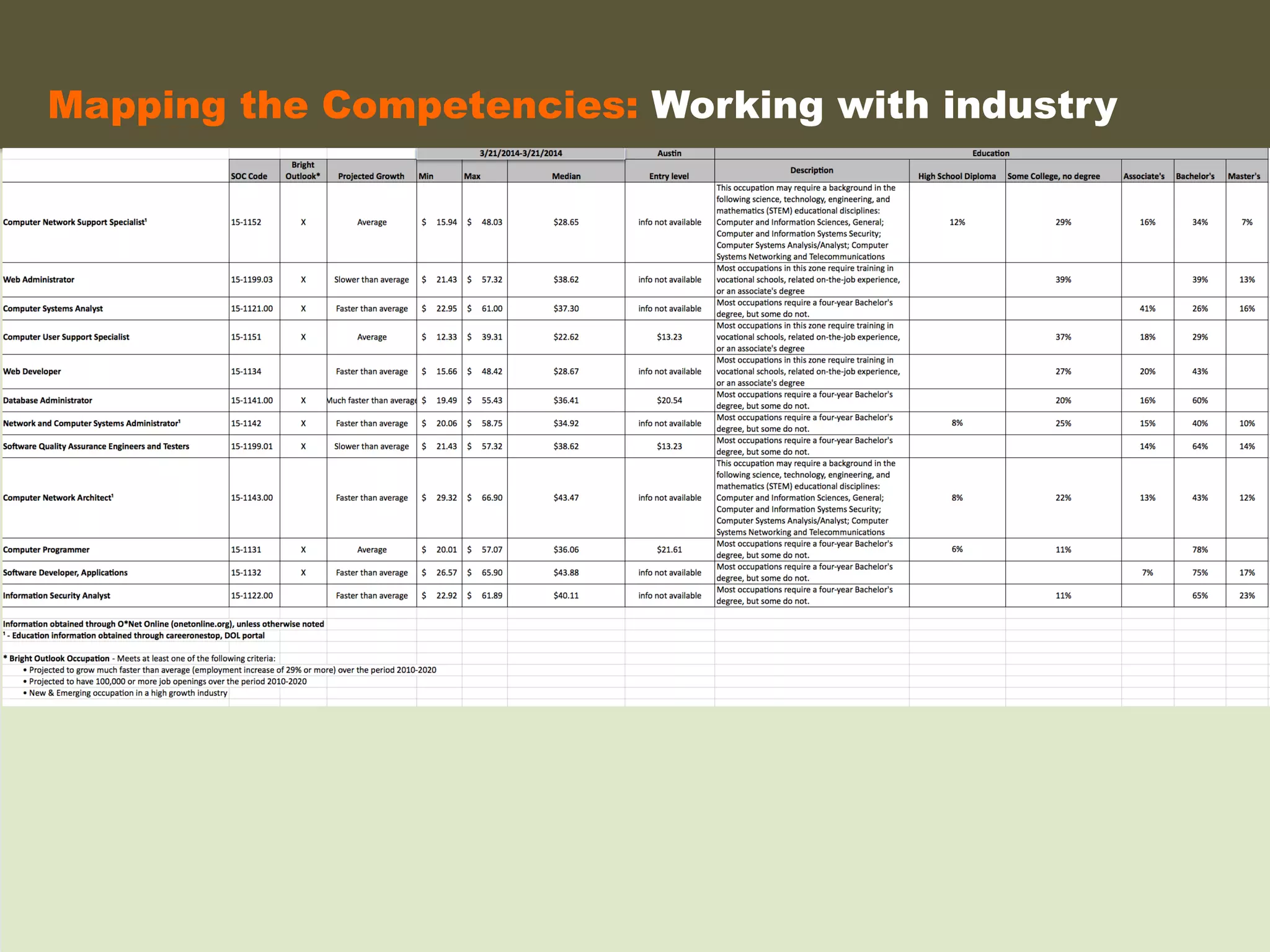
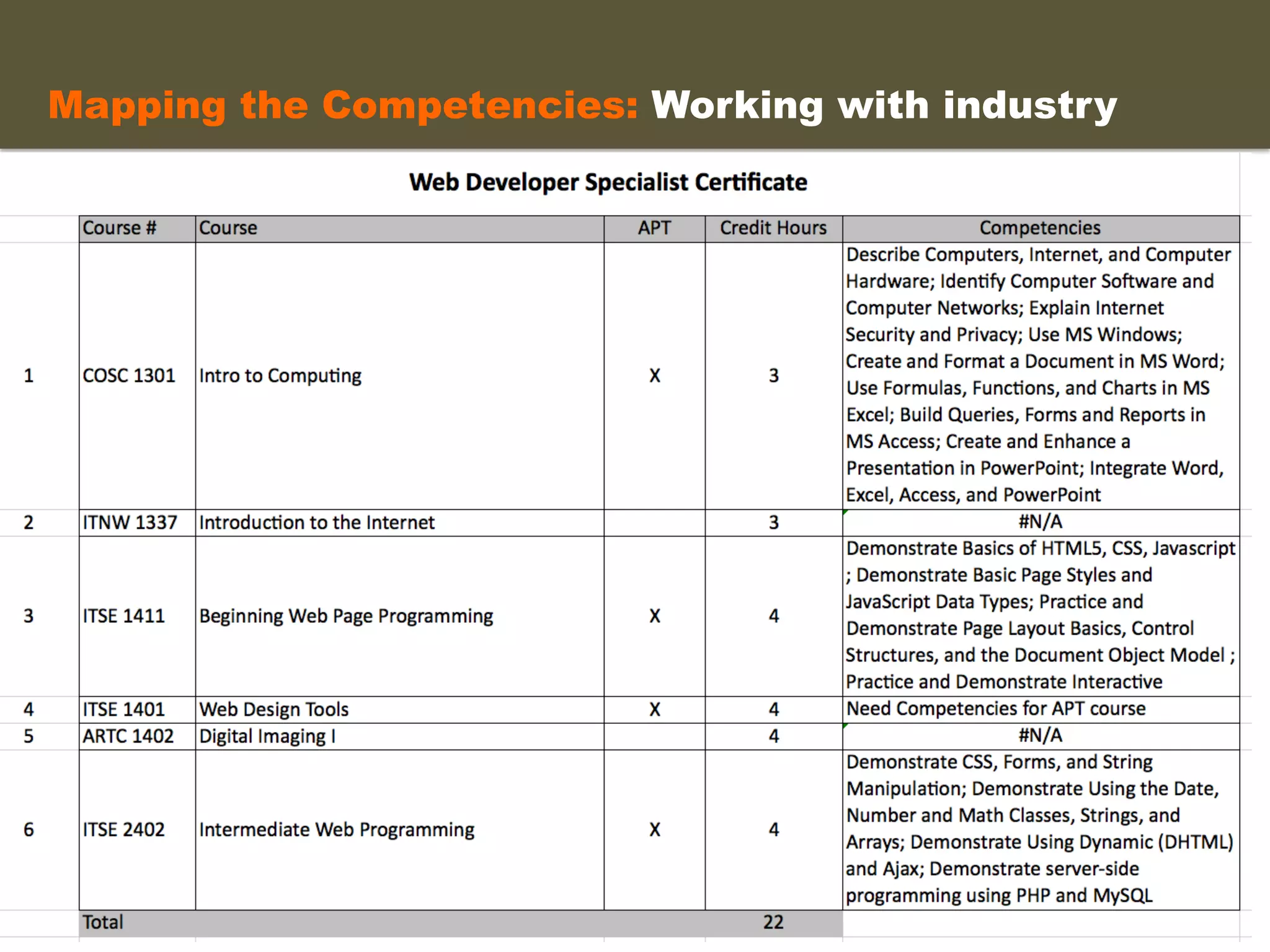
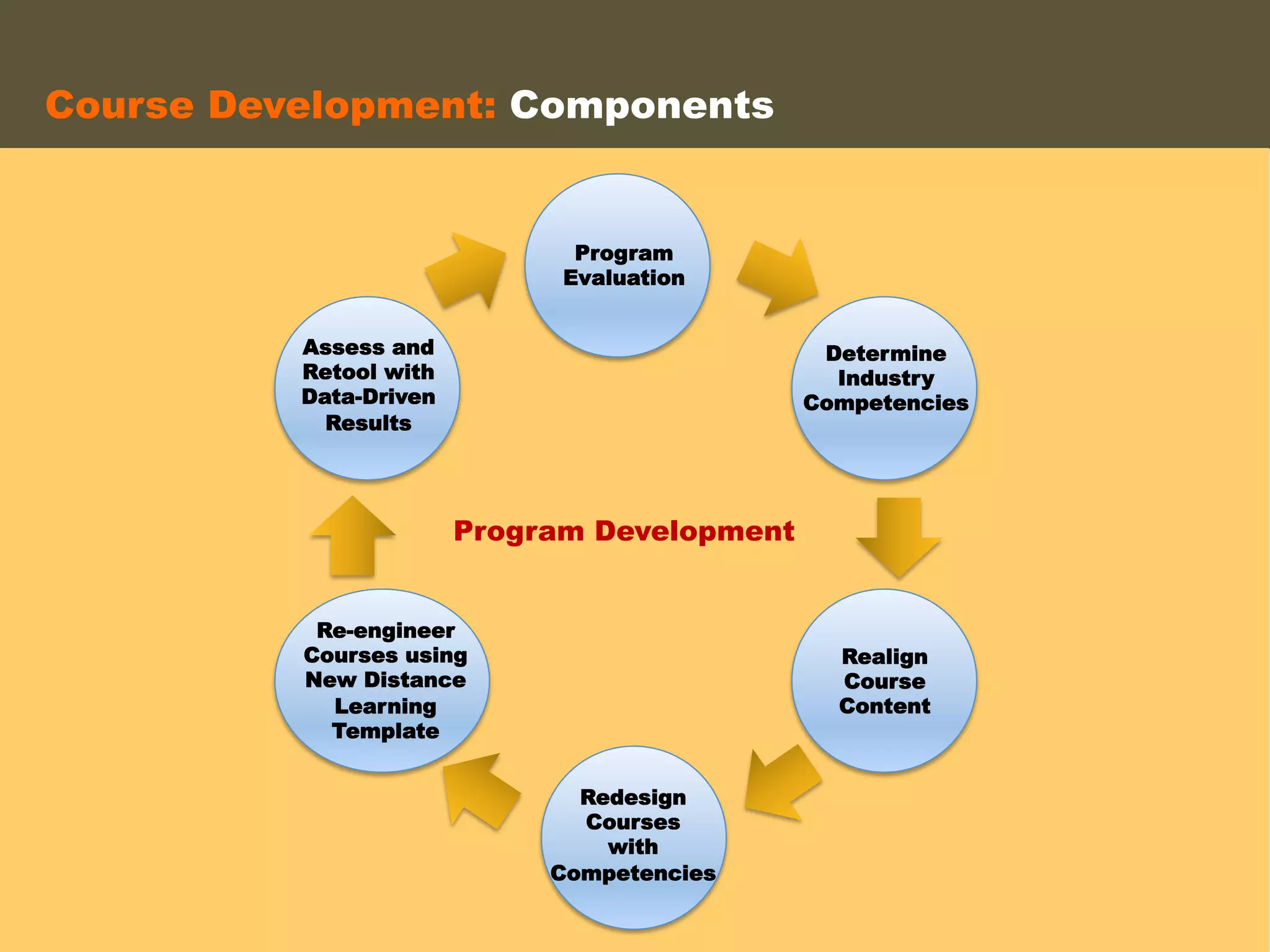
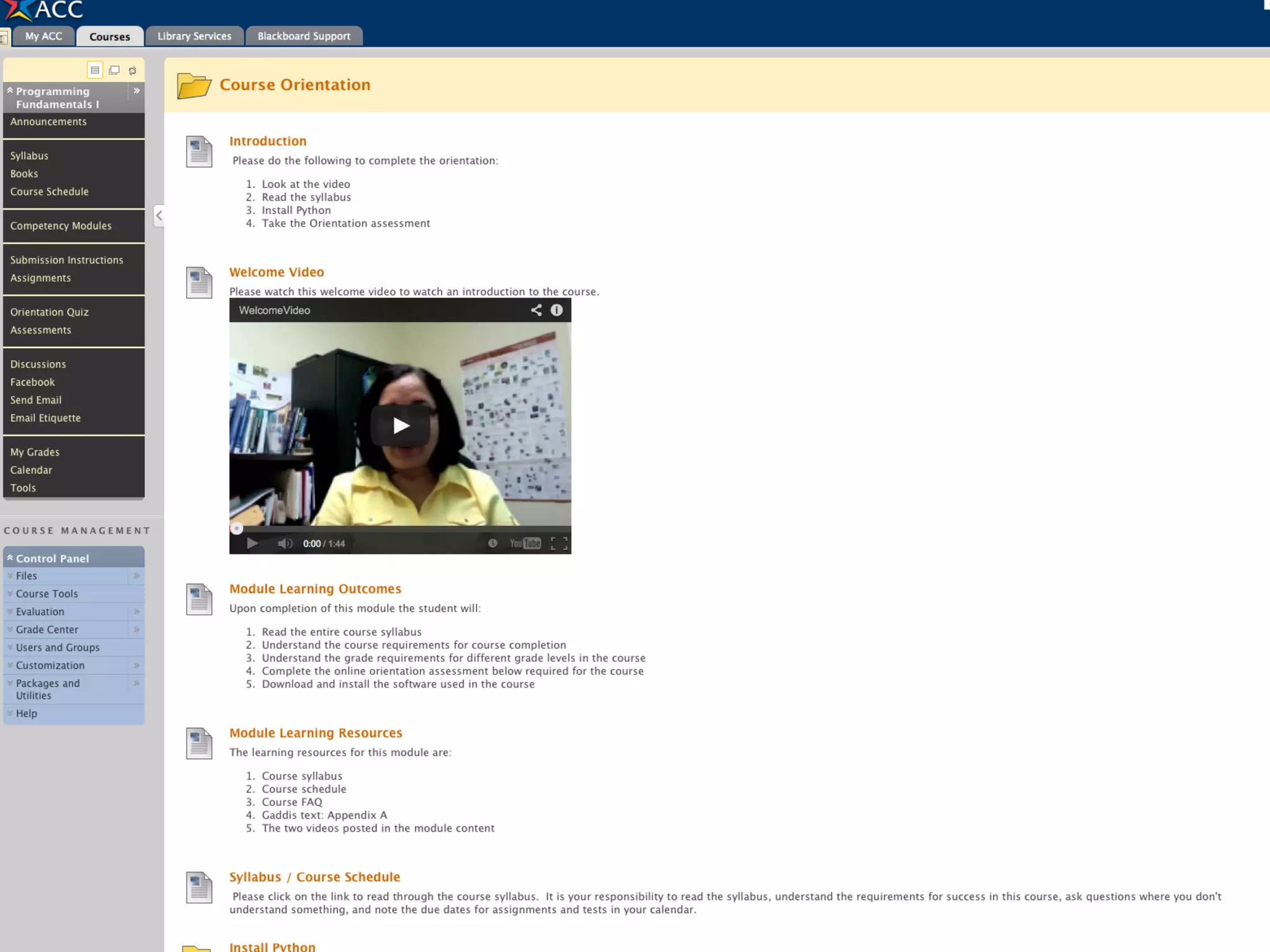
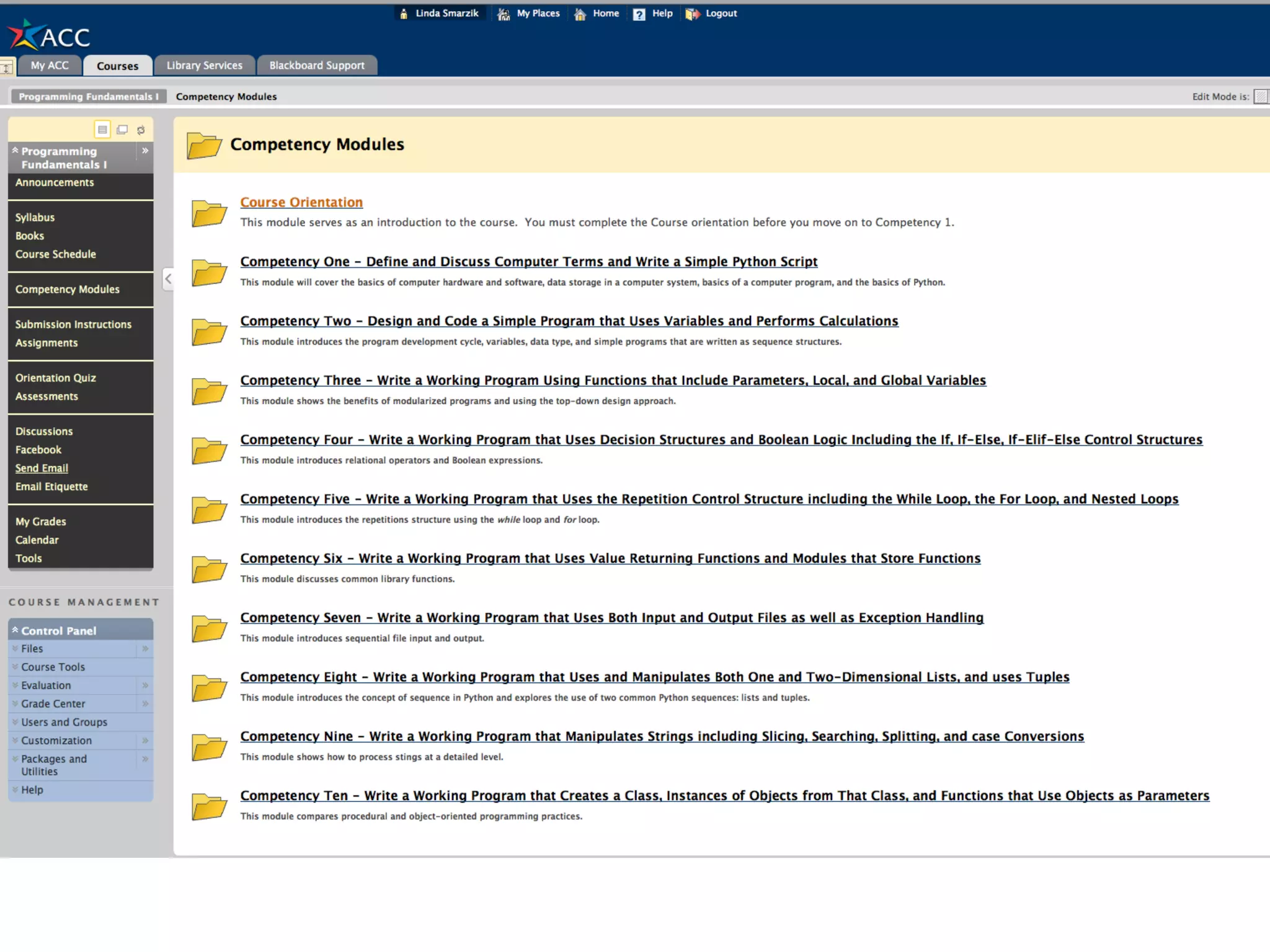
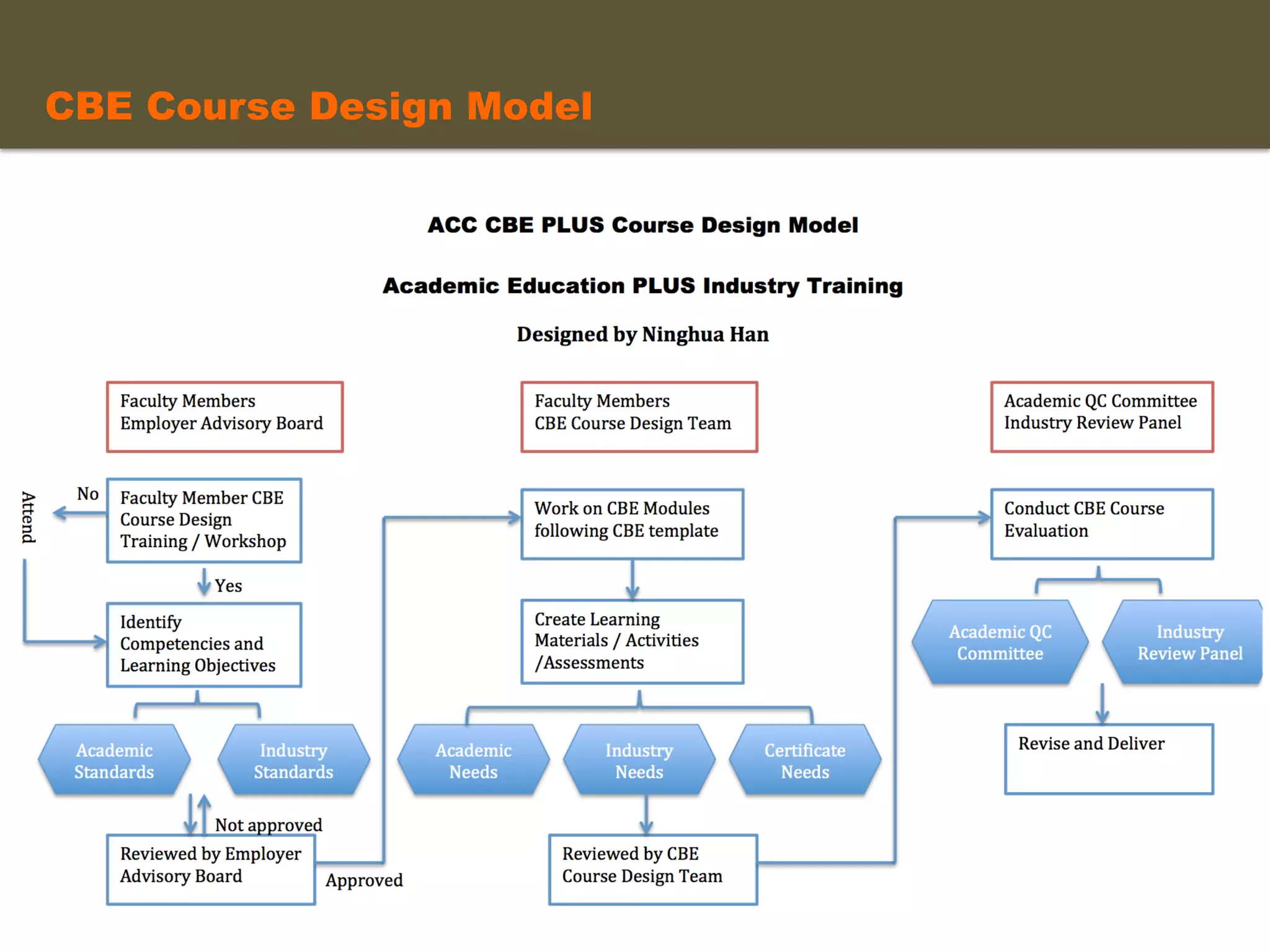
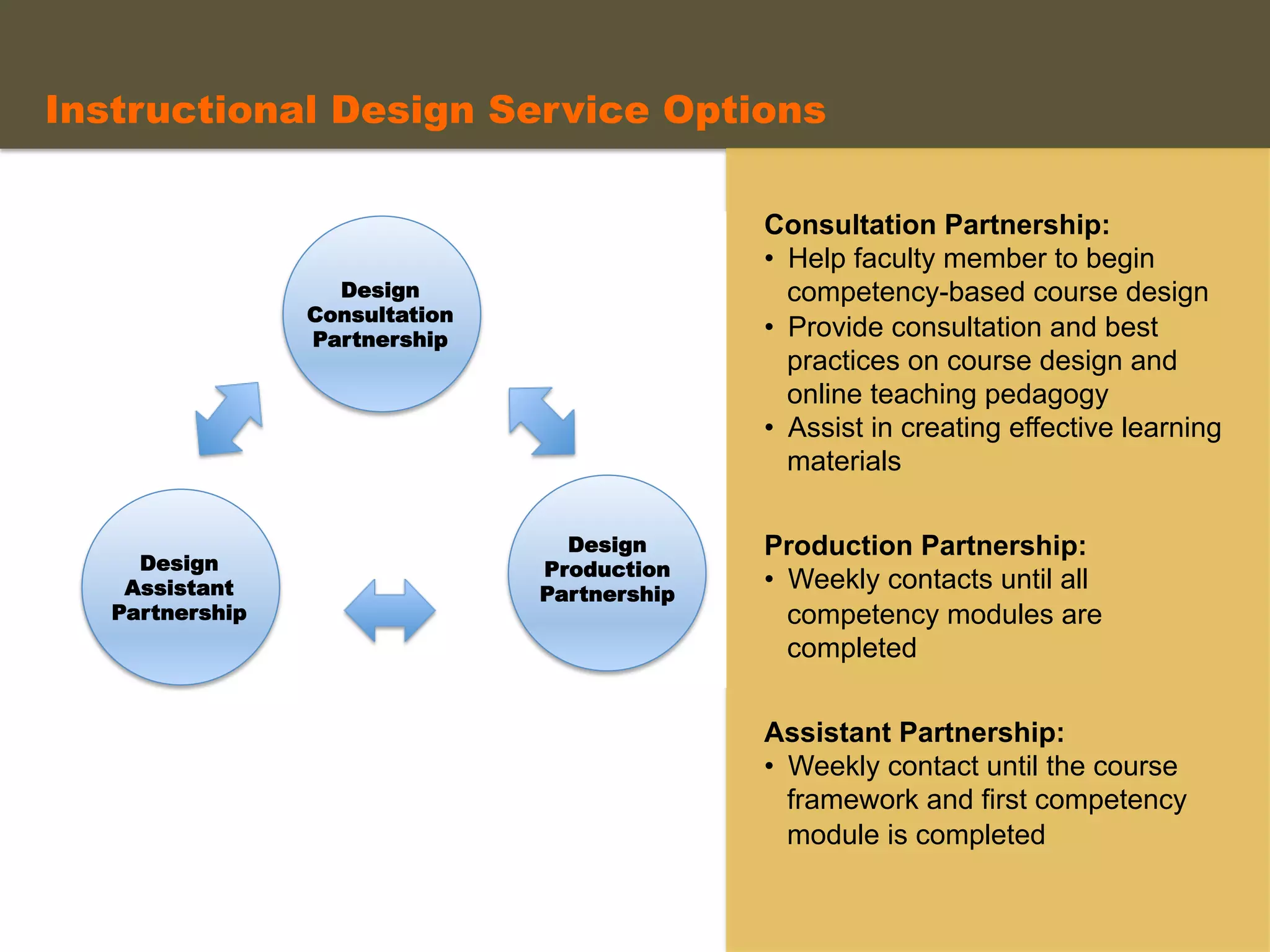
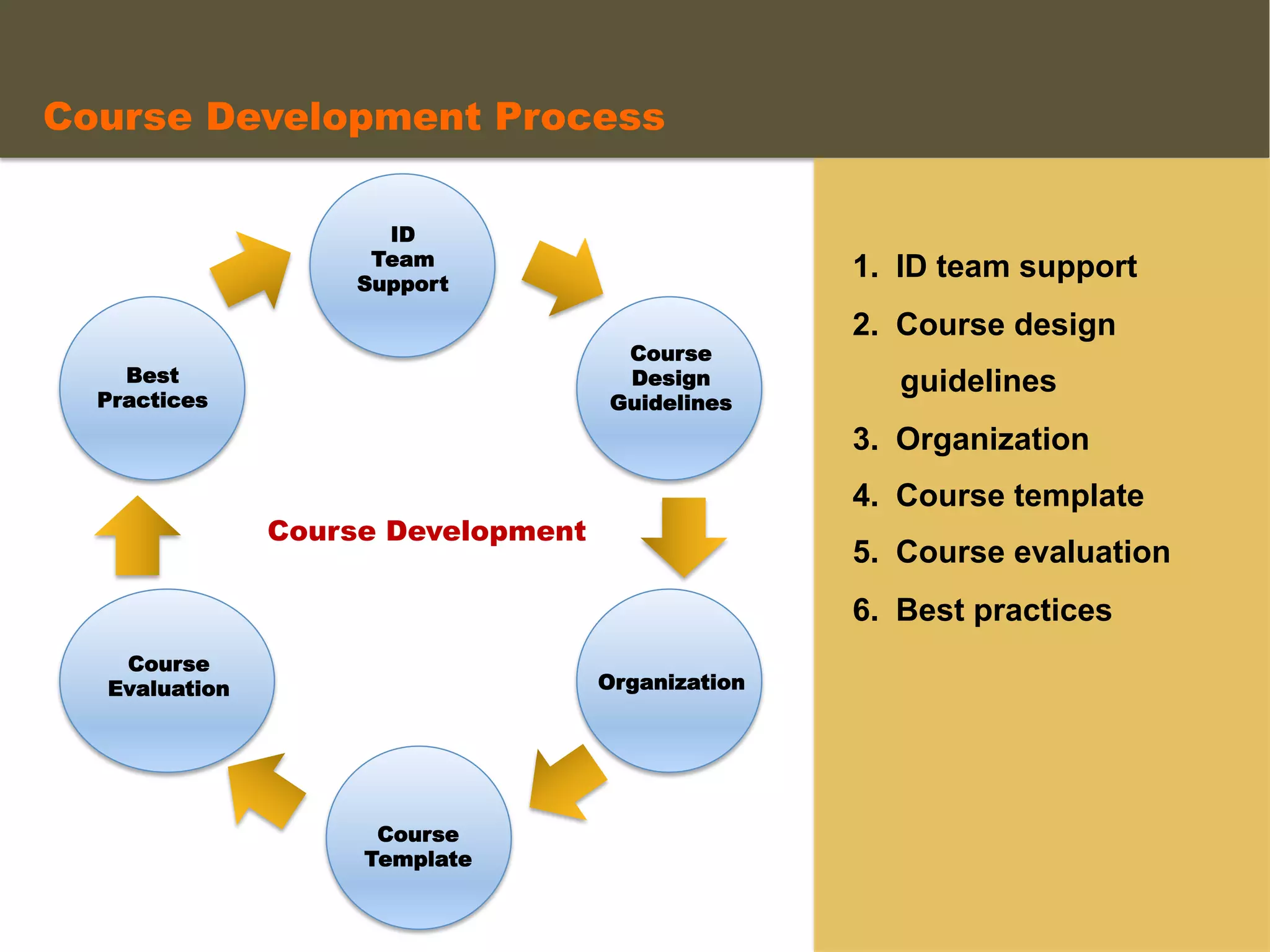
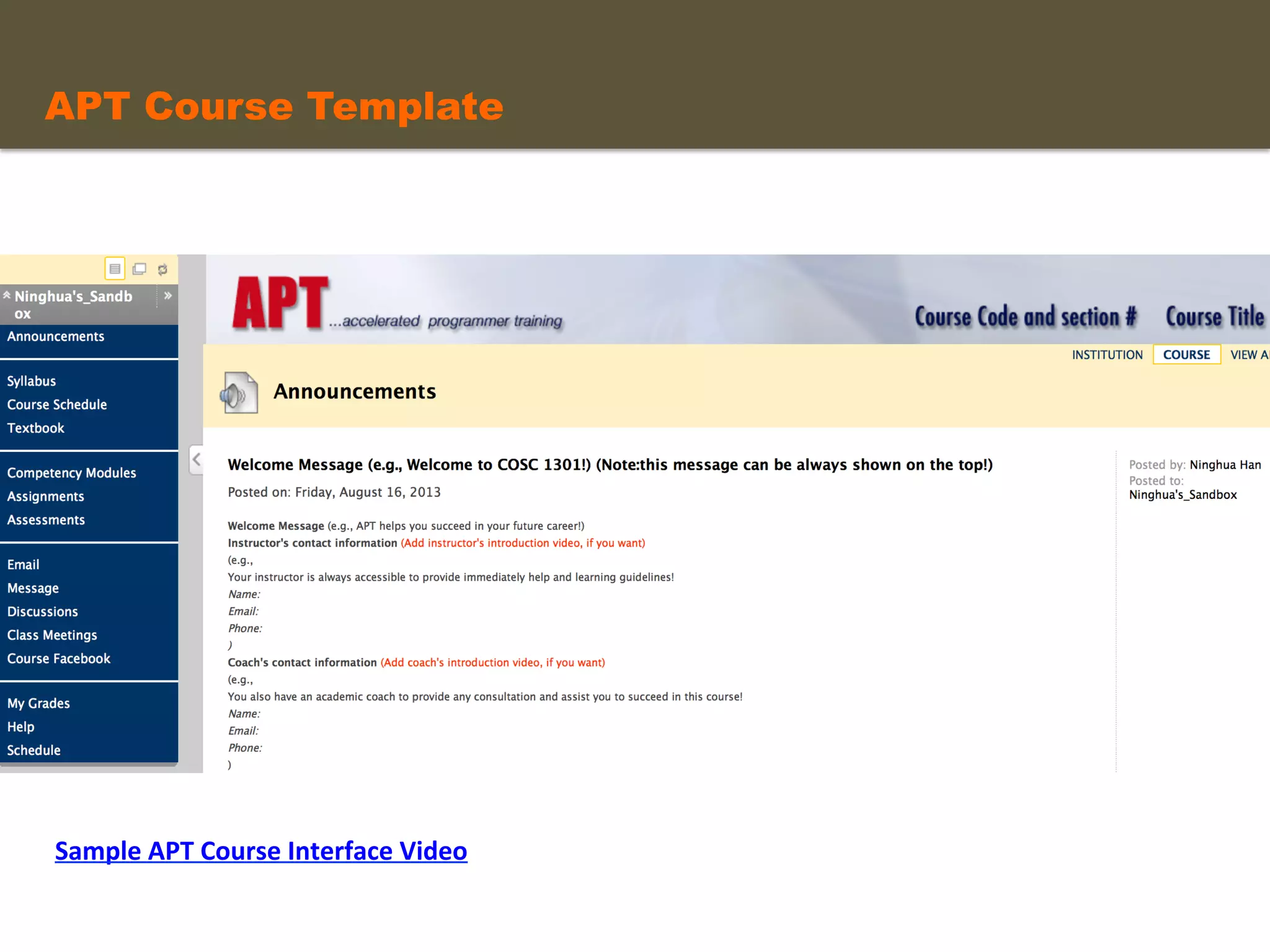
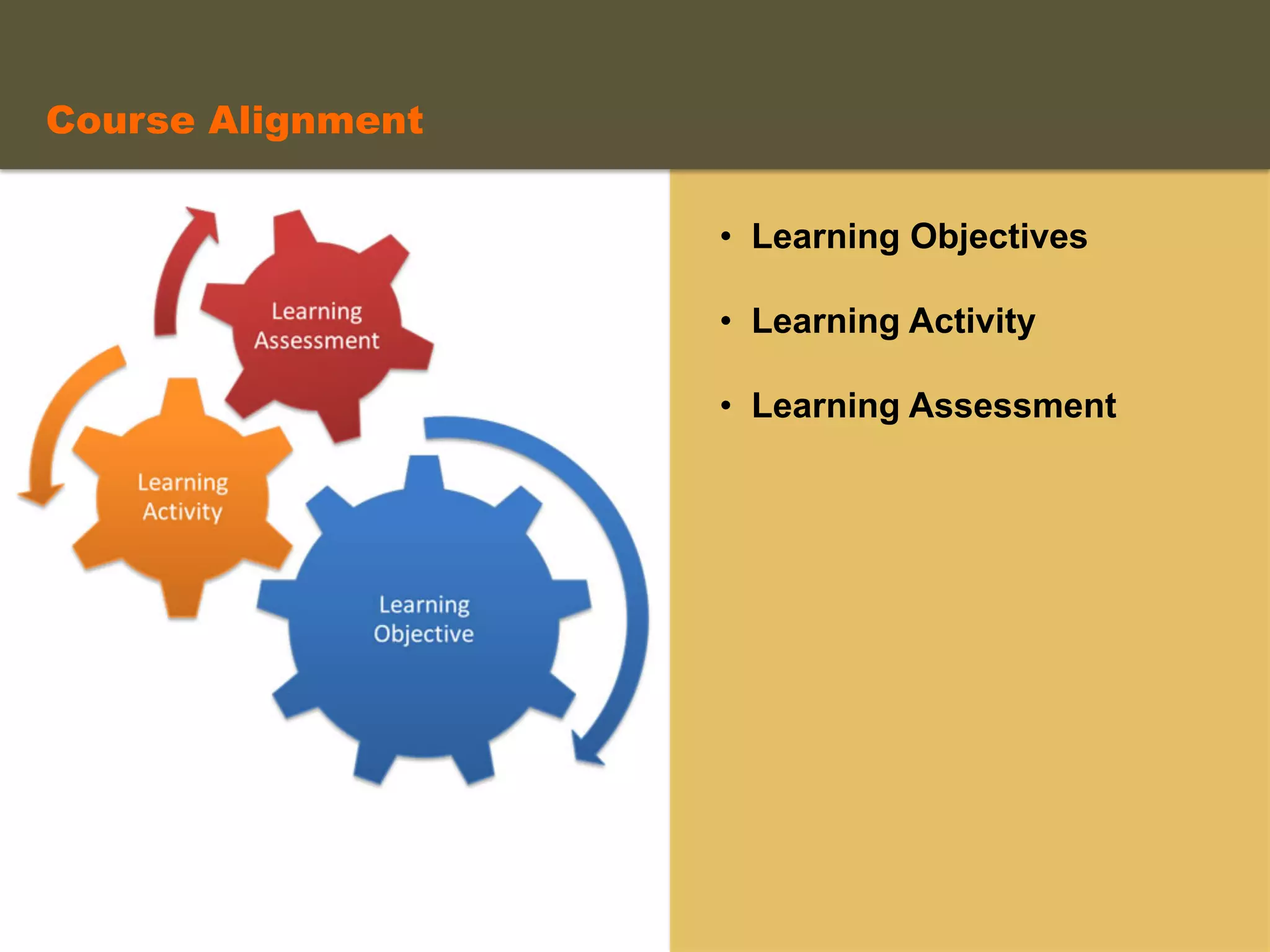
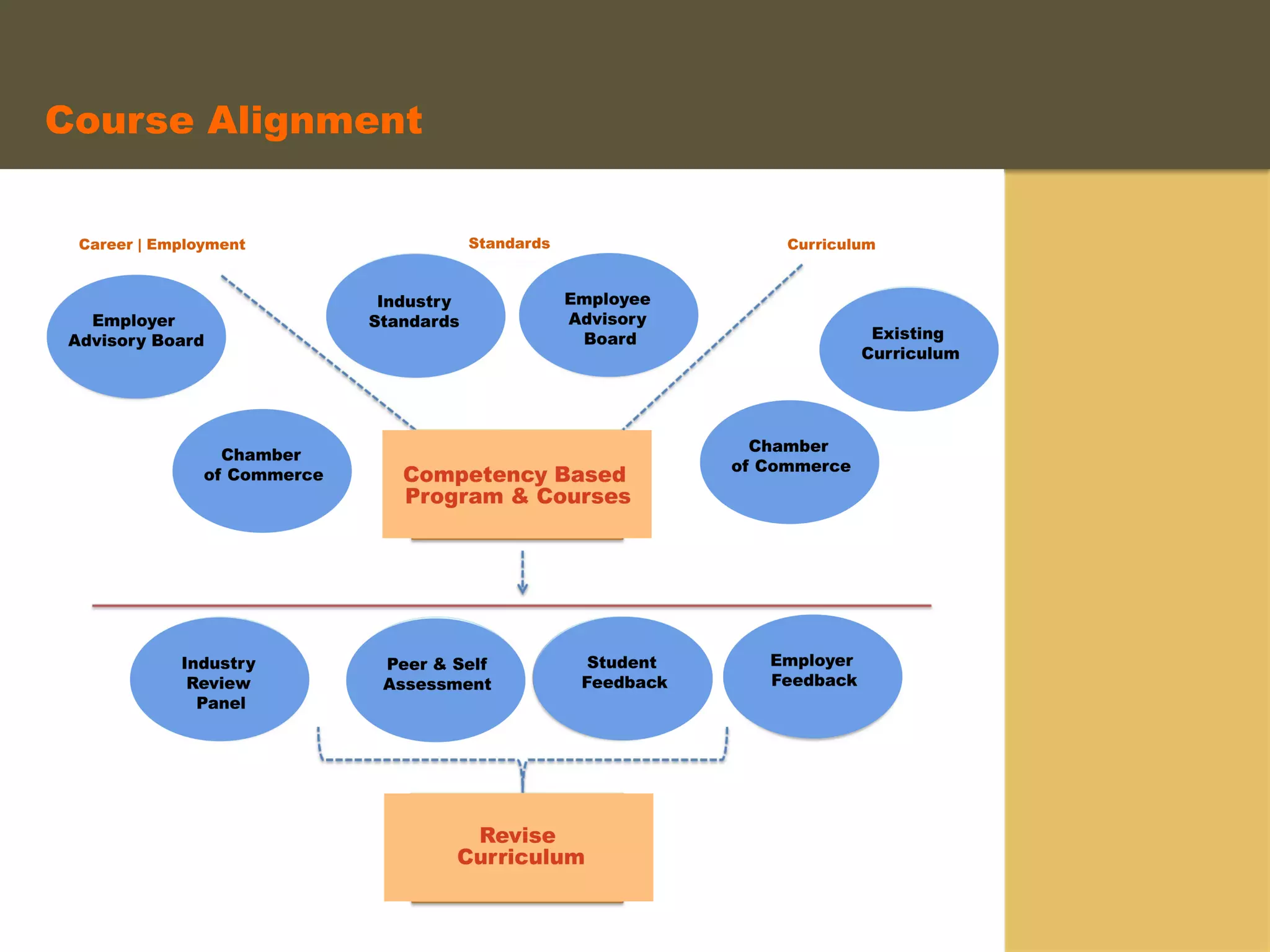
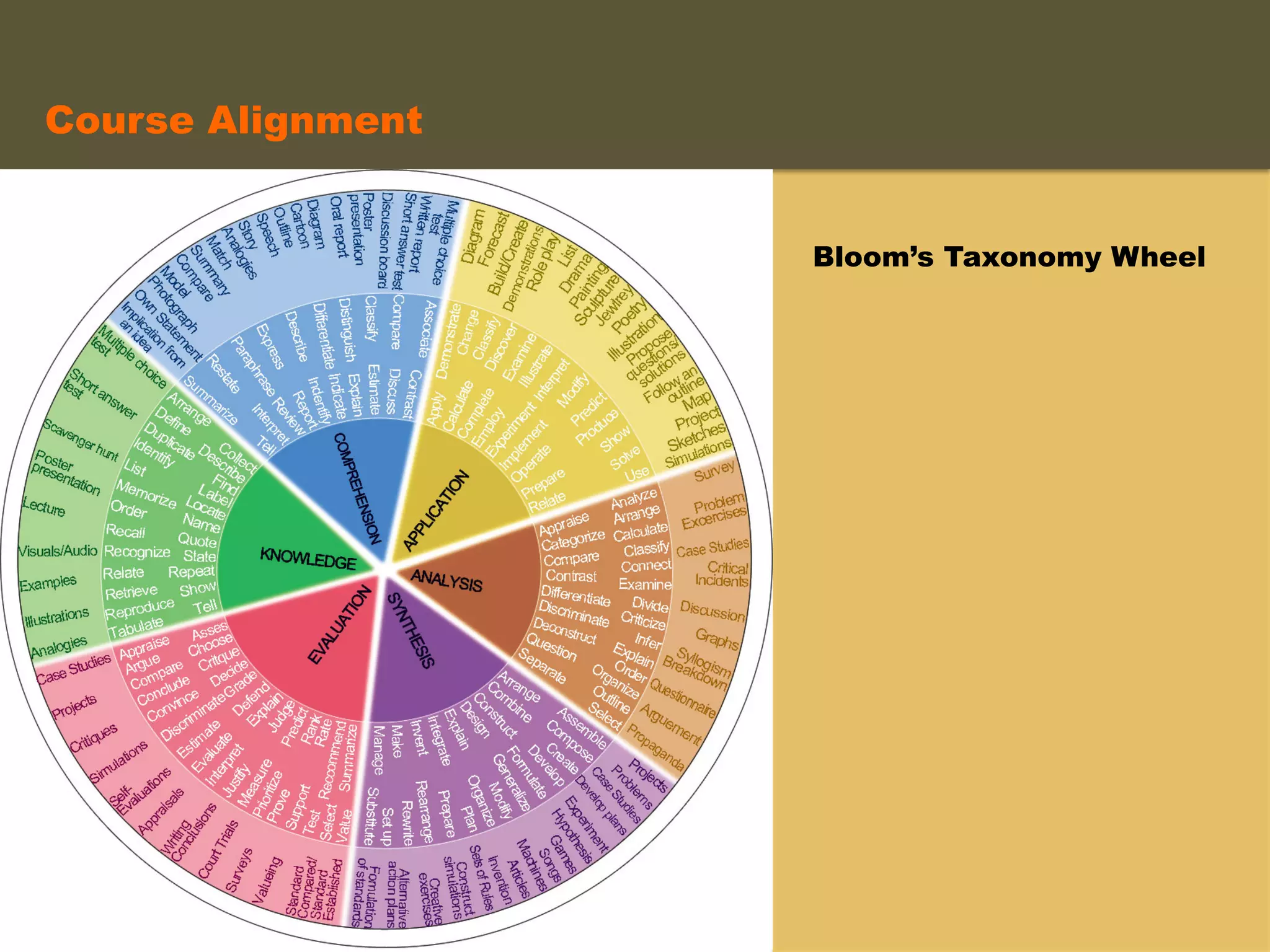
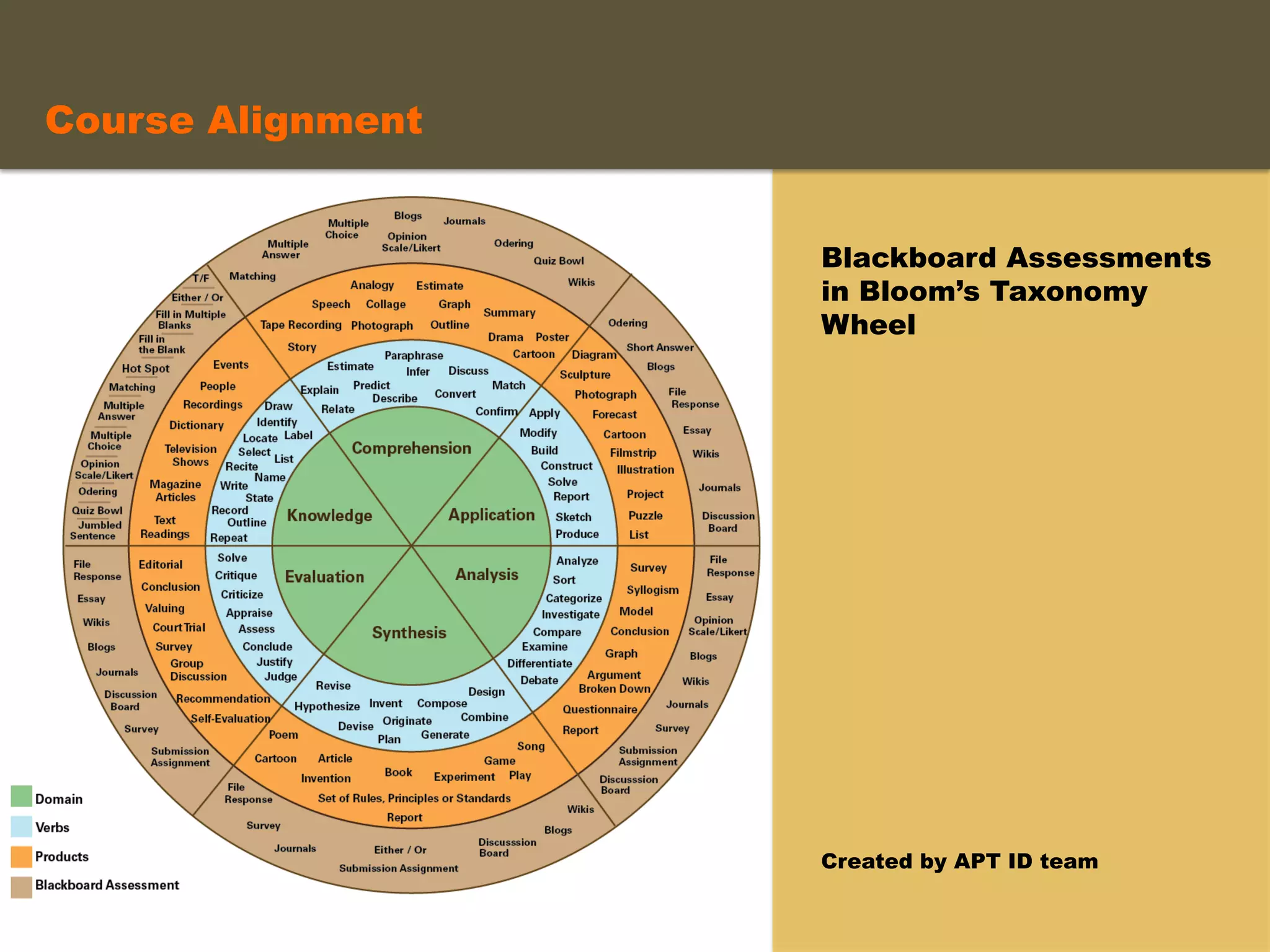
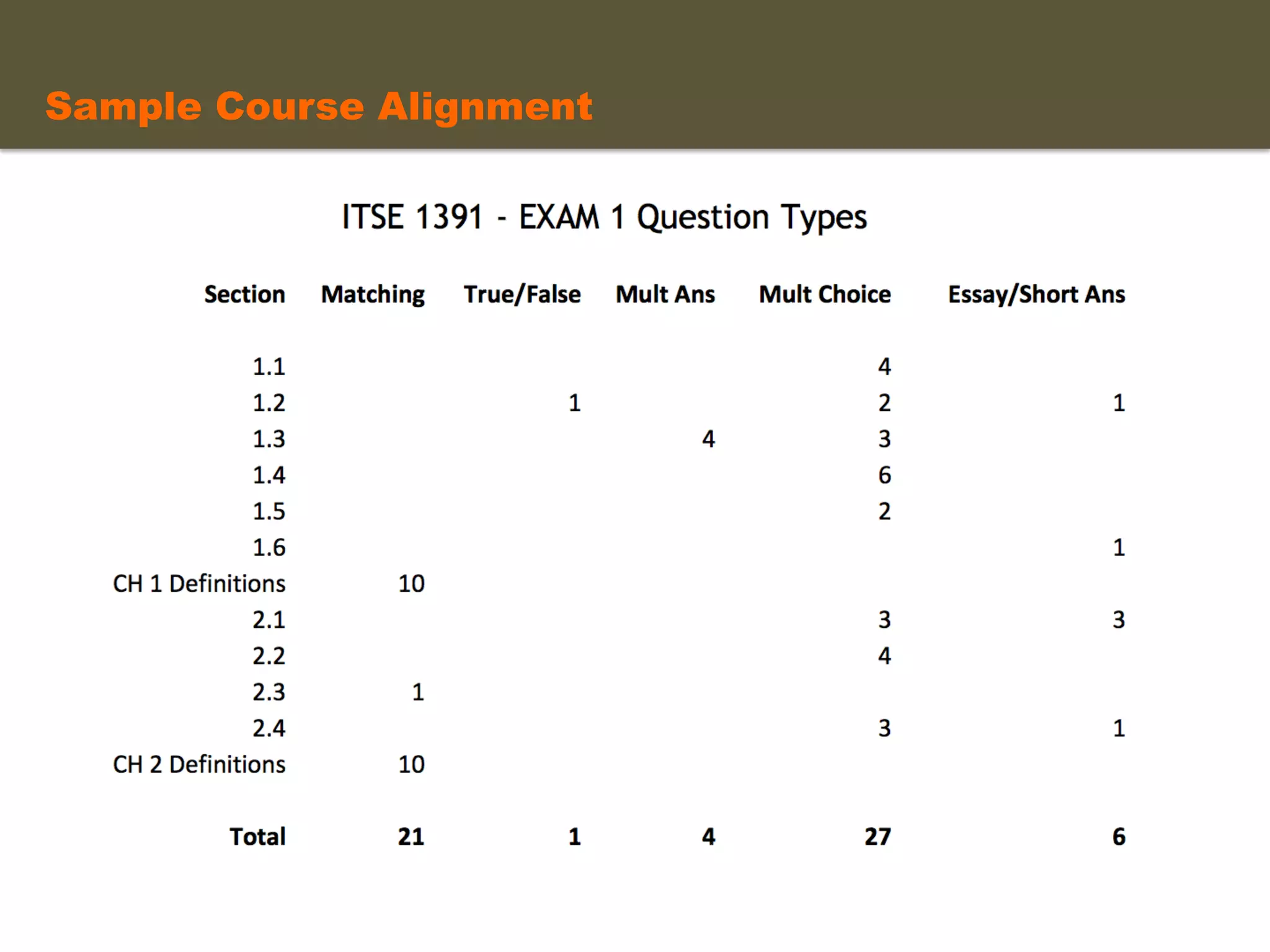
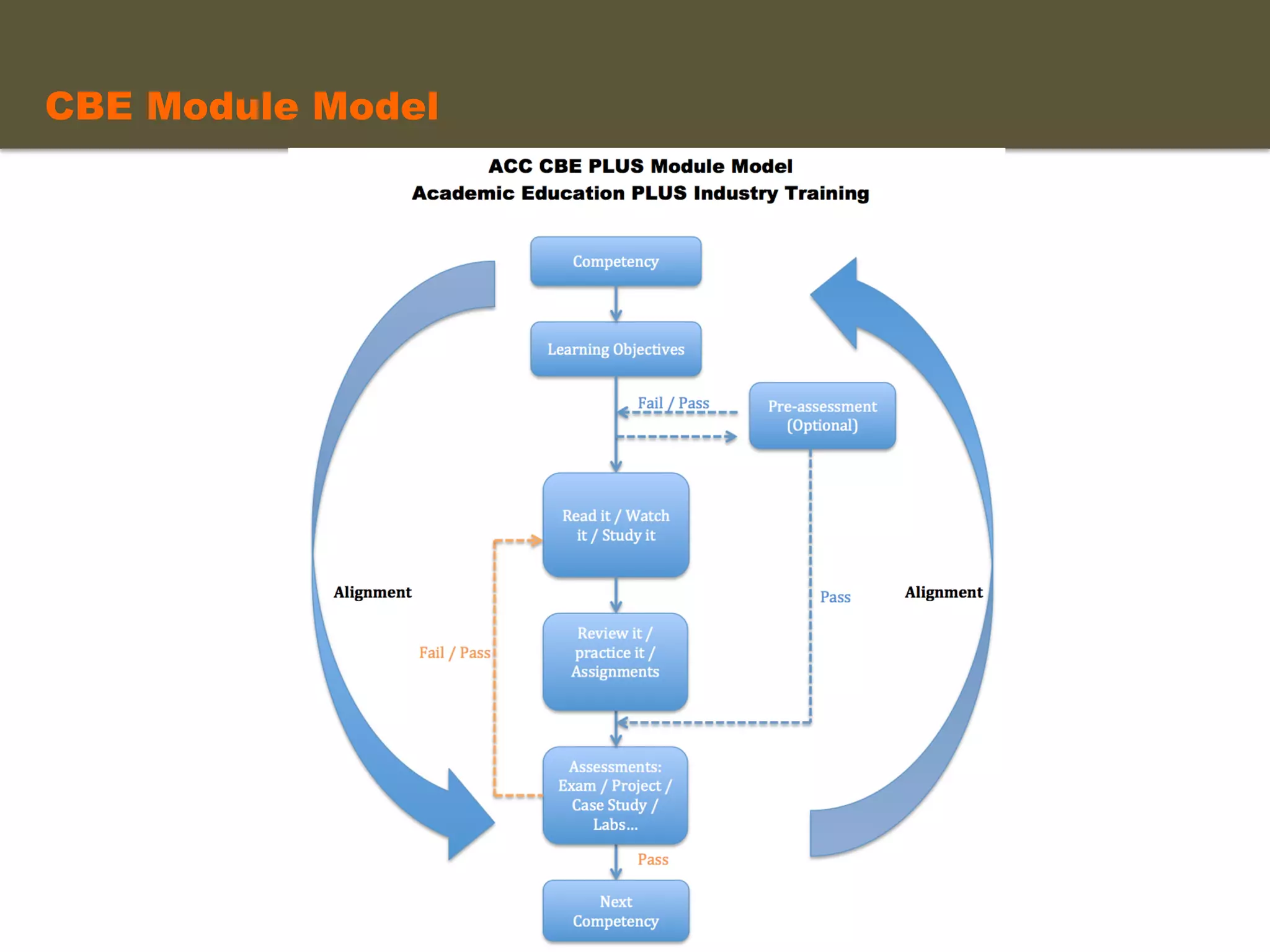
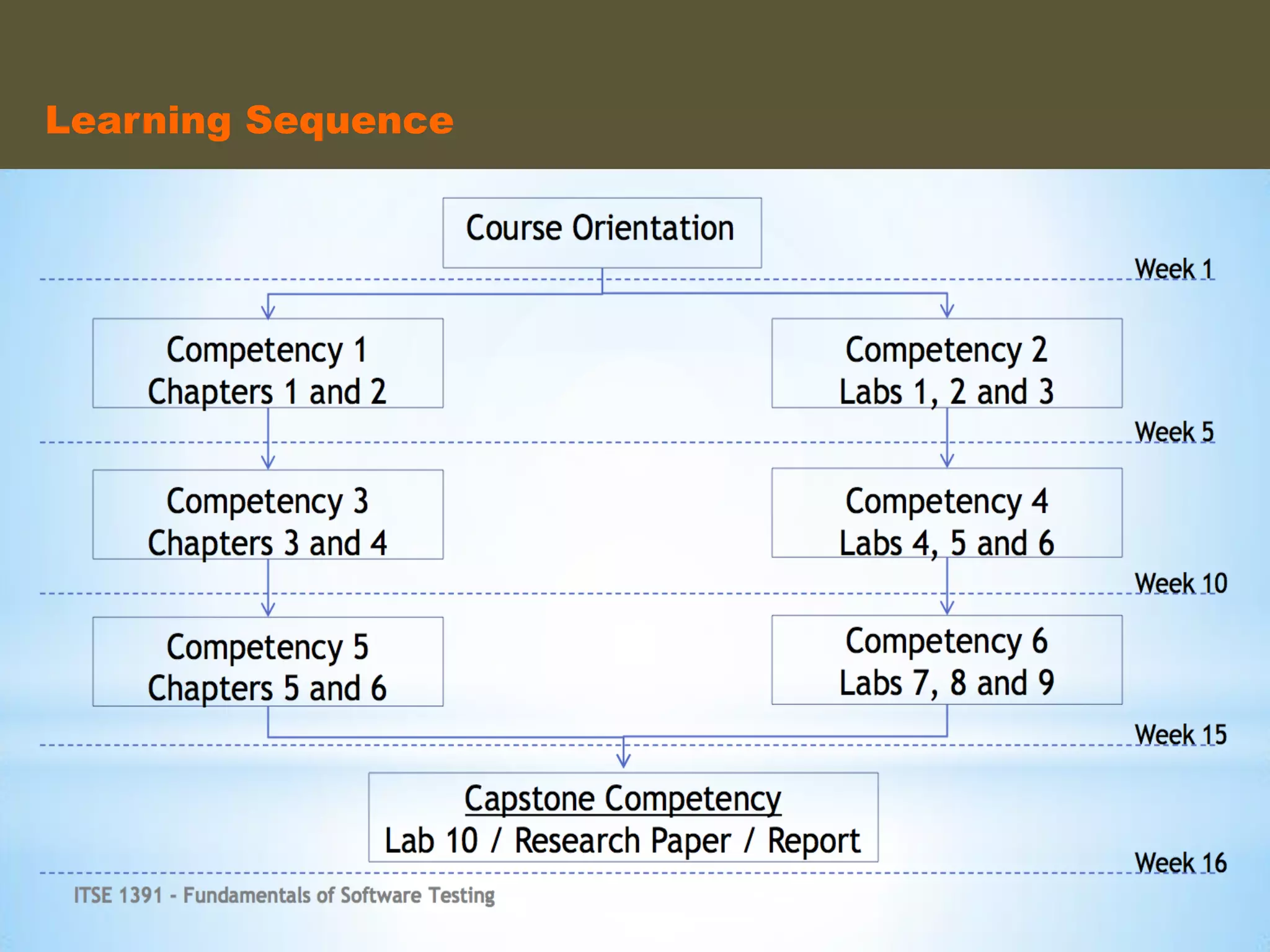
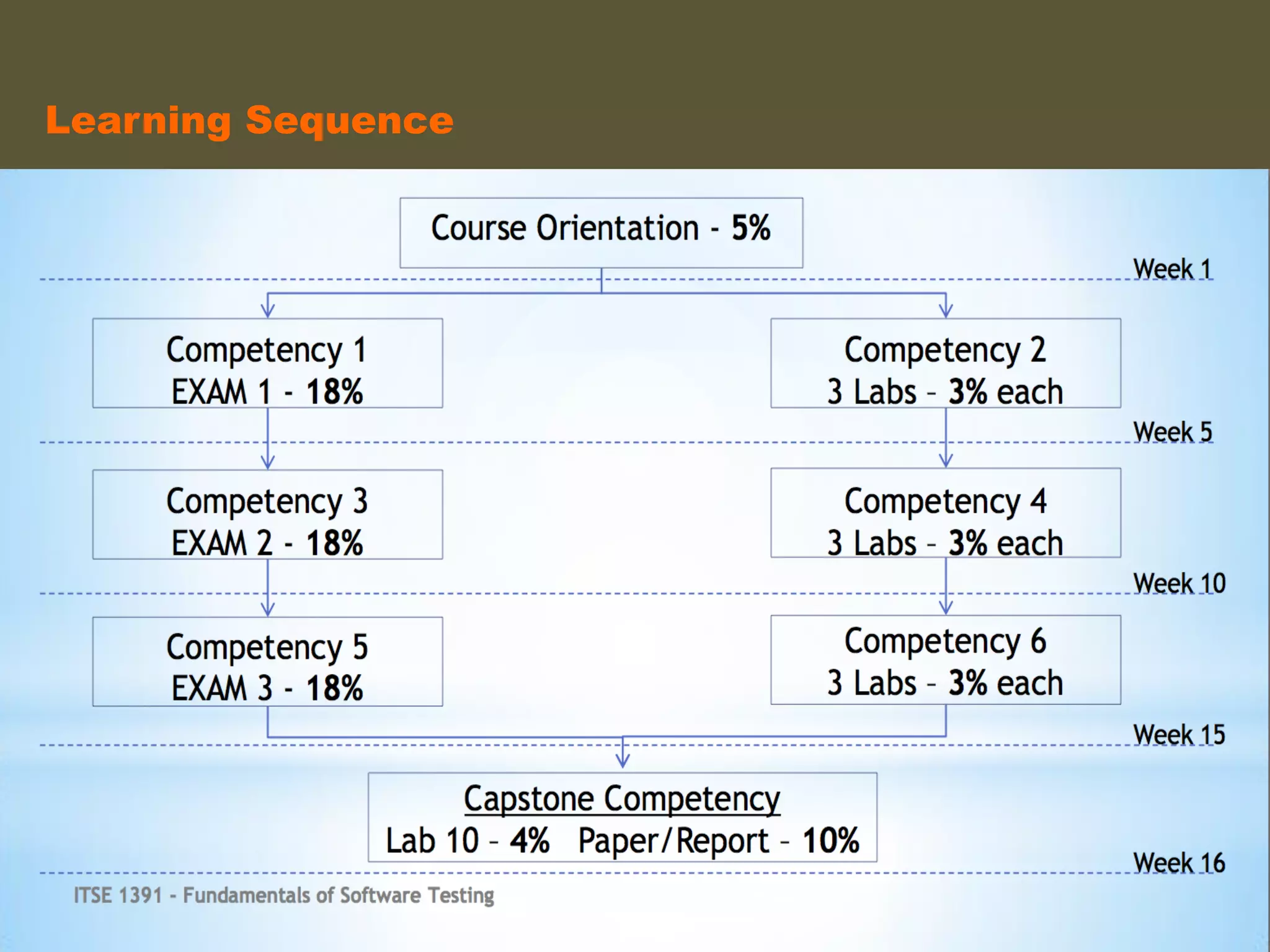
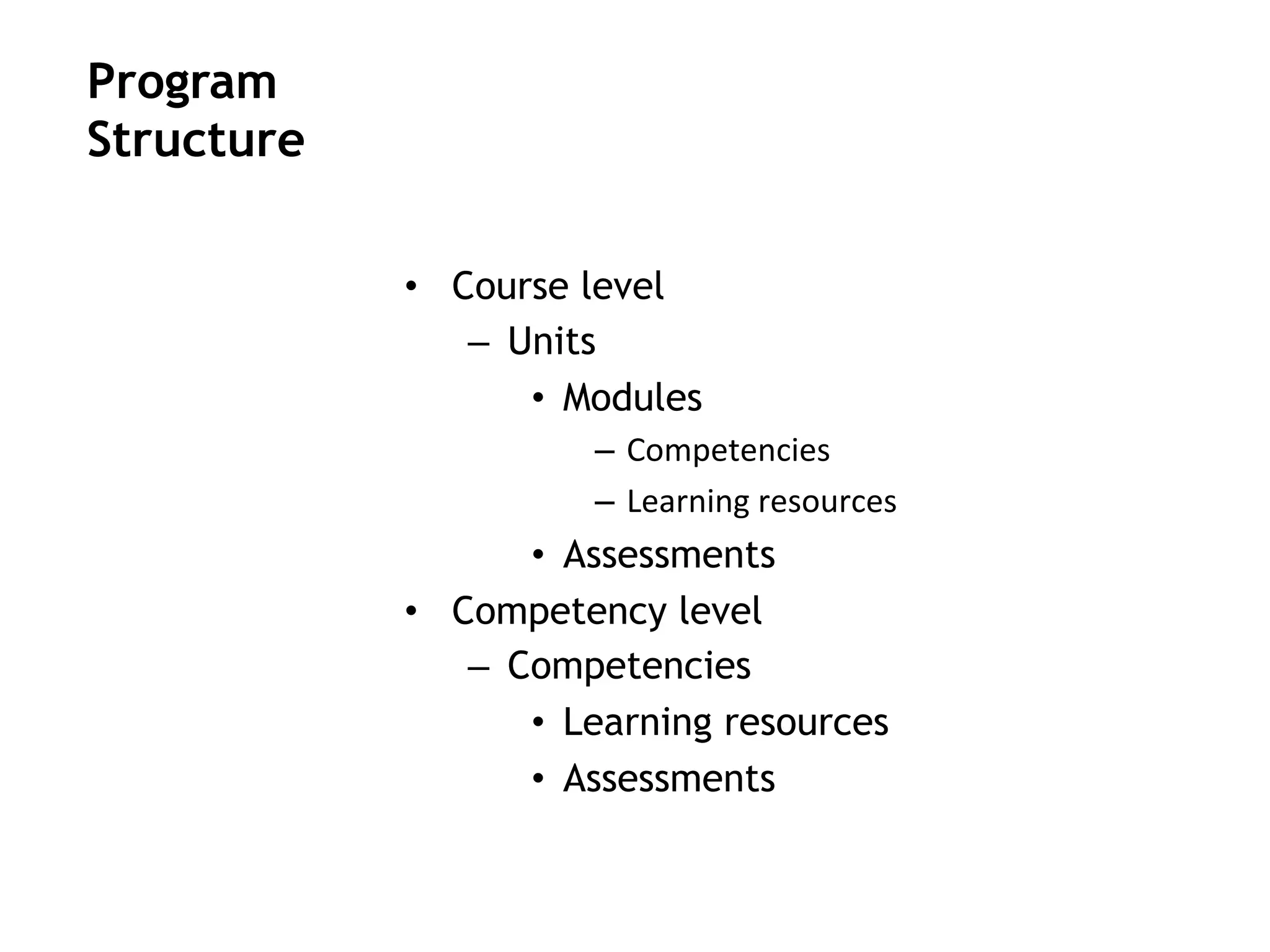
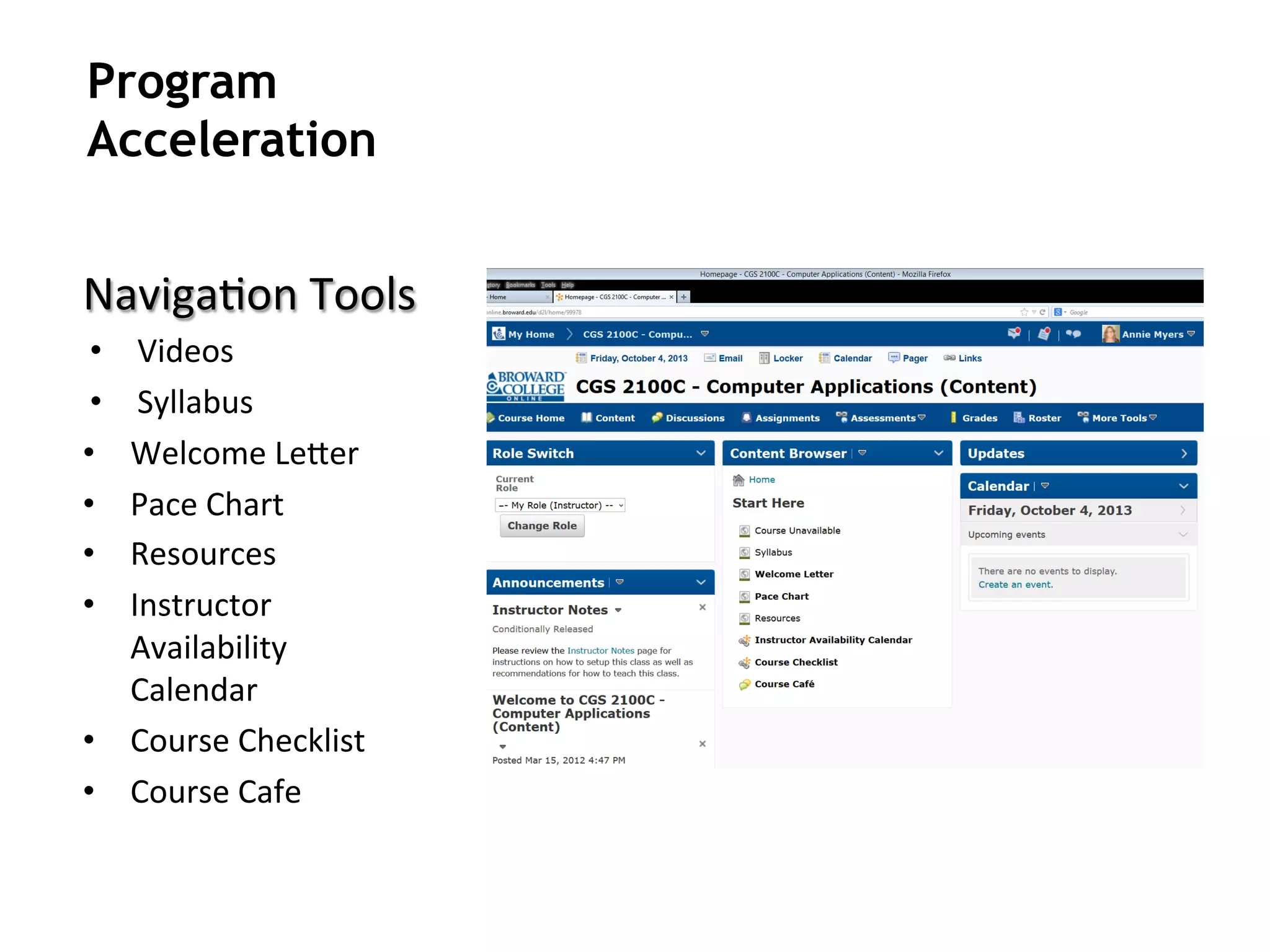
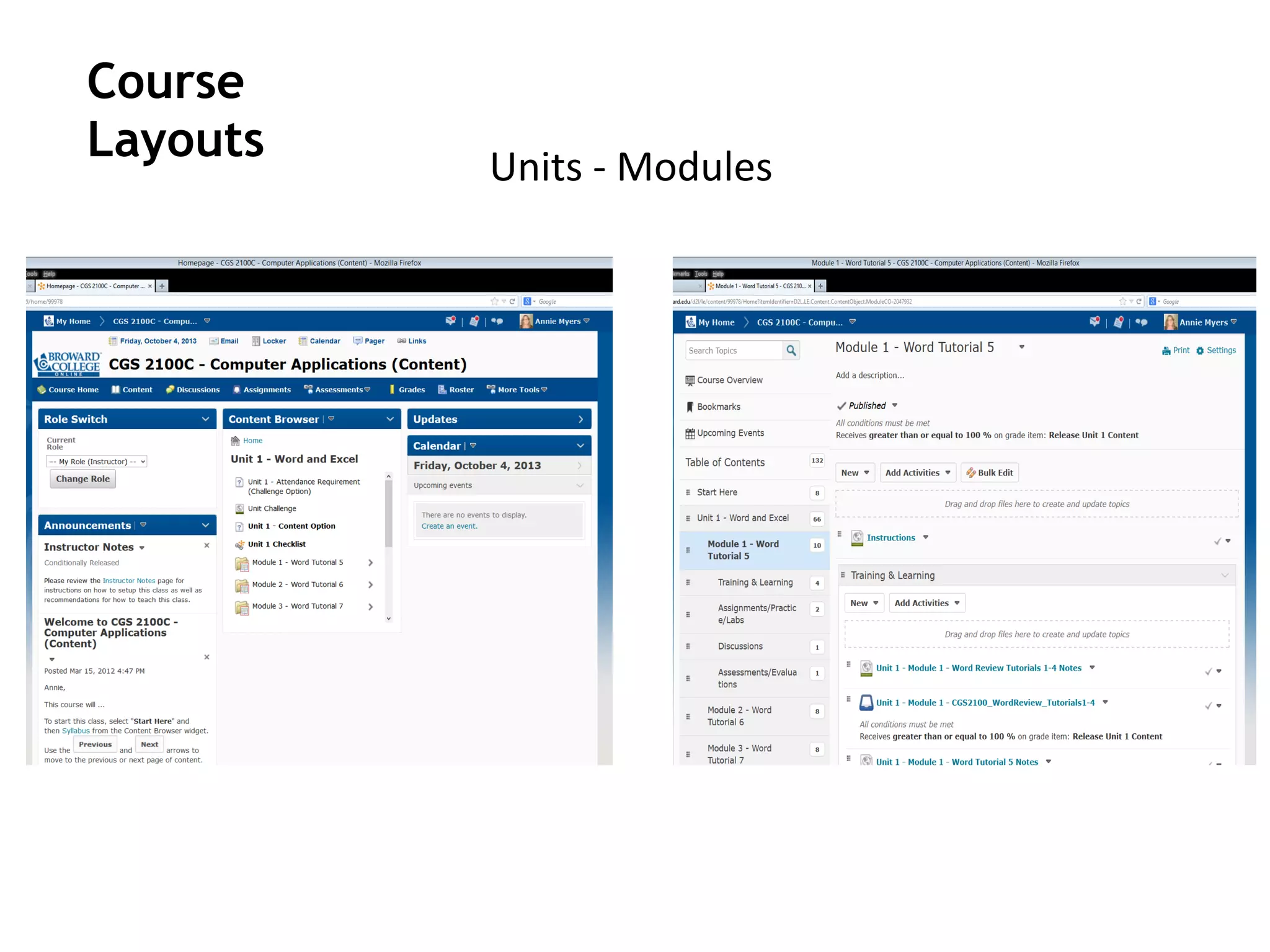
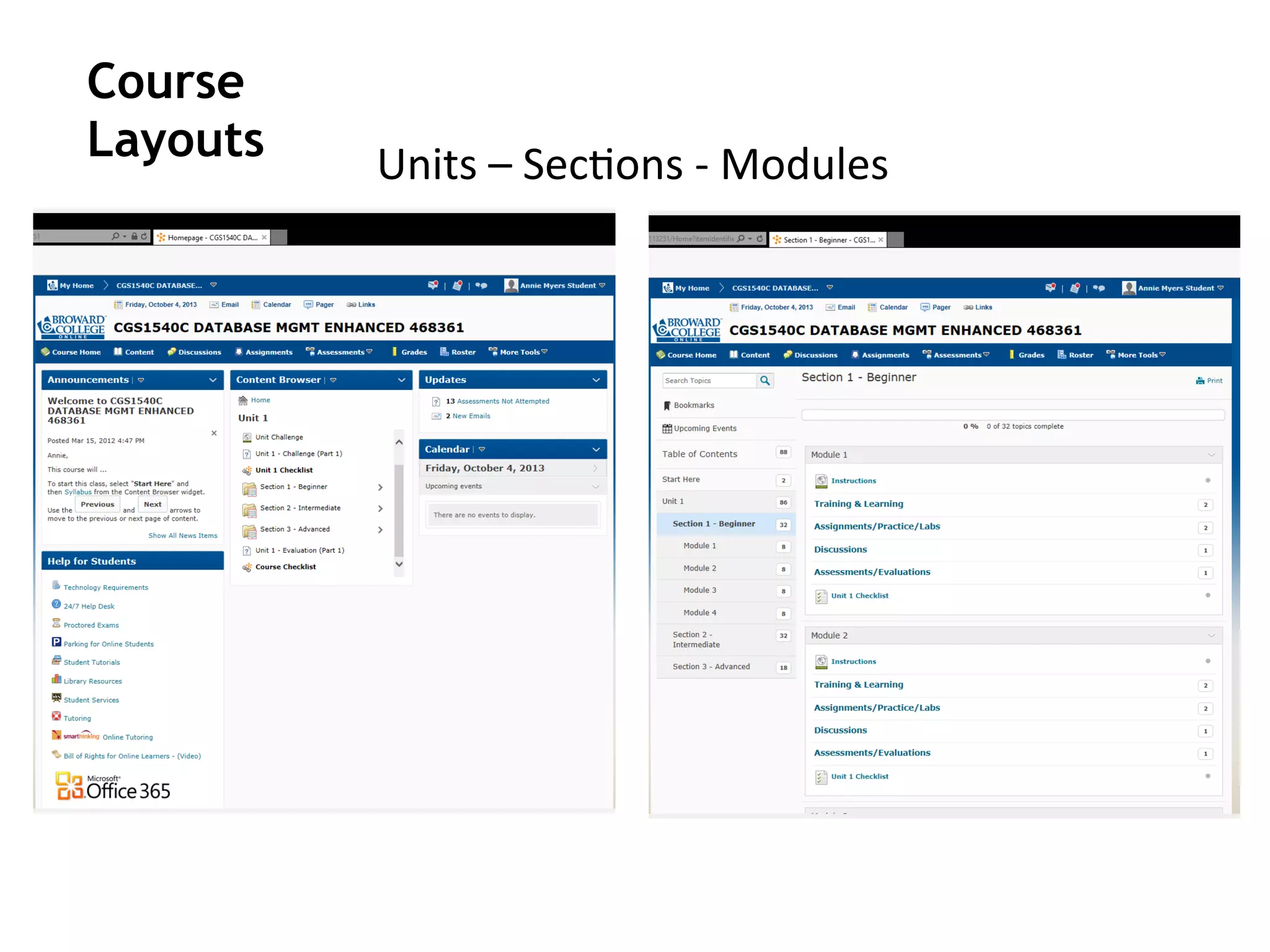
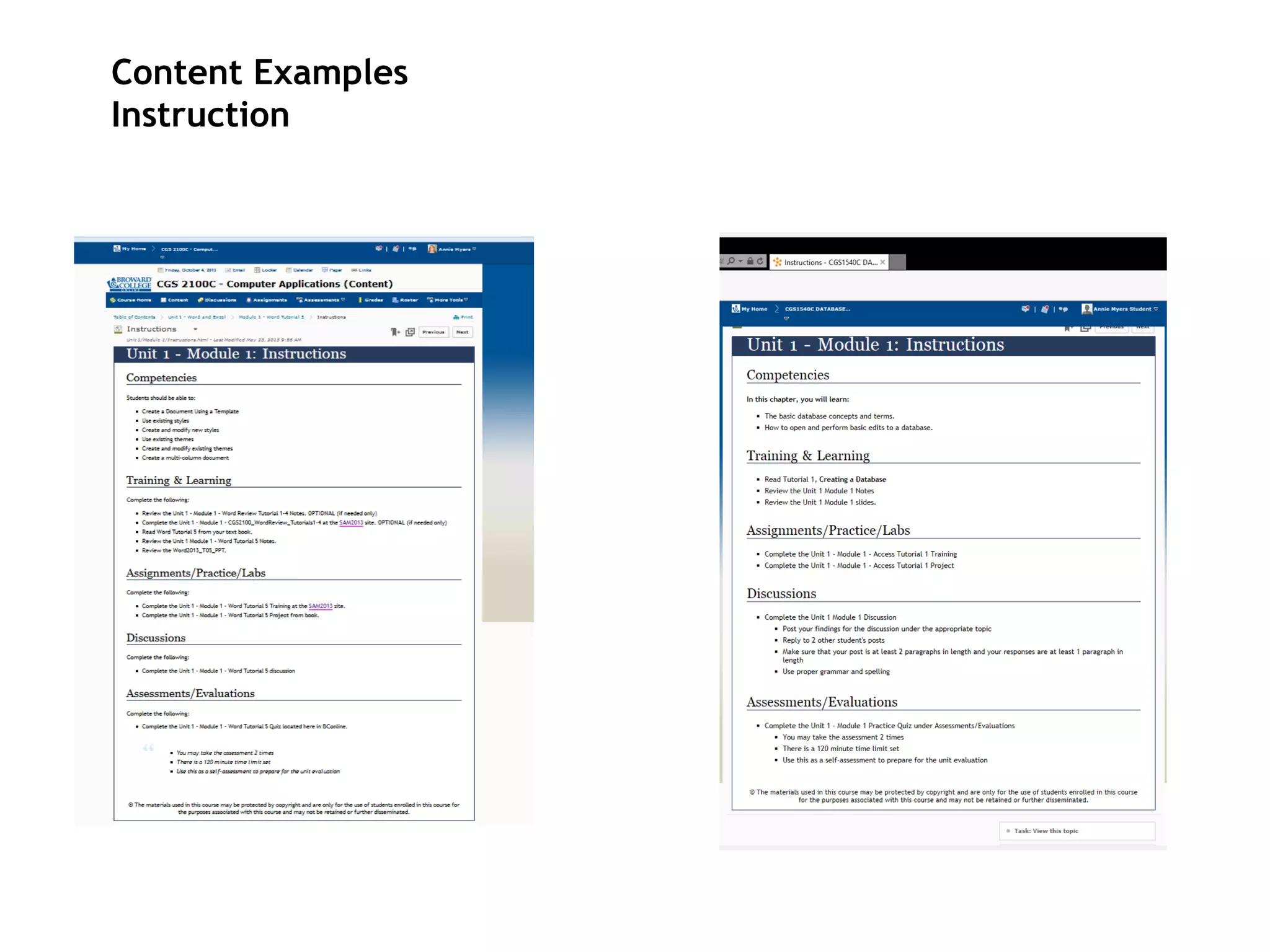
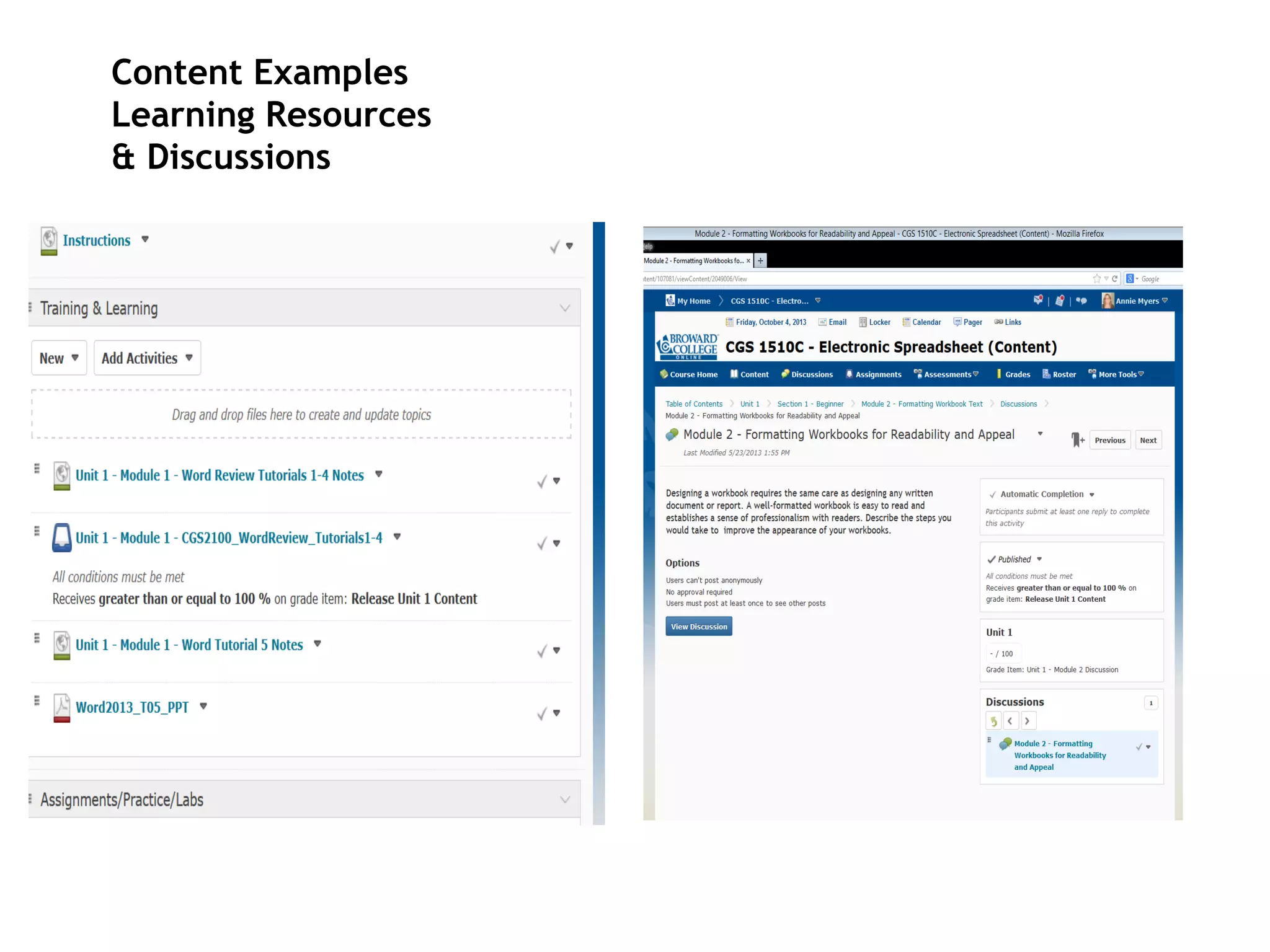
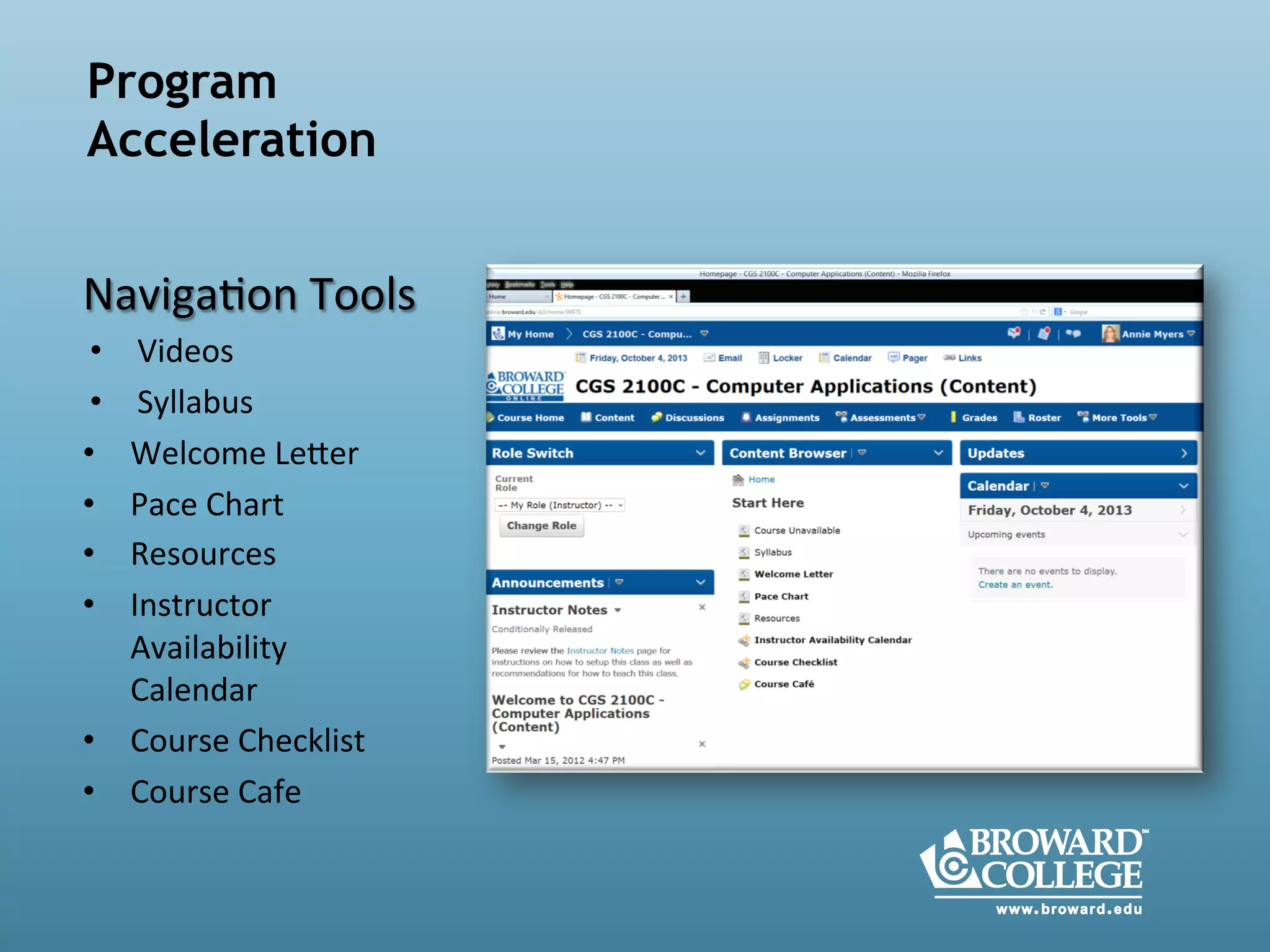
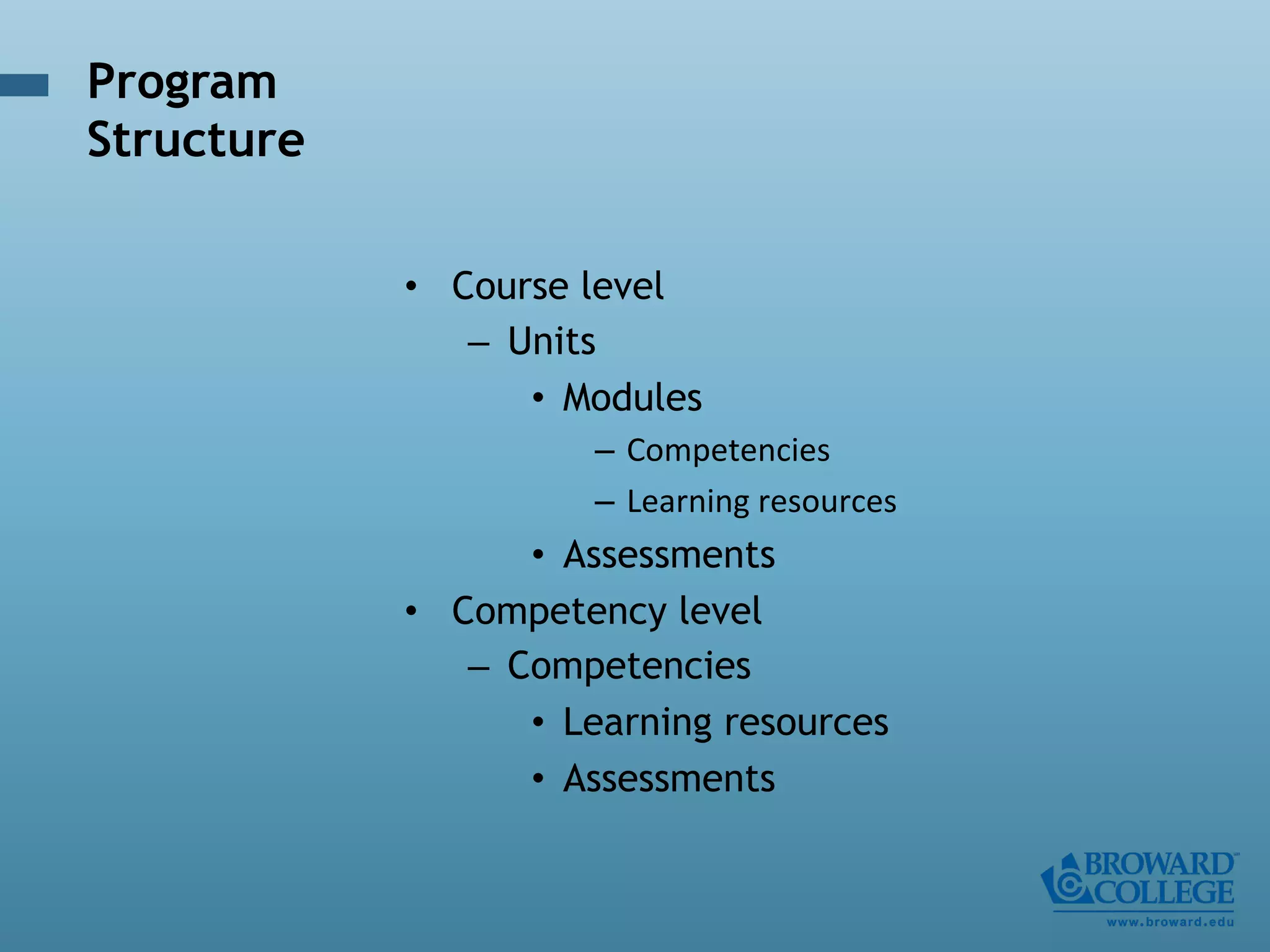
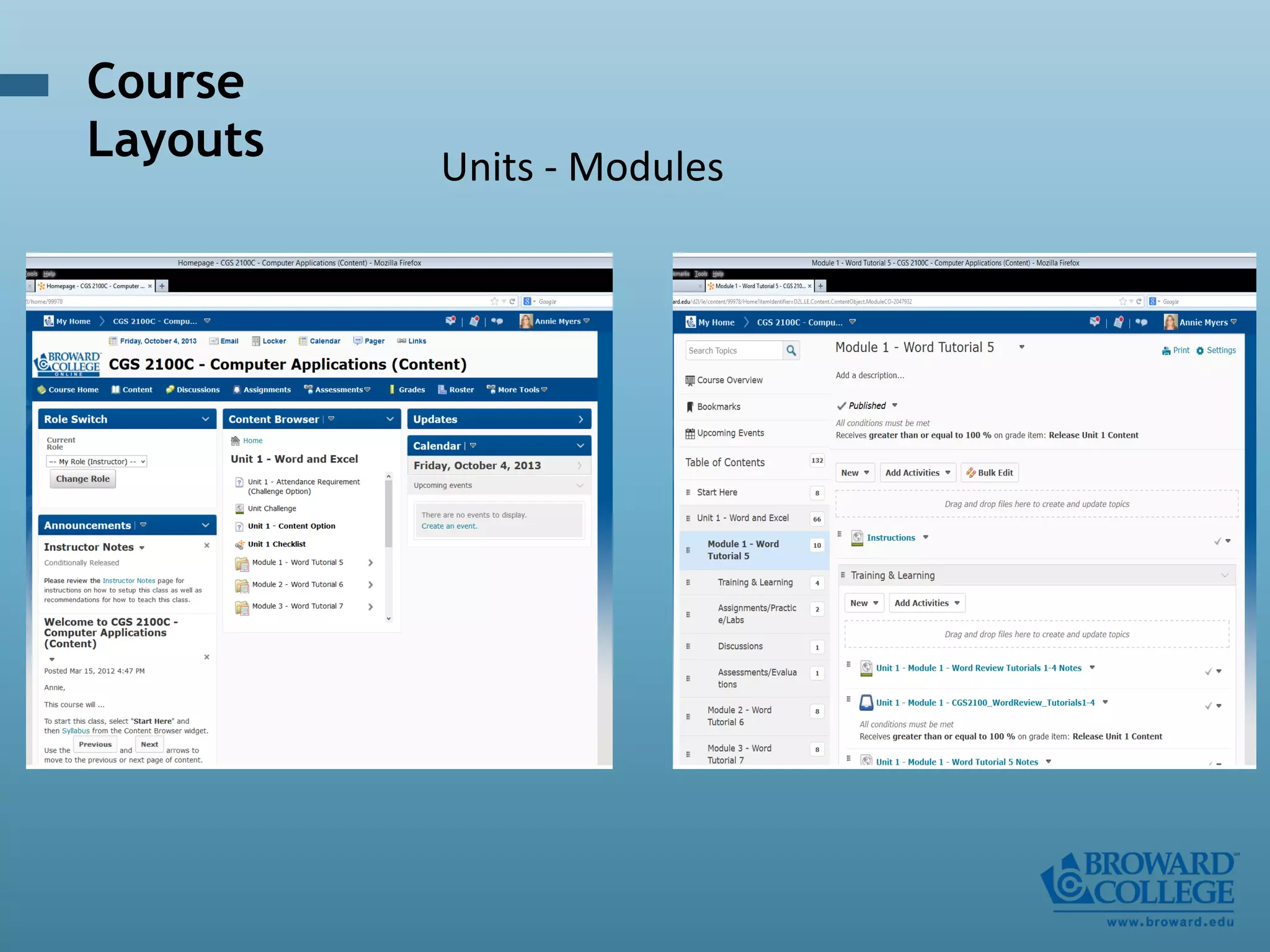
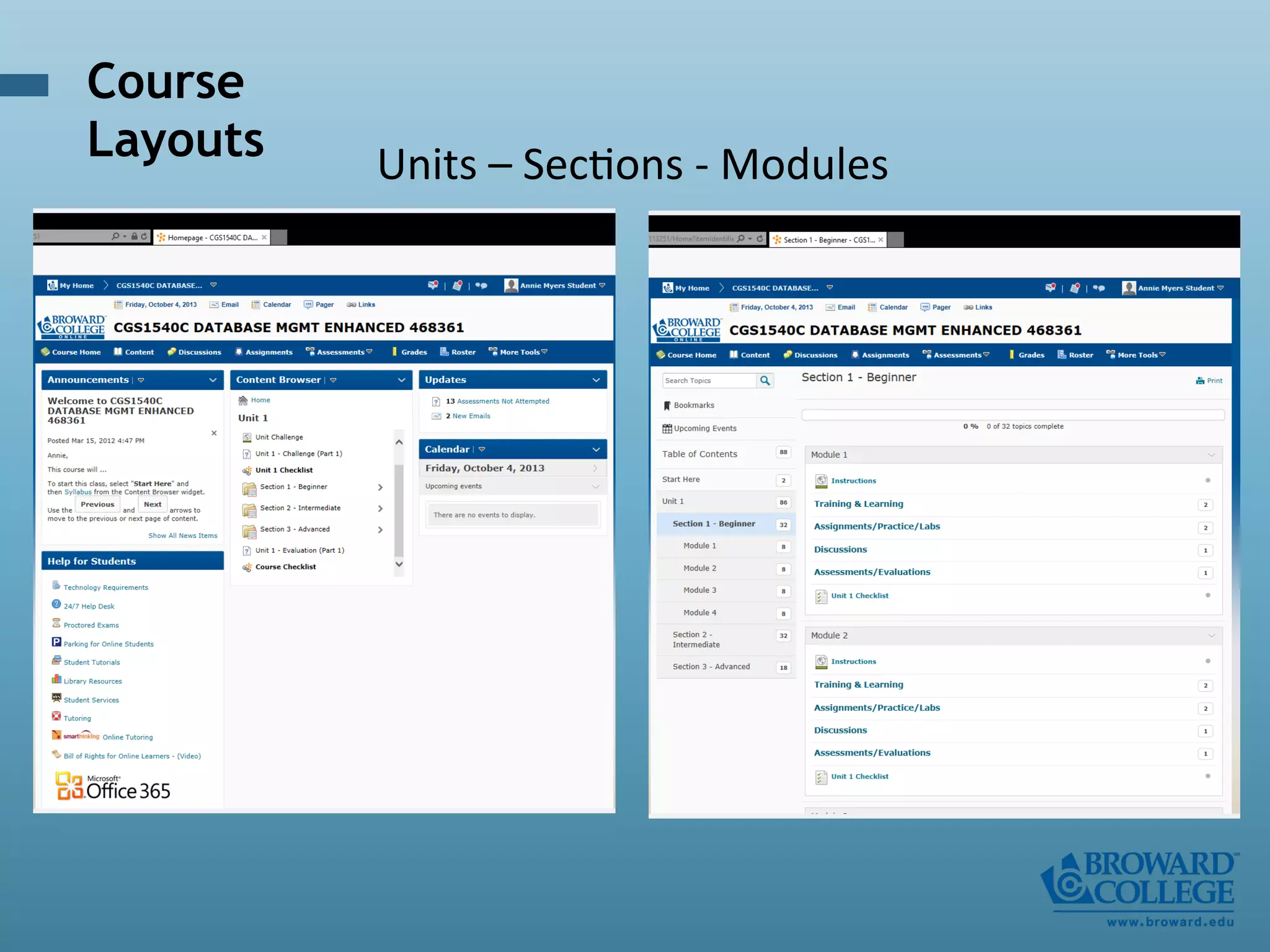
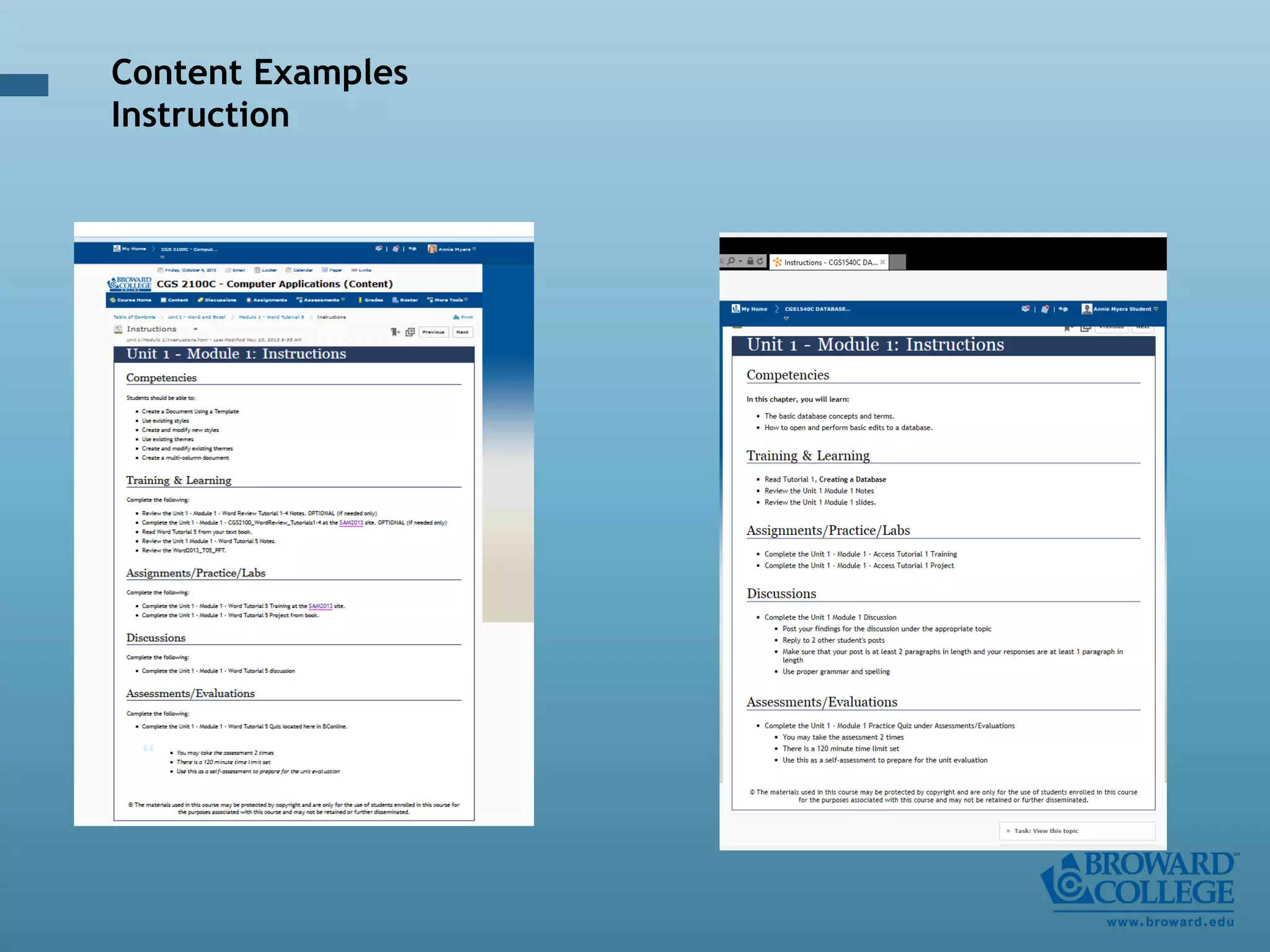
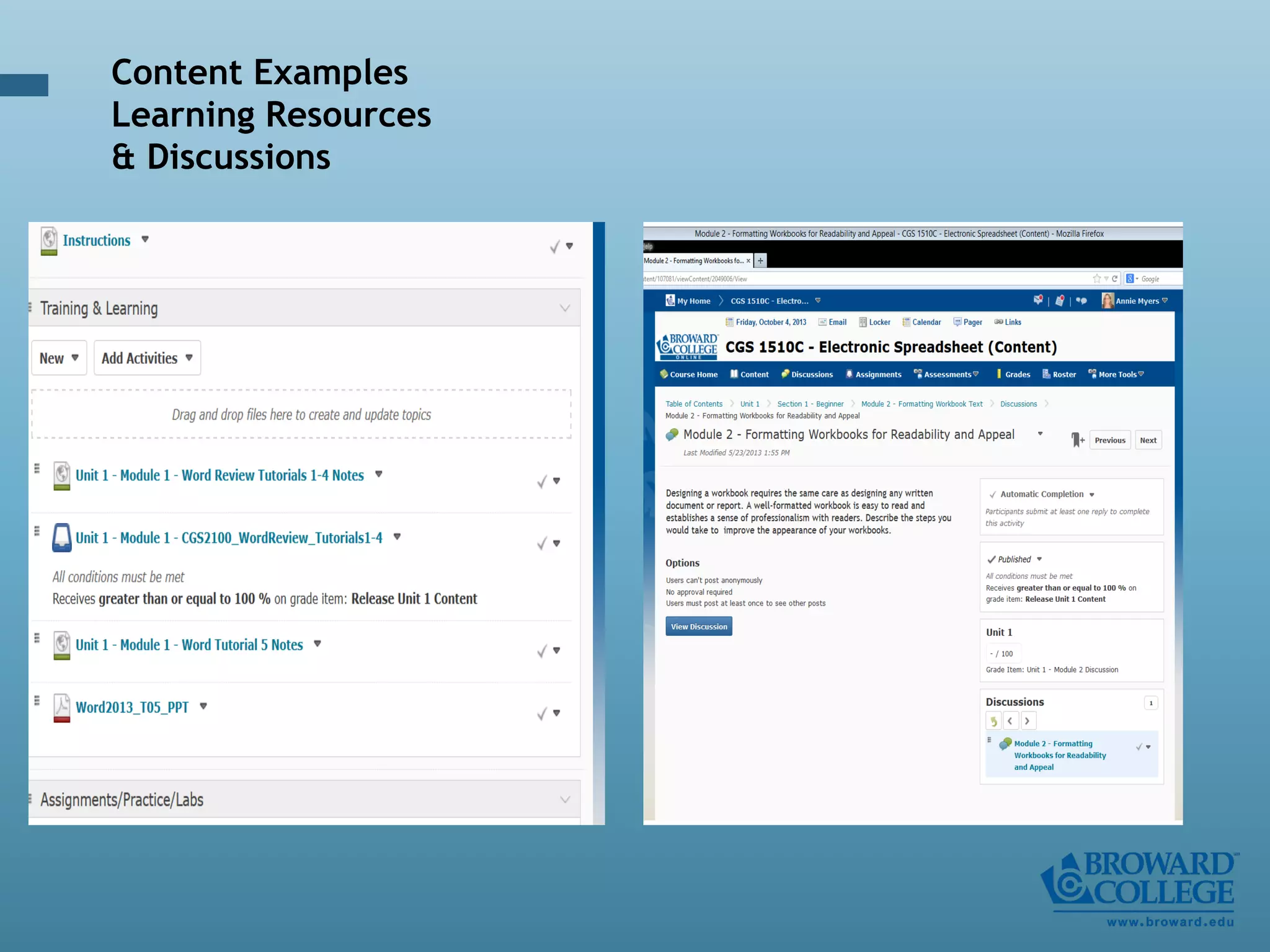
- An instructional designer support model provides consultation, production assistance, or full partnership to help faculty design competency-based courses. Guidelines outline a 14 step process and templates provide examples of course alignment and module models.
- Ongoing evaluation ensures course quality