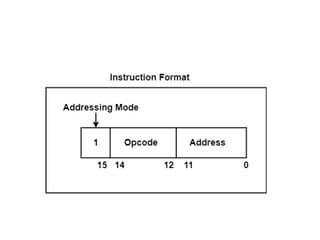
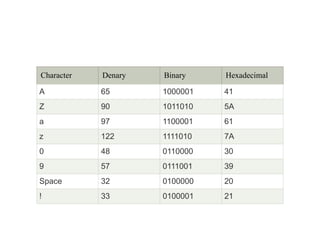
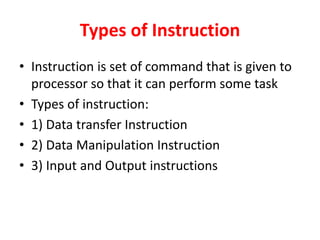
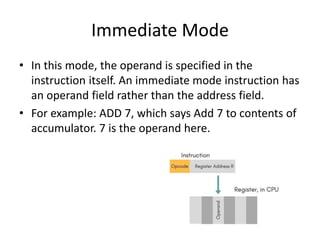
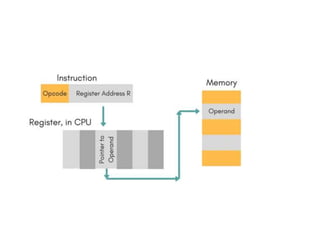
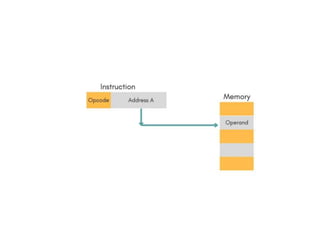
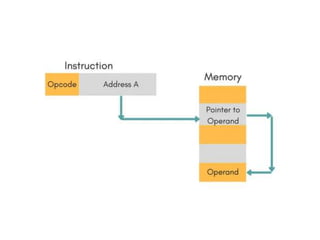
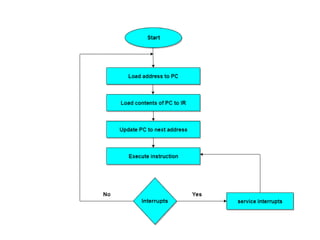
Instruction sets determine the operations a computer can perform. They include operation codes that specify actions and addresses or operands that indicate what data is used. There are different addressing modes like direct and indirect that specify how operands are accessed. Instructions also have formats like one, two, or three addresses depending on how many operands they include. The basic types of instructions perform data transfer, arithmetic/logic operations, and input/output. An instruction cycle fetches, decodes, and executes each instruction in a repeated process.