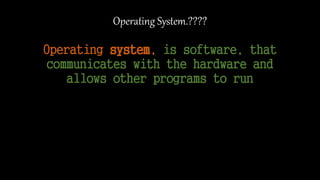
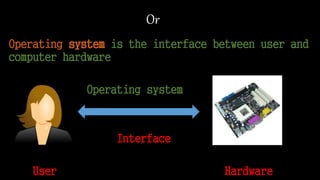
This document summarizes the evolution of operating systems over 5 phases:
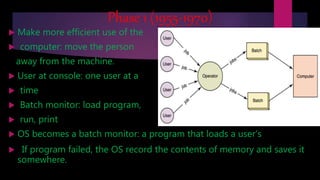
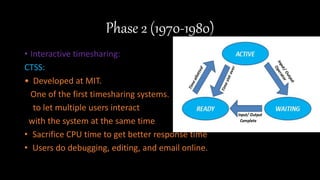
Phase 0 (1940-1955) had no operating systems and programs were manually loaded via card decks. Phase 1 (1955-1970) introduced batch processing with batch monitors. Phase 2 (1970-1980) enabled timesharing with systems like CTSS allowing multiple interactive users. Phase 3 (1980-1990) saw the rise of personal computers running single-user operating systems like MS-DOS. Phase 4 (1990-2000) focused on networking and client-server models. Phase 5 (2000-present) includes modern mobile and GUI-based operating systems on computers and phones.