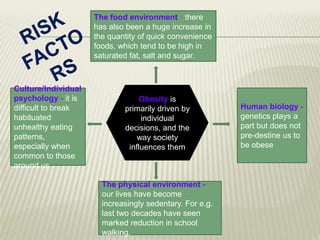
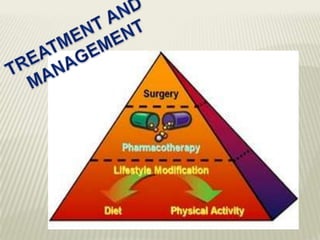
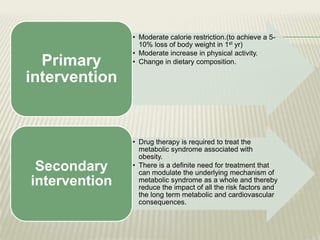
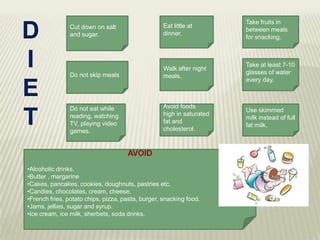
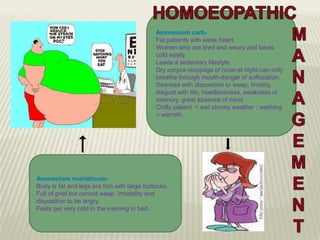
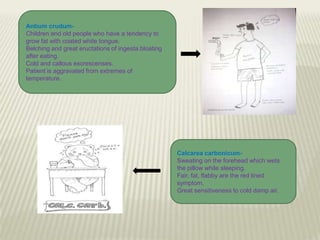
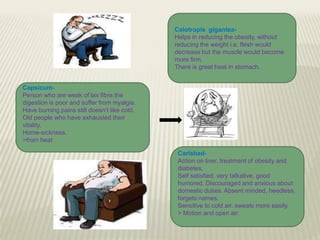
Obesity is defined as abnormal growth of adipose tissue due to enlargement of fat cells or an increase in their number. Central obesity is determined by waist circumference and other risk factors. BMI categories define underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity classes 1-3. Obesity is driven by individual decisions and societal influences like food environment and sedentary lifestyle. It increases risk for health conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cancer. Treatment involves moderate calorie restriction, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Medications may treat related metabolic issues. Various homeopathic remedies target obesity symptoms and management.