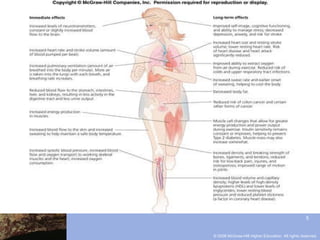
Physical fitness has five main components: cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition. Regular exercise provides numerous health benefits like reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, some cancers, diabetes and osteoporosis. It also improves psychological well-being by reducing stress and depression. When designing an exercise program, one should include cardiorespiratory, strength, and flexibility training multiple times per week following principles like specificity and progressive overload. Proper warmups, cool downs, injury prevention and a healthy diet are also important.