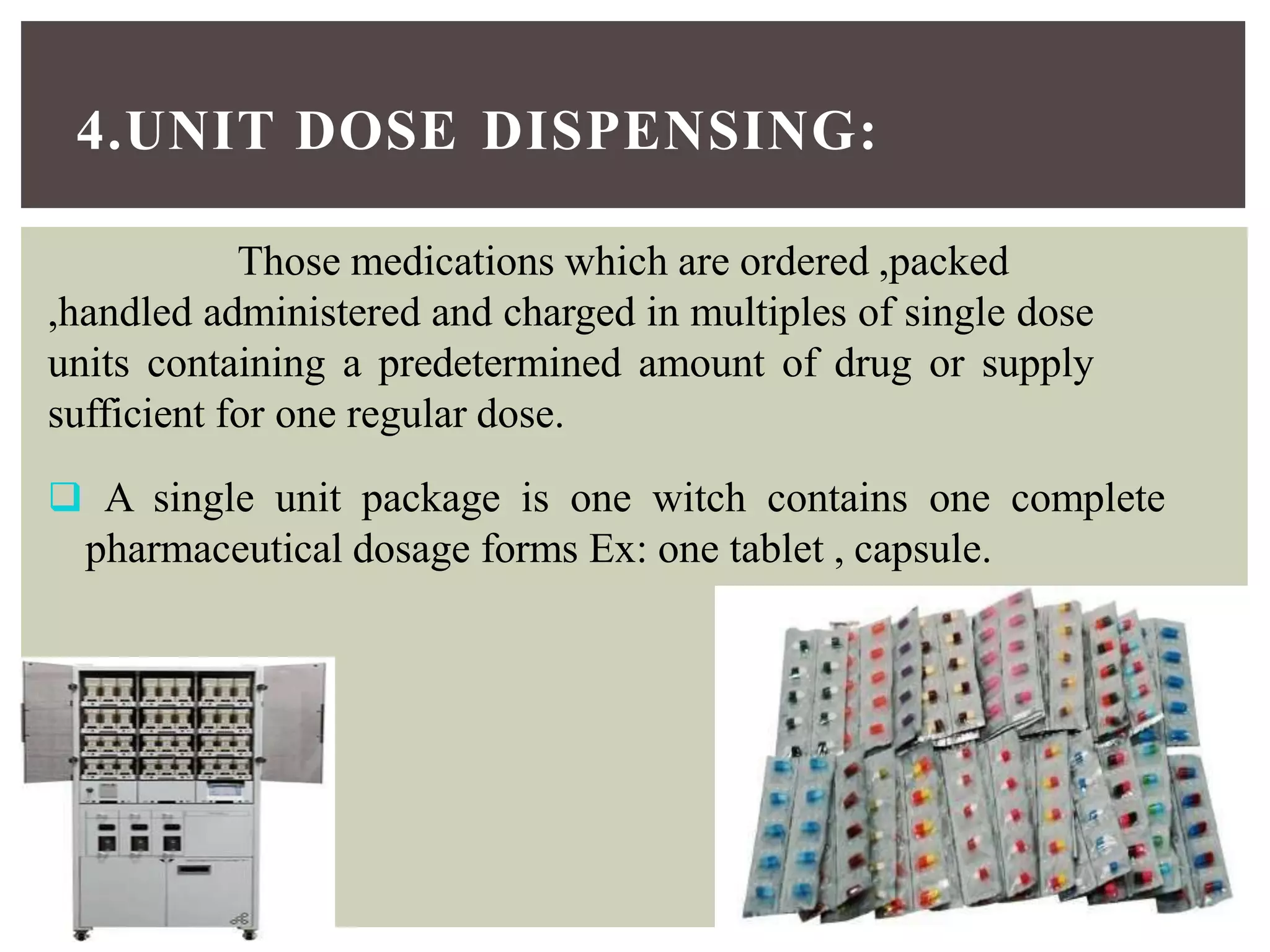
The document outlines the definitions and distinctions between outpatients and inpatients, detailing the processes for medication dispensing in both settings. It describes different dispensing systems for inpatients, including individual prescriptions, floor stock, and unit dose methods, as well as the structure for outpatient services. The document emphasizes the importance of medication management and collaboration among healthcare professionals in both inpatient and outpatient care.