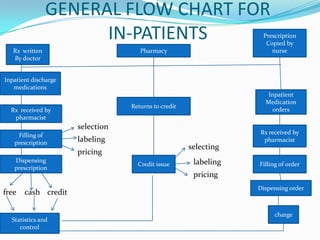
The document provides an outline of key information about hospital pharmacy including:
1) It defines hospital pharmacy as the department that procures, stores, dispenses, and distributes drugs in a hospital under the supervision of a qualified pharmacist.
2) It lists the main functions of hospital pharmacy such as purchasing drugs, proper storage, manufacturing medications, dispensing prescriptions, and providing drug information.
3) The objectives of hospital pharmacy are to ensure the availability of correct medications at low cost, professionalize pharmaceutical services, provide counseling, and participate in research and teaching.