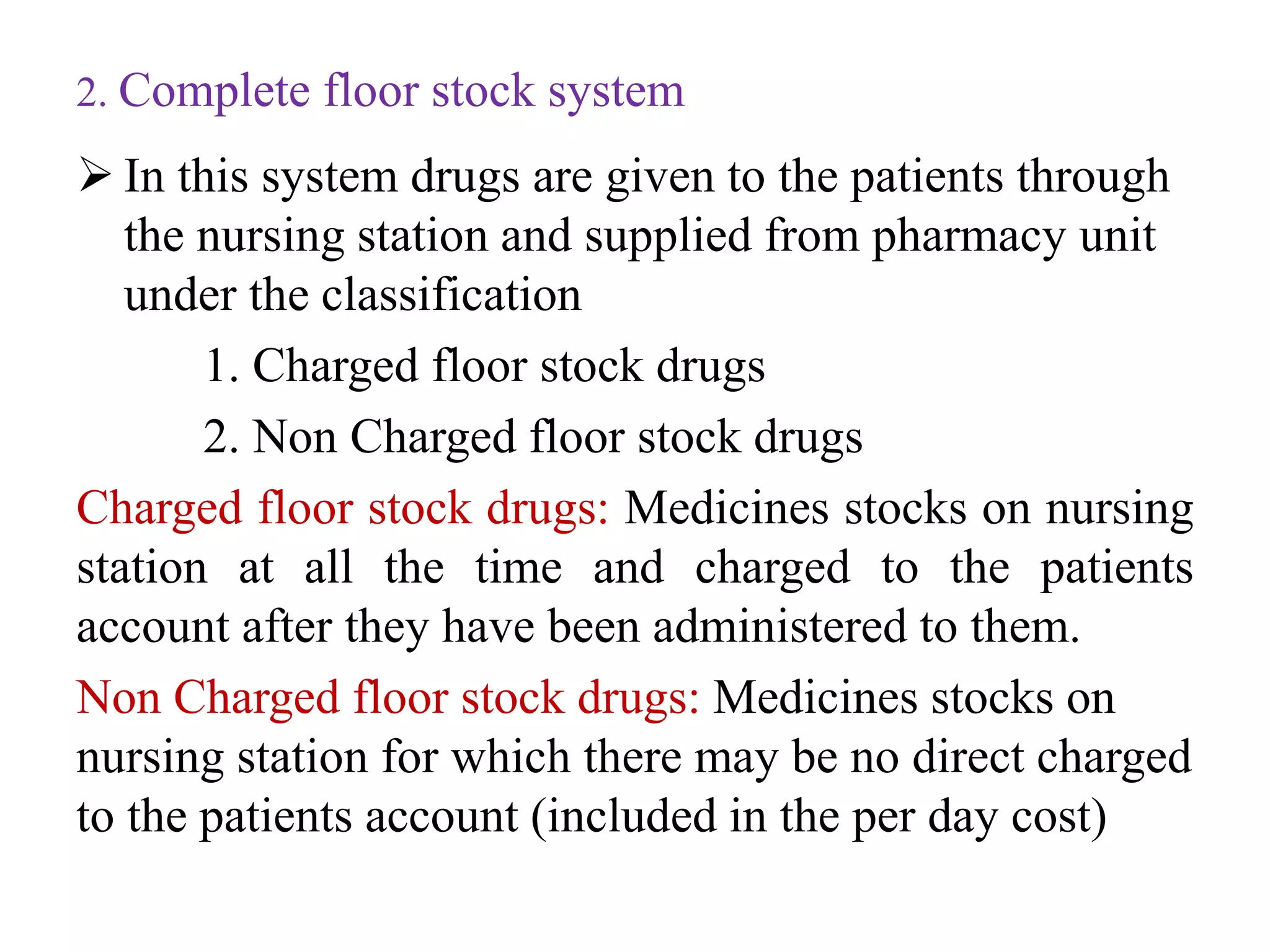
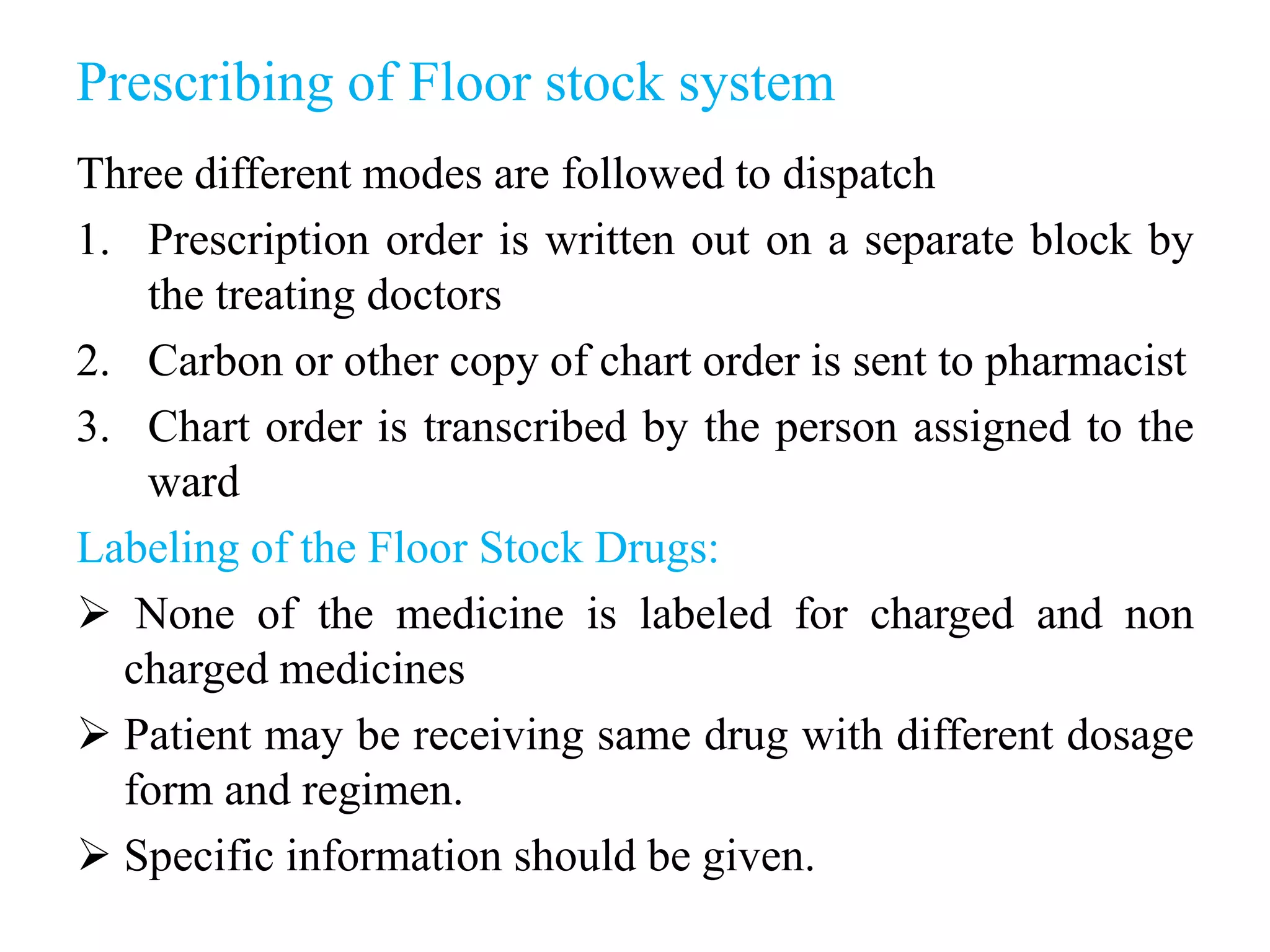
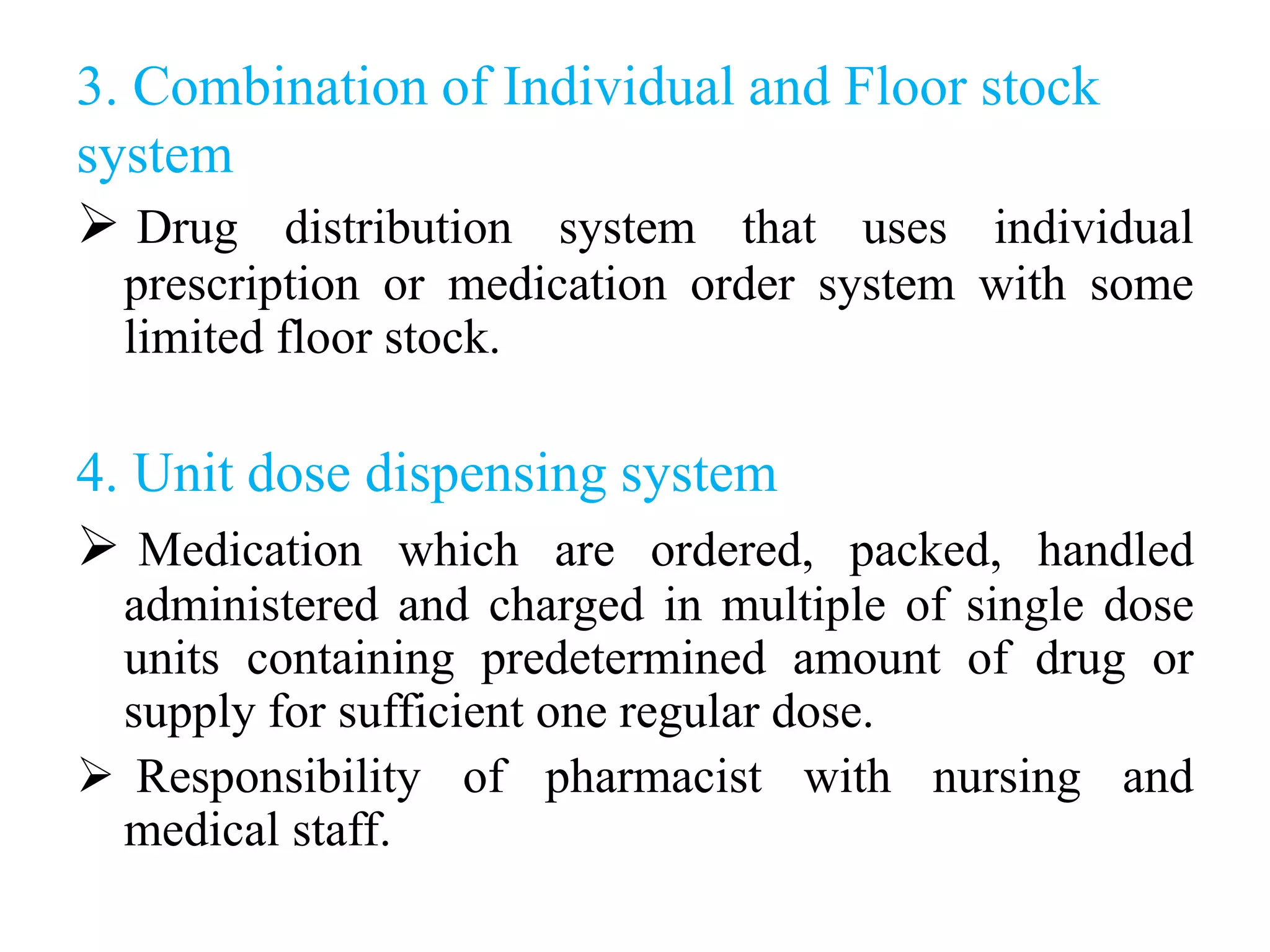
This document discusses different drug distribution systems used in hospitals, including individual prescription ordering, complete floor stock, a combination of the two, and unit dose systems. It describes the advantages and disadvantages of each. Complete floor stock involves charging drugs to patients and having non-charged drugs available on nursing floors. Unit dose packaging provides single doses of medications and allows accurate tracking of administered drugs. The document also covers dispensing drugs to outpatients and policies for controlling narcotics and other regulated substances in hospitals.