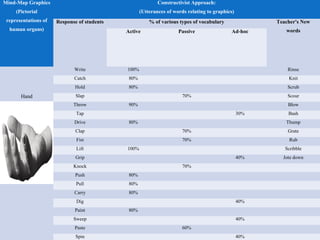
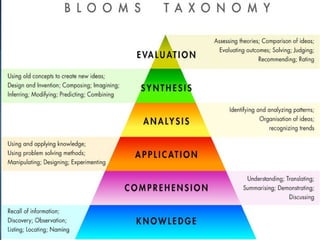
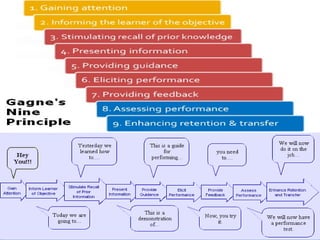
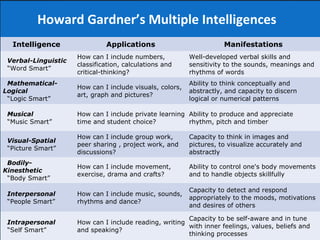
The document presents innovative teaching methodologies emphasizing the importance of leadership, analytical and problem-solving skills in students. It discusses the constructivist approach, where teachers facilitate active learning through methods like role play and mind mapping, and highlights Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences to cater to diverse learning styles. Additionally, it outlines essential teaching techniques to engage students, assess learning, and provide constructive feedback.