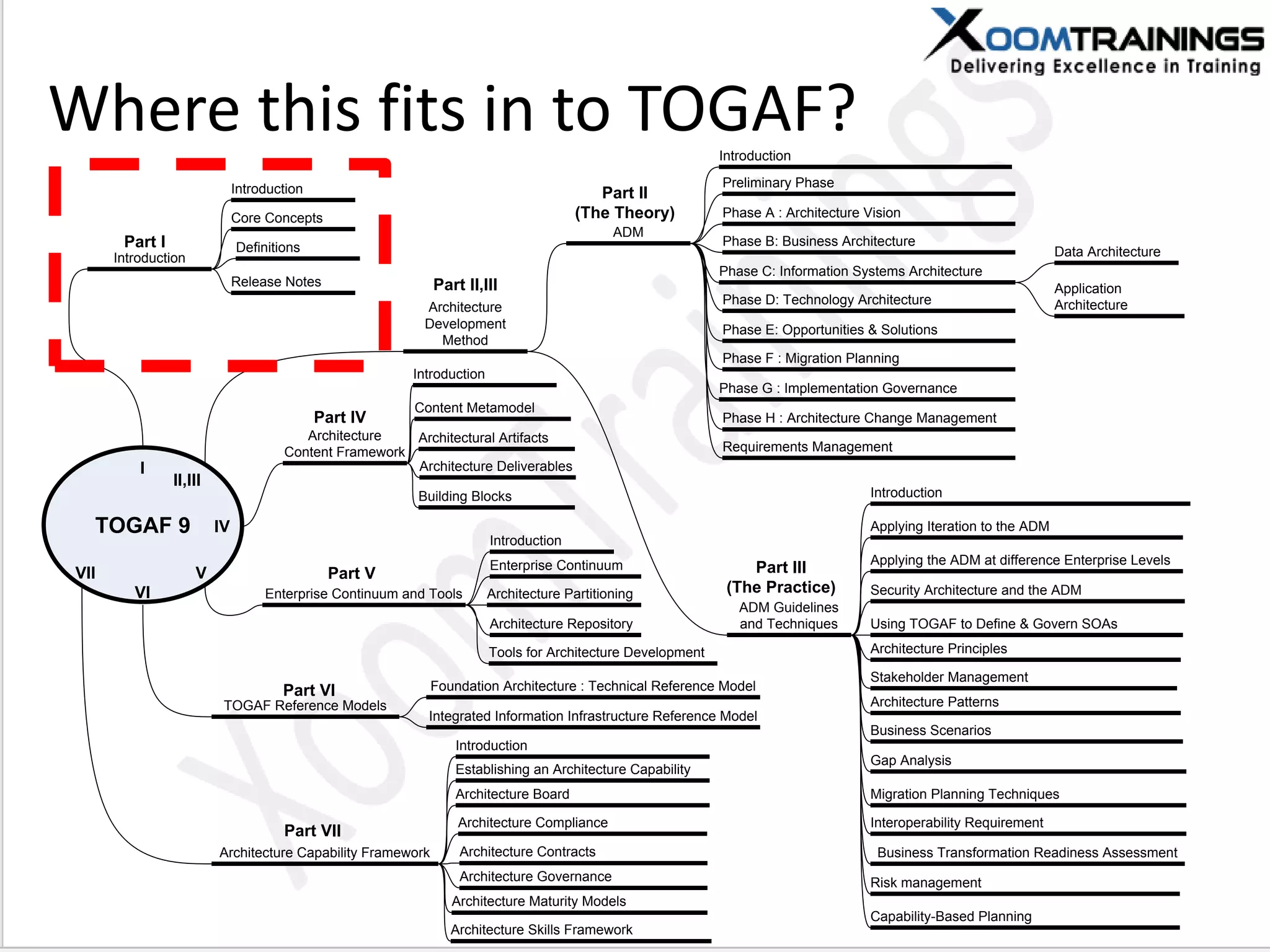
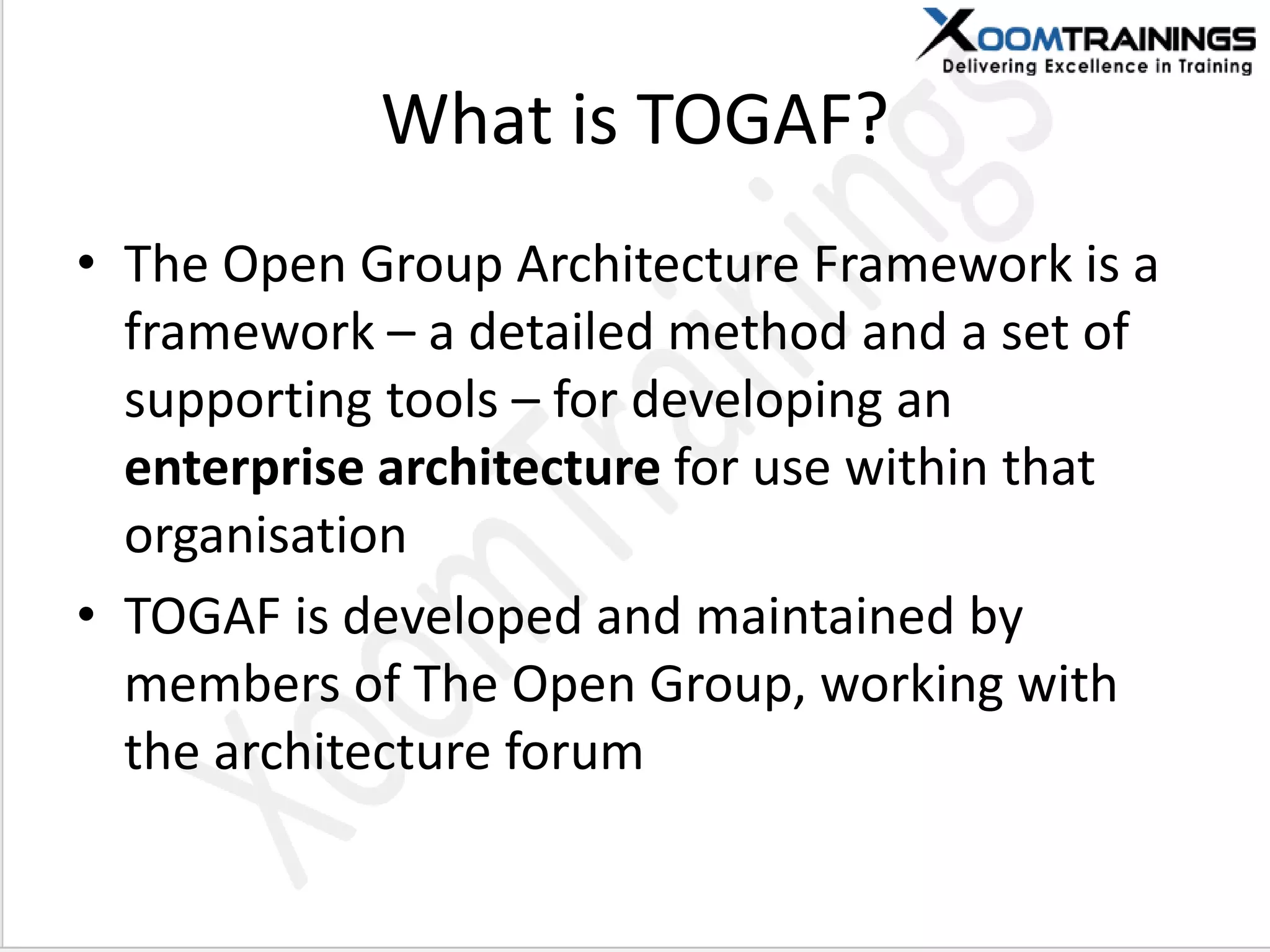
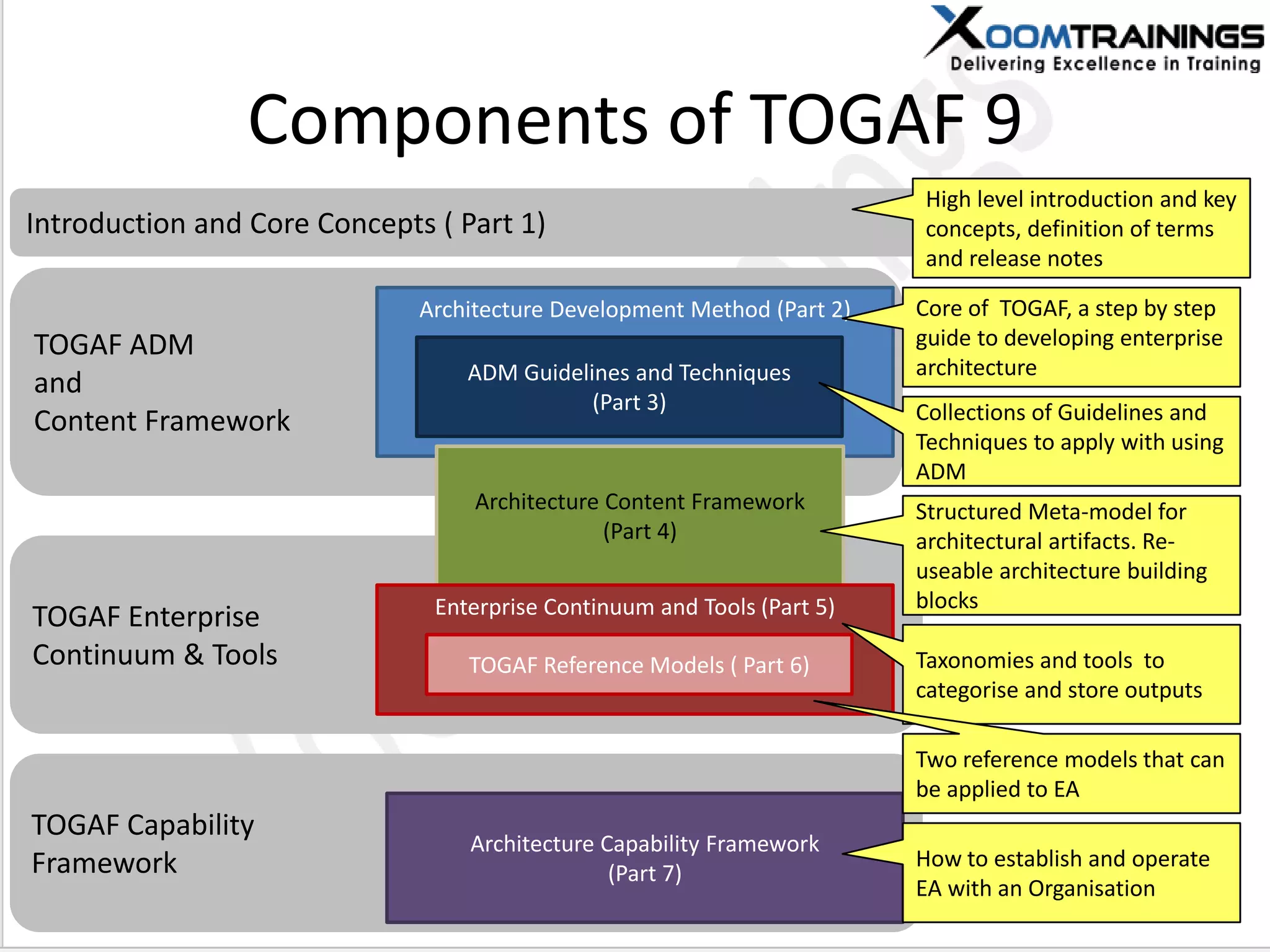
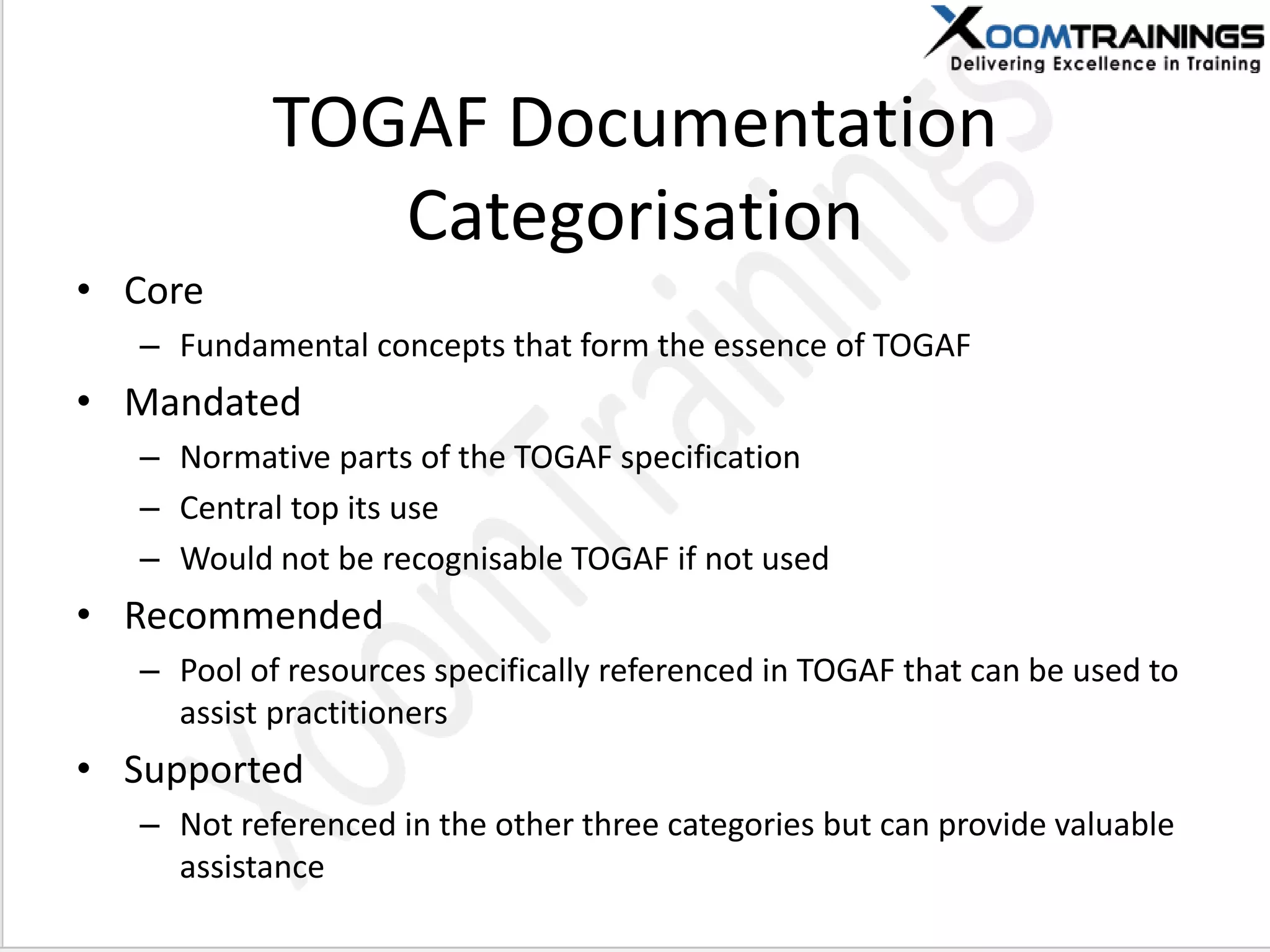
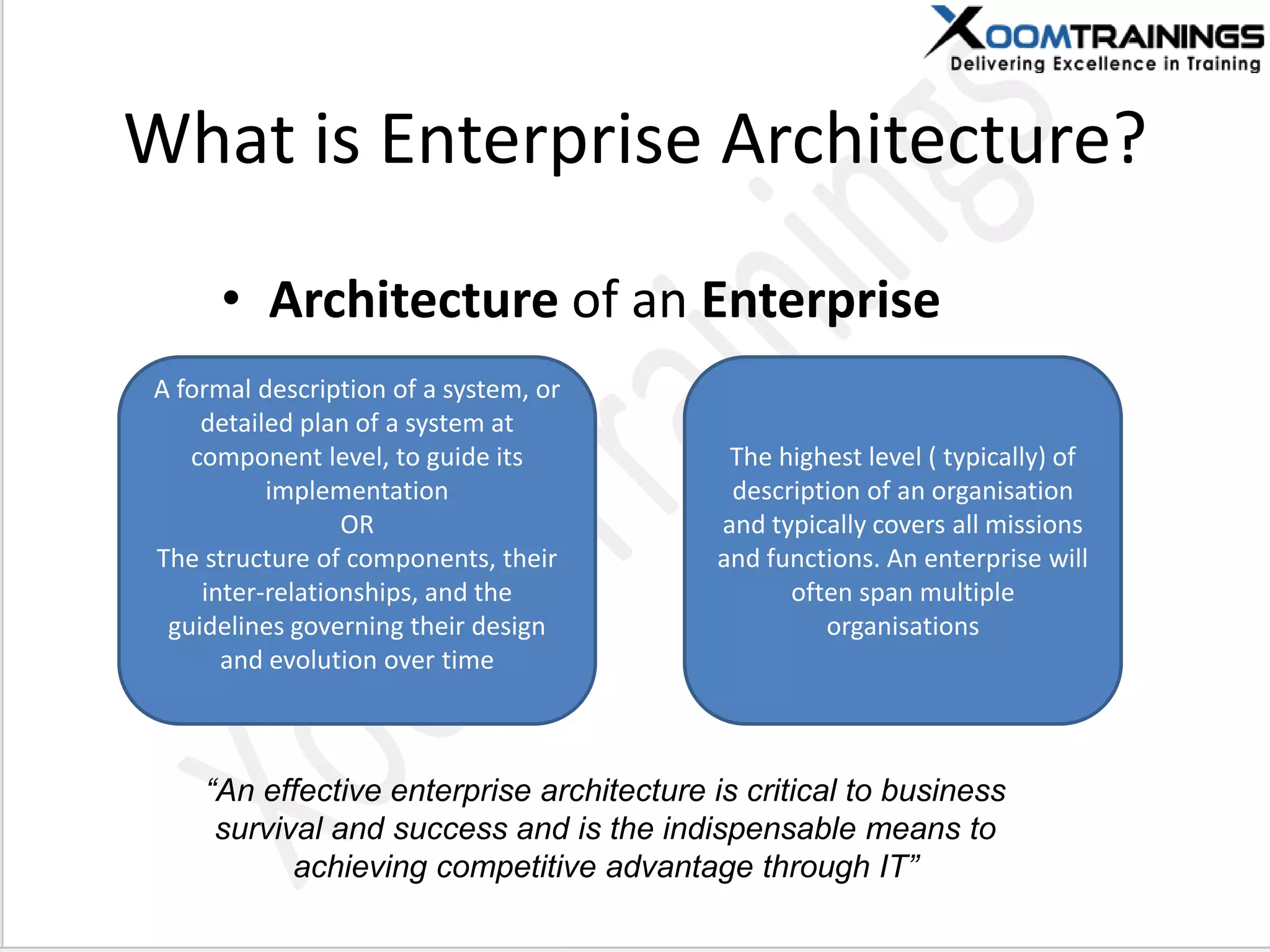
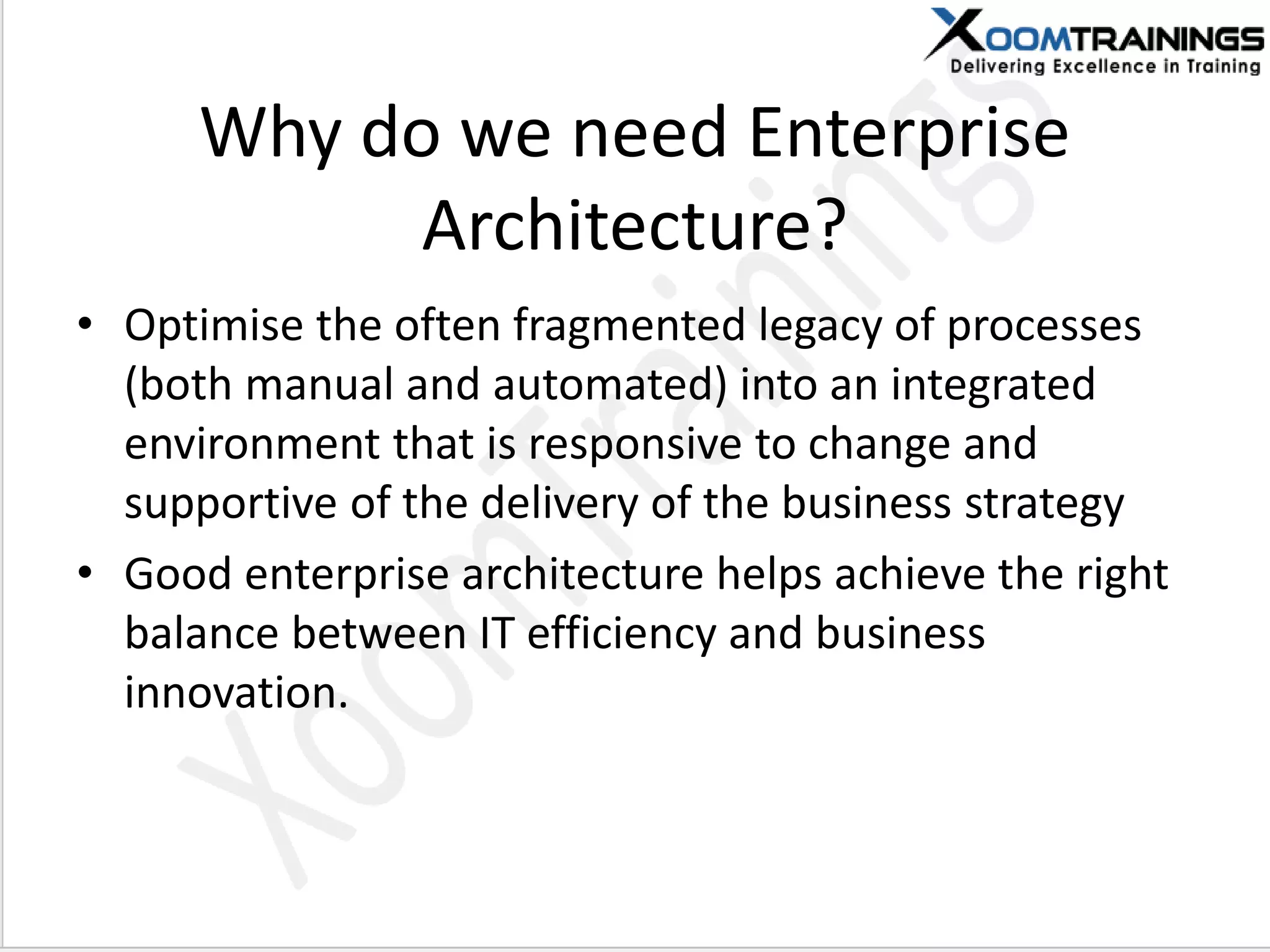
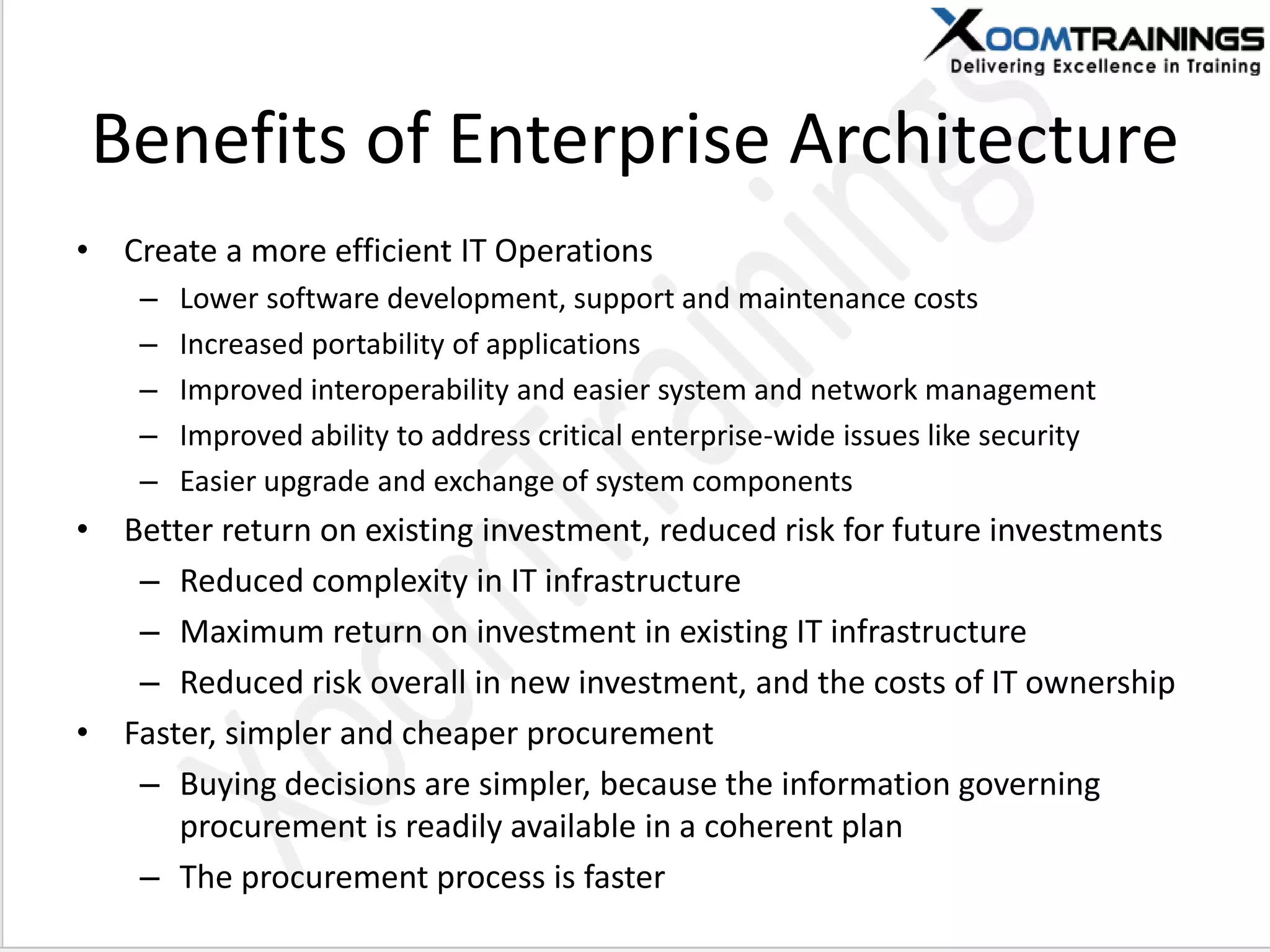
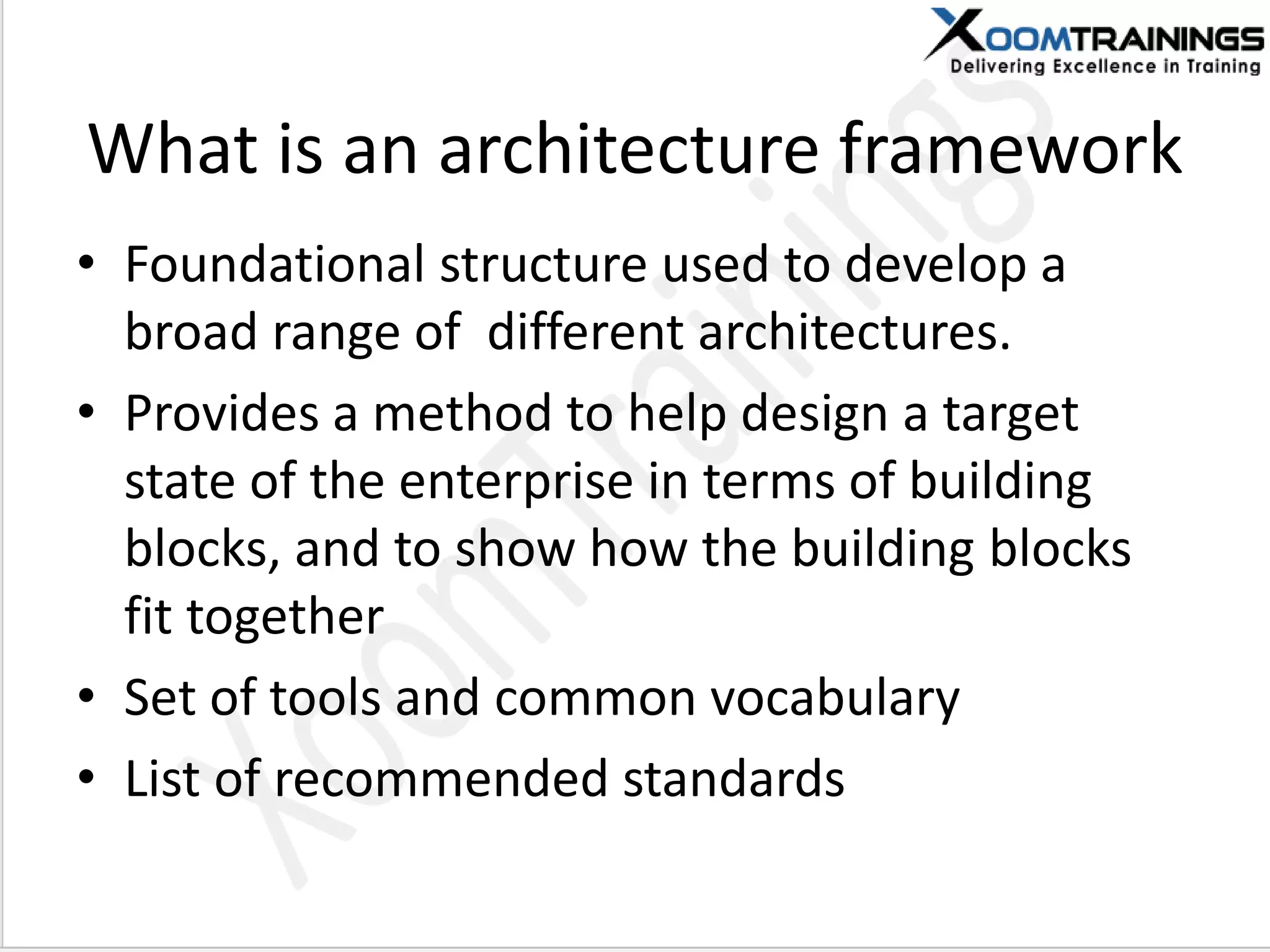
TOGAF 9.1 is a framework for developing enterprise architecture, detailing a method, tools, and guidelines for various architecture phases including architecture vision, information systems, business, and technology architectures. The framework emphasizes interoperability, strategic planning, and the importance of aligning IT with business objectives to optimize enterprise operations. The document outlines the history, core concepts, and benefits of using TOGAF for enterprise architecture development.