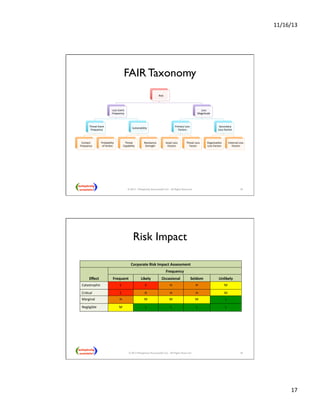
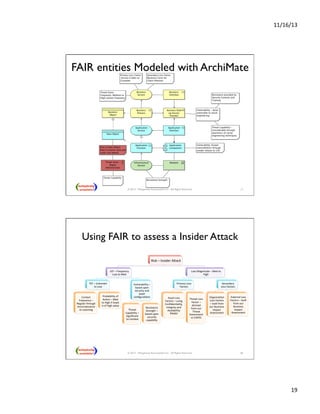
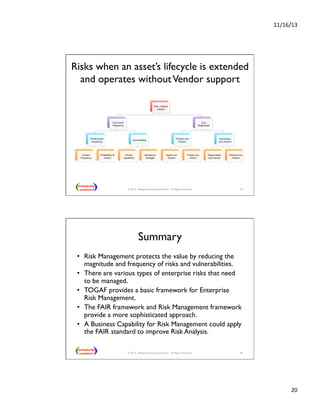
This presentation discusses how enterprise architects can utilize risk management for developing and operating enterprise architecture, focusing on frameworks like TOGAF 9 and the FAIR taxonomy. It covers types of enterprise risks, risk management processes, and the importance of integrating risk management into governance and architecture phases. Additionally, it explores applying risk analysis methods and assessing risks at various stages of architecture development.