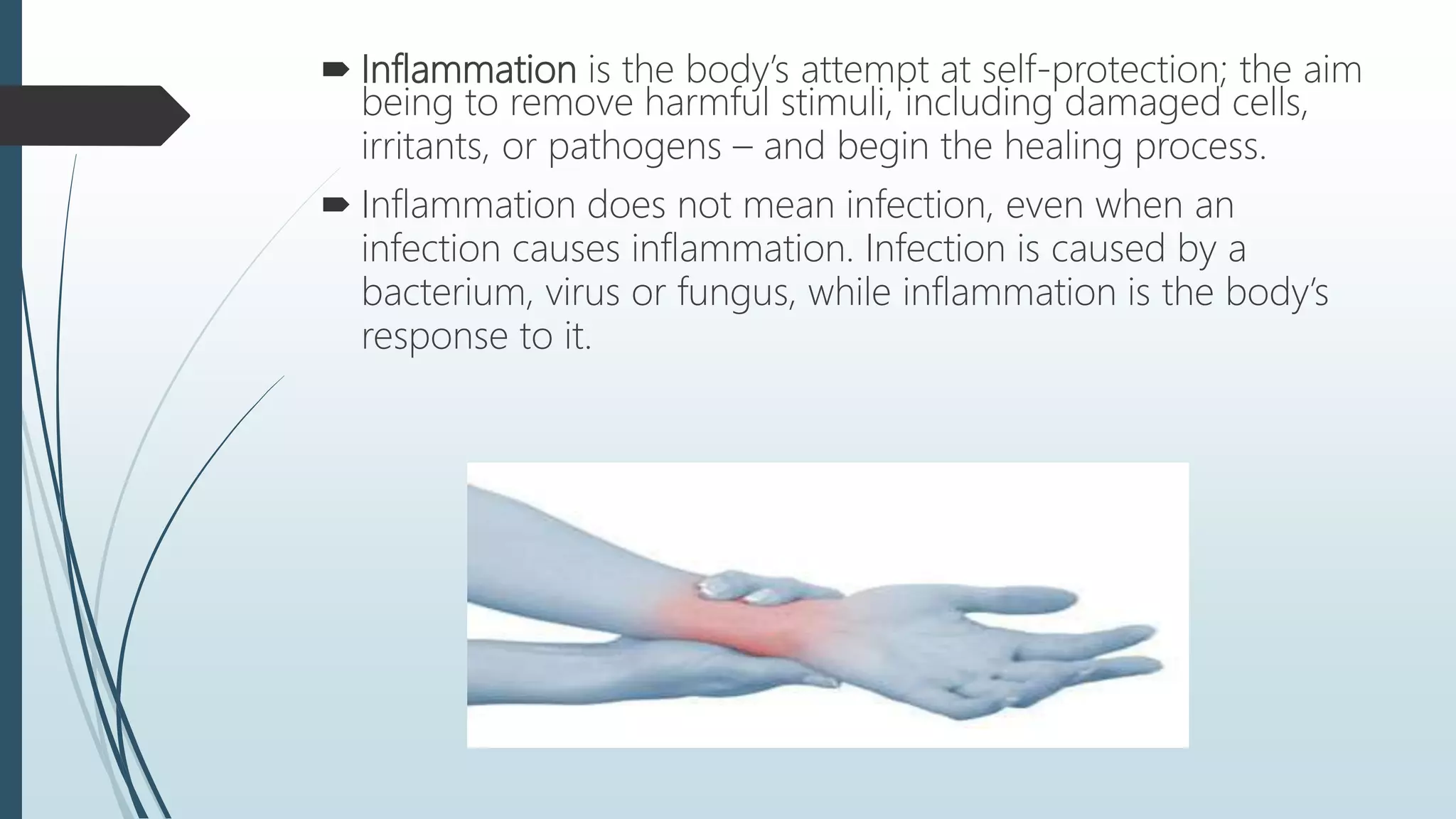
This document discusses inflammation and its role in the body's healing process. It describes acute and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is the initial rapid response to harmful stimuli and involves increased blood flow, capillary permeability, and migration of neutrophils and macrophages to the injured site. The five cardinal signs of acute inflammation are pain, redness, immobility, swelling, and heat. Chronic inflammation is a prolonged inflammatory response that can last months or years and result from failure to eliminate the initial trigger, an autoimmune response, or persistent irritation. Chronic inflammation can lead to diseases like arthritis and atherosclerosis if not well regulated.