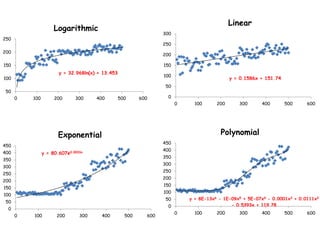
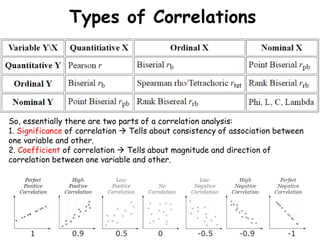
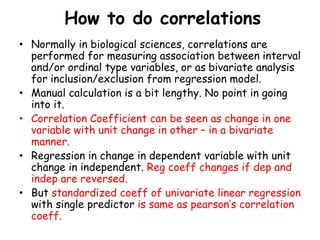
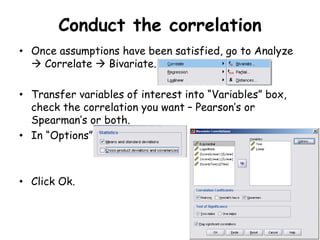
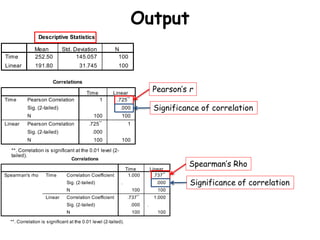
This document discusses correlations and how to perform them using SPSS. It defines correlation as finding a relationship between two variables, without implying causation. There are two parts to a correlation analysis: 1) assessing the significance of the correlation, which indicates how consistent the association is between variables, and 2) the coefficient of correlation, which indicates the magnitude and direction of the correlation. The document outlines the assumptions that must be met to perform correlations in SPSS, such as having quantitative variables, no outliers, and normally distributed data. It then provides step-by-step instructions for conducting correlations in SPSS and interpreting the output.