This document discusses correlation and provides examples to illustrate key concepts:
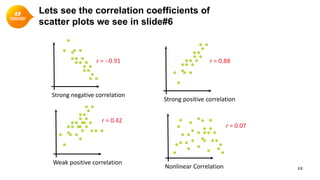
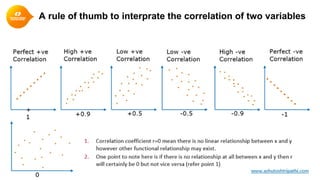
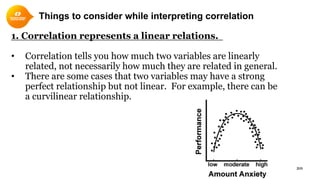
1. Correlation quantifies the linear relationship between two variables and ranges from -1 to 1. Values closer to 1 or -1 indicate a stronger linear relationship.
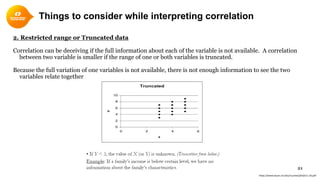
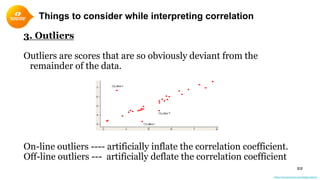
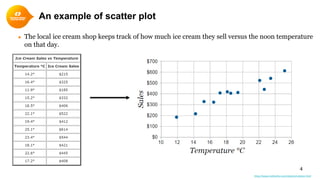
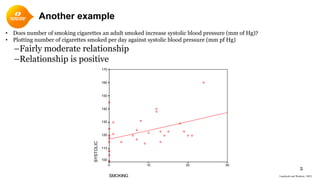
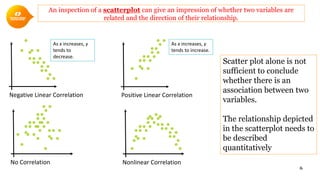
2. Scatterplots visually depict the relationship and can show if variables are positively or negatively correlated.
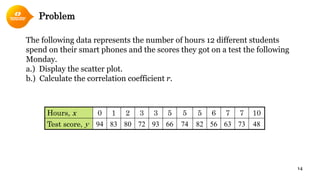
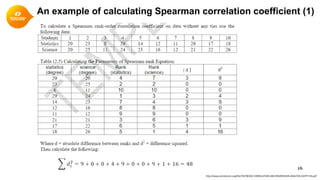
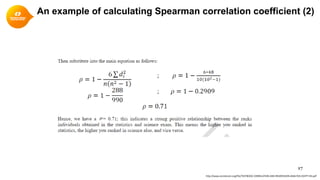
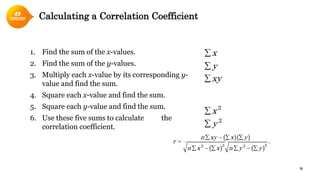
3. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) is a common measure of linear correlation calculated using variables' means, sums, and standard deviations.
4. Correlation only captures linear relationships and does not prove causation between variables. Additional analysis is needed to interpret correlated variables.





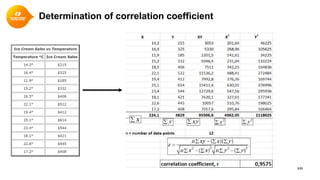
![Alternative Method
11
Step 1: Find the mean of x, and
the mean of y
Step 2: Subtract the mean of x
from every x value (call them "a"),
do the same for y (call them "b")
Step 3:
Calculate: ab, a2 and b2 for every
value
Step 4: Sum up ab, sum
up a2 and sum up b2
Step 5: Divide the sum of ab by
the square root of [(sum of a2) ×
(sum of b2)]
https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/correlation.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/correlation-201117212038/85/Correlation-analysis-11-320.jpg)