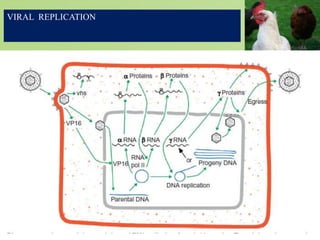
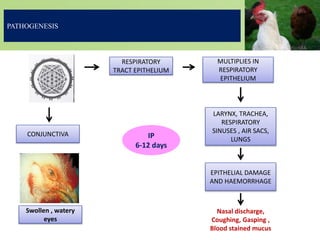
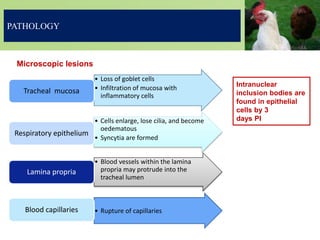
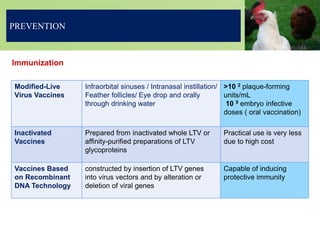
Infectious laryngotracheitis is a highly contagious respiratory disease of chickens and pheasants caused by gallid herpesvirus 1. The virus infects the upper respiratory tract, causing swelling and the production of bloody mucus. Clinical signs range from mild illness to high mortality depending on the strain. The virus establishes latency in trigeminal ganglia. Diagnosis involves detecting viral antigens or DNA in samples. Vaccines include live-attenuated and inactivated versions. Prevention relies on vaccination programs, biosecurity, and cleaning between flocks.