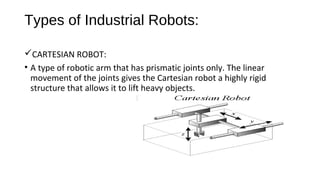
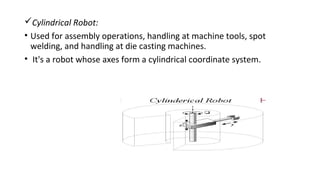
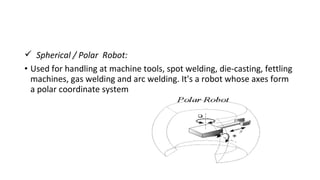
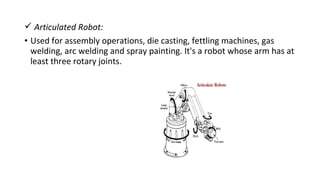
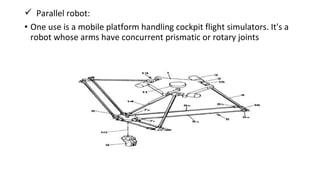
The document presents an overview of industrial robotics, defining what a robot is and detailing its components such as robot arms, sensors, end parts, controllers, and drives. It also categorizes various types of industrial robots, including Cartesian, cylindrical, spherical, SCARA, articulated, and parallel robots, highlighting their applications. Additionally, it includes a bibliography of resources for further information on the topic.