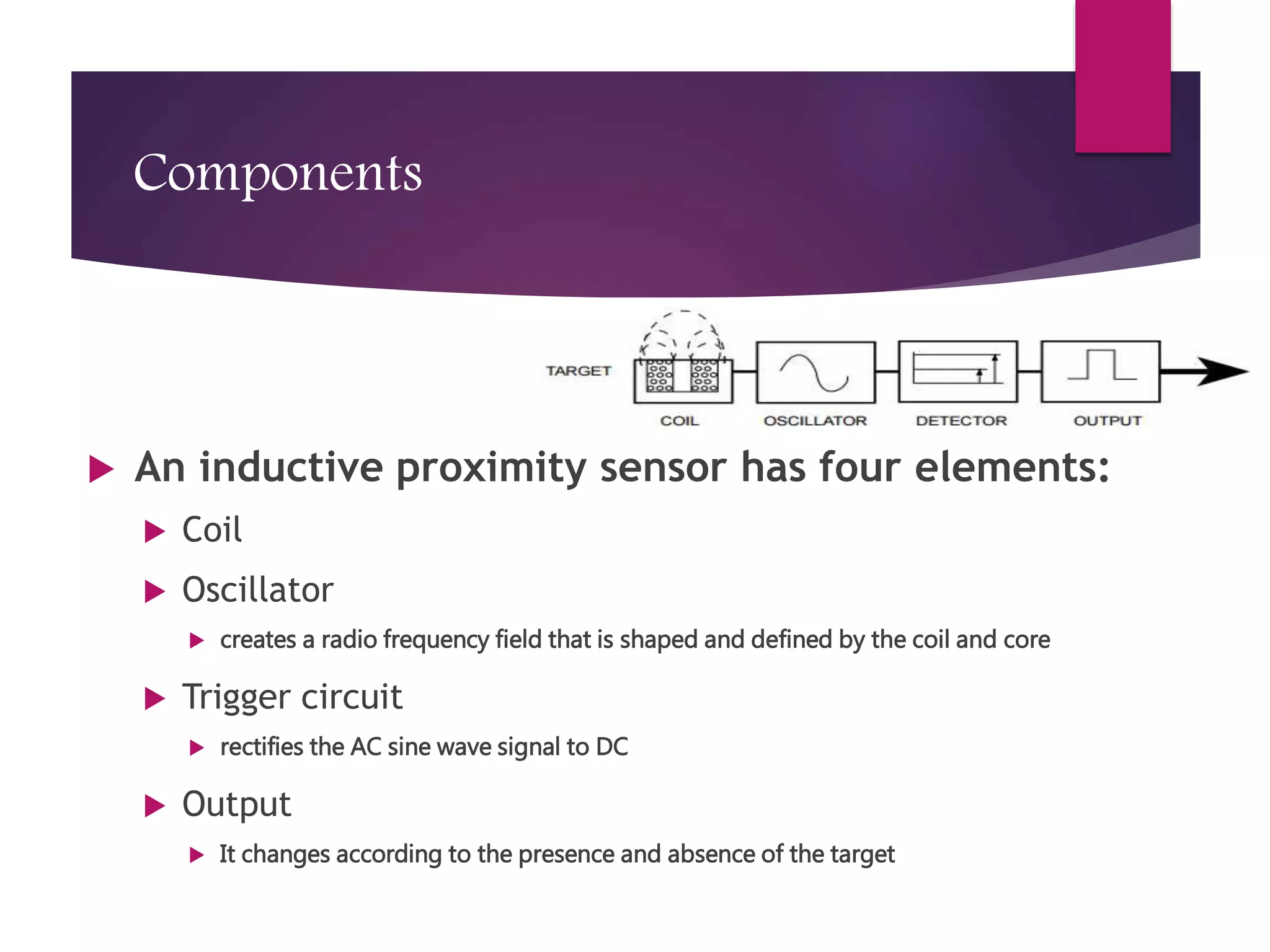
Inductive proximity sensors consist of a coil, oscillator, trigger circuit, and output, operating on the principle of inductance to detect metallic objects through changes in electric fields. They are used in various applications, including robotic hands and wind turbines, offering advantages like high accuracy and adaptability to harsh conditions. However, their limitations include the inability to detect non-metallic targets and a potentially limited operating range.