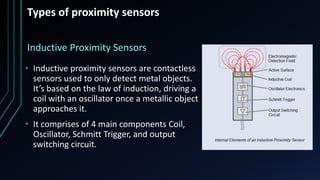
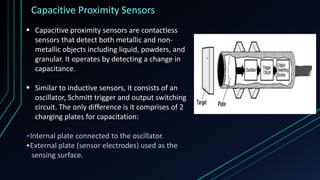
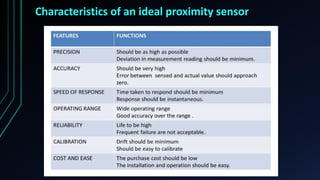
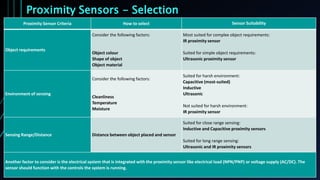
Proximity sensors are contactless sensors that detect the presence or movement of nearby objects without physically touching them. They work by sensing electromagnetic fields (inductive), capacitance changes (capacitive), ultrasonic waves (ultrasonic), or infrared light (IR). Proximity sensors have a long service life since they have no moving parts, can detect objects in various environments and conditions, and are used in a wide range of applications including smartphones, industrial automation, and more. The ideal proximity sensor quickly and accurately detects objects without being affected by surface properties or environmental factors.