This document provides information on programmed instruction and learning. It defines programmed instruction as a systematic, step-by-step, self-instructional program to ensure learning of stated behaviors. The key aspects discussed include:
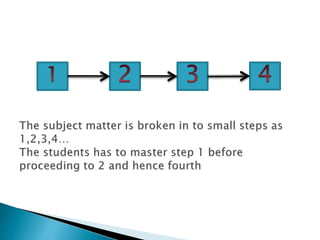
- Content is broken into small, easy steps called frames arranged sequentially. Learners get immediate feedback.
- Principles include small steps, active responding, reinforcement, self-pacing, and evaluation.
- Types include linear, branched, mathetics rules-based, and computer-assisted programming.
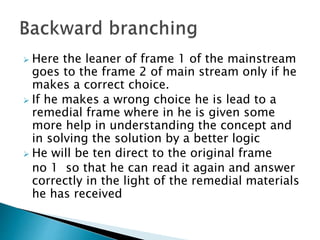
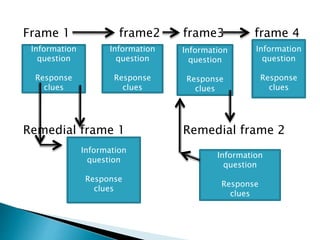
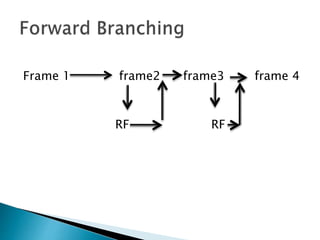
- Branched programming allows learners to choose paths based on responses and includes remedial frames for incorrect answers.