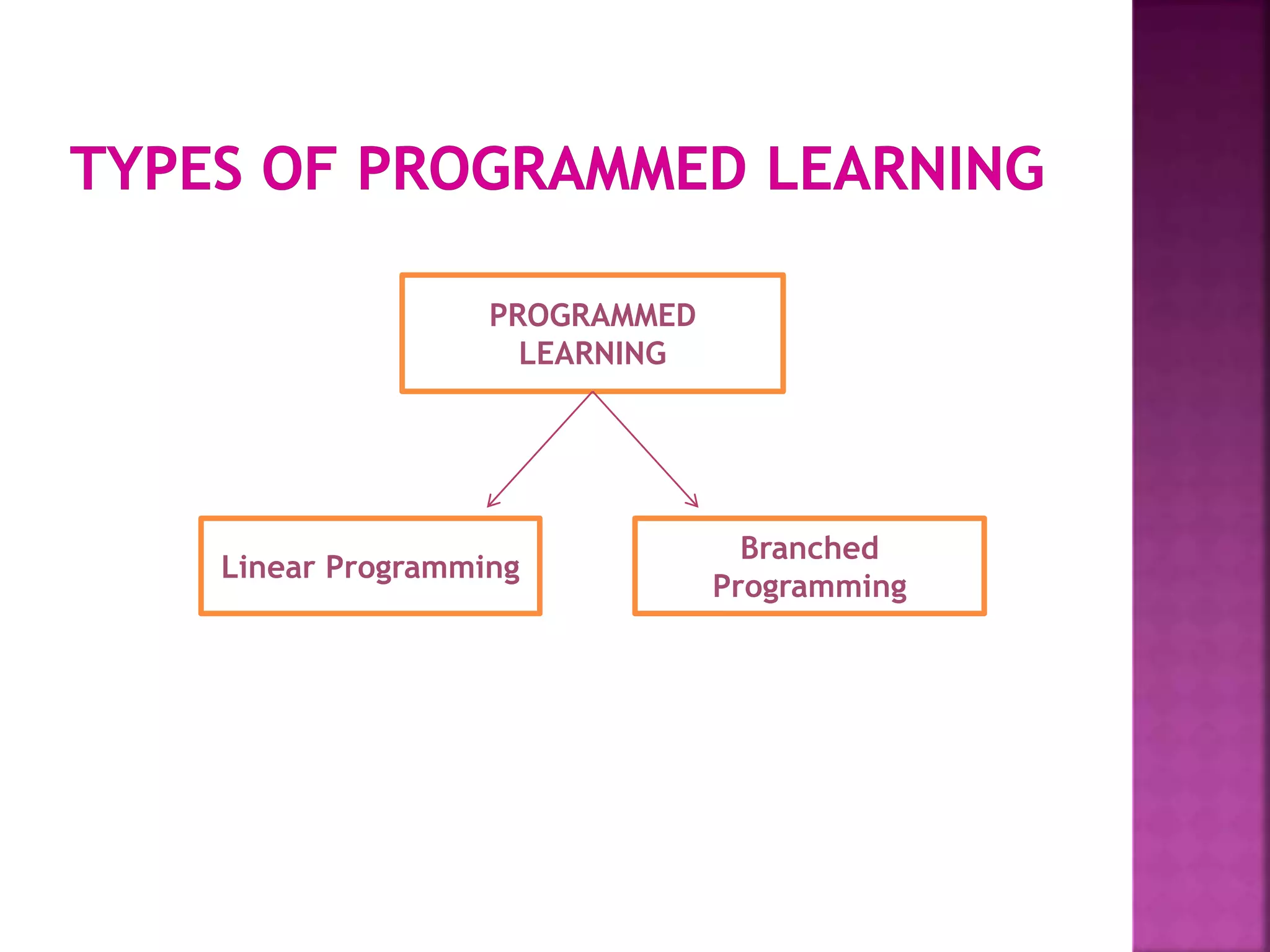
The document discusses programmed instruction, which breaks educational content into small interactive parts called frames. Students move sequentially through the frames, receiving confirmation of correct answers and redirection to remedial frames if wrong. There are two main types: linear programming which requires a set path, and branched programming which allows student choice. While programmed instruction individualizes learning and provides motivation through success, it also eliminates teacher contact and can be time consuming.