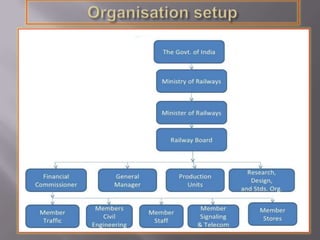
The document summarizes the history and development of Indian Railways from its inception in 1853 to modern times. Some key points:
- The first train journey in India was on April 26, 1853 from Bombay to Thane, covering 22 miles.
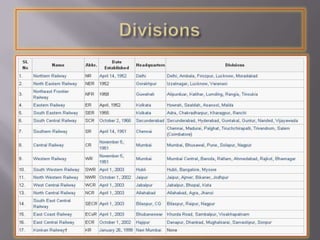
- At independence in 1947, India had 42 rail systems which were later nationalized into one unit.
- Today, Indian Railways has over 65,000 km of tracks and is the world's third largest rail network, serving as the primary mode of long distance transport.
- Reforms under the Fifth Five-Year Plan in the 1970s focused on modernization while more recent plans emphasize capacity expansion, technology upgrades, and generating non-fare revenue






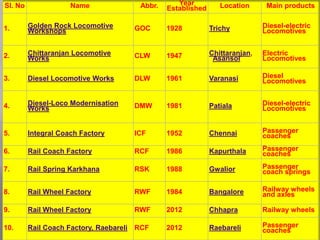
![ Bharat Wagon and Engineering Co. Ltd. (BWEL)
Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS)[17]
Container Corporation of India Limited (CONCOR)
Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited
(DFCCIL)
Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation Limited
(IRCTC)
Indian Railway Construction (IRCON) International Limited
Indian Railway Finance Corporation Limited (IRFC)
Konkan Railway Corporation Limited (KRCL)
Mumbai Railway Vikas Corporation (MRVC)
Railtel Corporation of India Limited (Rail Tel)
Rail India Technical and Economic Services Limited (RITES)
Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indianrailways-130916105629-phpapp01/85/Indian-railways-10-320.jpg)